Understanding Soil Texture and Composition
Soil texture is defined by the proportion of sand, silt, and clay particles, with various combinations creating different textural classes. The USDA Textural Triangle helps classify soil types based on these components, with examples and descriptions provided. Coarse fragments, such as gravel, stones, and boulders, also play a role in soil composition. Understanding these elements is essential for assessing soil quality and determining suitable agricultural practices.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
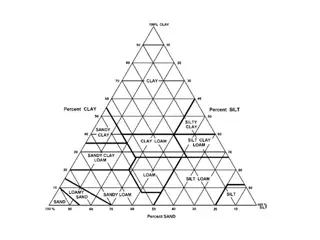
Soil Texture Definition (USDA ) - the weight proportion of the soil separates less than 2.0 mm in size (sand, silt, and clay). Or, more commonly, the relative proportions of sand, silt, and clay Sand = 2.0 to 0.05mm Silt = 0.05 to 0.002mm Clay = < 0.002mm Sand, silt, and clay in various proportions make up 12 textural classes
USDA Textural Triangle Example Clay < .002 mm Textural Class The percentage of sand sized particles + % of silt sized particles + % of clay sized particles Example: 35 % sand 55 % silt 10 % clay Texture is silt loam Sand 0.05 - 2.0 mm Silt 0.002 to .05 mm
Coarse Fragments Mineral particles larger than 2.0 mm = rock fragments (gravels, stones, or boulders) Modifiers = 0 - 15%, 15 - 35%, 35 - 60%, 60-90%, > 90%
Coarse Fragments Gravels: 2.0 to 75 mm Cobbles: 76 to 250 mm
Coarse Fragments Stoney: 250 to 600mm Boulders: 600mm+