Plant Reproduction: Pollination and Seed Dispersal Mechanisms
Explore the fascinating world of plant reproduction through pollination and seed dispersal mechanisms. Learn about the different types of pollination, such as self-pollination and cross-pollination, and the importance of fruit and seed dispersal. Discover how plants use various strategies to ensure successful reproduction, from attracting pollinators to dispersing their seeds effectively.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Fruit and Seed dispersal
Fruit and Seed dispersal 1- Anemochory. 2- Autochory. 3- Hydrochory. 4- Myrmeco-chory. 5- Zoochory: general dispersal by animals, here there are two ways: A- Exozoic:. B- endozoic.
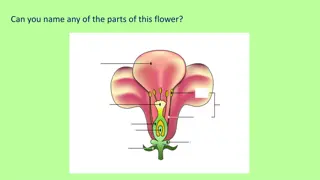
Plant reproduction Sexual reproduction in seeded plants: A/Pollination :- It is the transfer of pollen grains from microsporangia to the ovule or stigma. There are two types of pollination 1- Self-pollination: It is the transfer of pollen from the stamens to the stigma in the same flower. This type of pollination happened in the following: A- Hermaphrodite flowers B- Cleistogamus flowers as in Avena 2- Cross-pollination
Mechanisms favouring cross- pollination 1- Being dioecious 2- Being monoecious 3- The maturation of anthers and stigmas in different times 4- In heterostyled flowers 5- In self-incompatible flowers
B/Fertilization Inbreeding (also called selfing): Outbreeding(also called outcrossing or allogamy): Allautogamy( means have both outcrossing and selfing flowers )
Kinds or agencies of pollination in Angiosperm plants:- Animal pollination Types of animal pollination: Insect pollination (entomophily) A- Bee pol B- Butterfly pol. C- Beetle pol. Bat pol. 1. 2. Wind pollination Water pollination