Understanding Responses in the Human Eye and Ear
Explore the functions of the semi-circular canals and cochlea in the human eye and ear system. Test your knowledge with interactive quizzes and learn about how these components play a crucial role in our sensory perception.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
3.5.3 Responses in the Human Eye and Ear Follow-Me iQuiz
Q. What is the function of the semi-circular canals? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the function of the cochlea? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is connected to the middle ear by the Eustachian tube? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What surrounds the bones in the middle ear? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name two sense organs, other than the ear and the eye, in the human body. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the function of the lens of the eye? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the function of the retina of the eye? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Outline the role of the suspensory ligaments in vision. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Outline the role of the cones in vision. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Outline the role of the optic nerve in vision. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Outline the role of the brain in vision. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Explain how the iris works. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Suggest a reason why two eyes are better than one. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
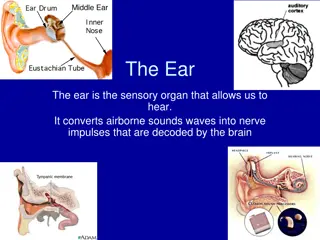
Q. In which part of the ear are nerve impulses generated? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. In which part of the eye are nerve impulses generated? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Suggest one way by which the ear may be protected. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. The hammer (malleus) is a very small bone located in the ... Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Which is present in the middle ear, gas or liquid? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. In which part of the eye would you find rods and cones? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the function of the Eustachian tube? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. TRUE or FALSE. The semi-circular canals in the ear are involved in balance. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name the coloured part of the eye. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the function of the pupil in the eye? Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name the type of chemical that carries messages between two neurons. Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Equalise pressure on the eardrum Air Iris Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Muscular contraction in response to light intensity, pupil size changes, allows more or less light in Allow light in FALSE TRUE Allow light in FALSE TRUE Focus light onto the retina Balance Focus light onto the retina Balance Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Brings impulses from retina; Brings impulse to brain Gas Neurotransmitter Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Cochlea or semi-circular canals Hearing Retina Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Holds lens in place; Changes shape of lens Convert light into nerve impulses; Image forms on it Skin; Tongue; Nose Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Detect colour Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Skull/bone; Wax; Wear ear protection; Avoid noisy environments Increased visual field; Judge distance (depth); 3D vision Detect colour Ear Throat Interprets information received from retina Interprets information received from retina Ear Throat
CONGRATULATIONS You re Brilliant
Incorrect Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again