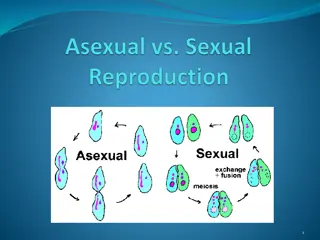
Understanding Rhizopus Reproduction: Triggers and Advantages
Discover the adverse conditions that trigger sexual reproduction in Rhizopus along with the advantages of zygospore formation. Explore the fungal lifecycle and ecological benefits provided by these processes in this informative iQuiz on fungi.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
3.1.4 Fungi 2 Follow-Me iQuiz
Q. Suggest an adverse condition that triggers sexual reproduction in Rhizopus. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Give two advantages to Rhizopus of zygospore formation. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What term is used to describe the process of asexual reproduction in yeast? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. How does asexual reproduction in Rhizopus differ from that in yeast? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What takes place in the sporangium? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name a fungus, other than Rhizopus or yeast, and explain how it is of benefit to humans. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. State a function of rhizoids. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What term is used to describe the nutrition of Rhizopus? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Which type of division, mitosis or meiosis, is involved in reproduction in yeast? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What are anaerobic conditions? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name the container in which you grew the leaf yeast Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What form of heterotrophic nutrition does Rhizopus have? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name one economically harmful member of the Fungi kingdom. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Give one beneficial use of fungi. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Outline the importance of saprophytic nutrition in nature. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. TRUE or FALSE. Rhizopus is a member of the animal kingdom. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Having finished the experiment on leaf yeast, what did you do with the agar plates? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name a fungus, other than Rhizopus or yeast, and explain how it is harmful to humans. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. State a function of the sporangiophore. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the purpose of using agar when growing fungi or bacteria in the laboratory? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Suggest one reason why leaf yeasts are more plentiful in July than in March. Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. How did you recognise the leaf yeasts when they appeared on the agar? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. In anaerobic conditions yeast produces ethanol and Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is meant by sterile? Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Anchorage; Absorption; Digestion; Enzyme secretion FALSE TRUE Mushrooms; Poisonous Antibiotic production Free from microorganisms or living things Petri dish Free from microorganisms or living things Antibiotic production Petri dish Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Autoclave in disposal bag Heterotrophic Pink colonies Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Holds up/supports the sporangium Production of spores; Reproduction Breaks down dead organisms; Recycling of nutrients Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus produces spores Budding Lack of oxygen Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis Rhizopus; Mildew; Rusts; Smuts; Blight; Dry rot; Athlete s foot Can survive drought; Dispersal Mitosis Meiosis More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic More leaves; More suitable temperature; More reproduction Carbon dioxide Saprophytic Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients Dehydration Mushrooms; Edible Source of nutrients
CONGRATULATIONS You re Brilliant
Incorrect Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again