Understanding Pollination, Fertilization, and Flower Features
Explore the intricate processes of pollination and fertilization in plants, including self-pollination and cross-pollination. Discover how wind-pollinated and insect-pollinated flowers differ in features and mechanisms. Dive into the fascinating world of plant reproduction through informative visuals and explanations. Access this educational resource for a comprehensive understanding of plant biology concepts.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Pollination and Fertilisation Standard Grade Biology
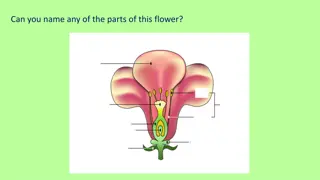
Pollination Self-pollination Pollen from the anther is transferred to the stigma
Cross Pollination Pollen from the anther of one plant is transferred to the the stigma of a different plant
Wind Pollinated Flowers Feature Reason small petals, often brown or dull green no scent no need to attract insects no need to attract insects no nectar no need to attract insects pollen produced in great quantities pollen very light and smooth because most does not reach another flower so it can be blown in the wind anthers loosely attached and dangle out to release pollen into the wind to catch the drifting pollen stigma hangs outside the flower stigma feathery or net like to catch the drifting pollen
Insect Pollinated Flowers Feature Reason large, brightly coloured petals to attract insects often sweetly scented to attract insects usually contain nectar to attract insects moderate quantity of pollen less wastage than with wind pollination to stick to insects pollen often sticky or spiky anthers firm and inside flower to brush against insects stigma inside the flower so that the insect brushes against it pollen sticks to it stigma has sticky coating
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.