Understanding Motion: Speed, Velocity, and Acceleration in Physics
Explore the concepts of motion, position, and reference points in physics through examples involving speed calculations, time measurements, and determining winners in races. Dive into the world of Peregrine falcons, tortoises, hares, and school hallways to grasp the fundamental principles of speed, distance, and time in motion analysis.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
LETS REVIEW Speed, velocity & acceleration
MOTION, POSITION, REFERENCE POINT How would you define motion? Motion is defined as a change in an objects position over time
MOTION, POSITION, REFERENCE POINT What is a reference point? A point of comparison used to determine an objects position
MOTION, POSITION AND REFERENCE POINT Identify the position of the globe in this classroom.
WHAT IS THE TRIANGLE FORMULA TO CALCULATE SPEED? d t s
SPEED The Peregrine falcon is the world s fastest known bird and has been clocked diving downward toward its prey at a constant vertical velocity of 97.2 m/s. If the falcon dives straight down from a height of 100 m. How much time does this give a rabbit below to consider his next move as the falcon begins his descent? 1.03 s
SPEED The tortoise and the hare are in a road race to defend the honor of their breed. The tortoise crawls the entire 1000 m distance at a speed of 0.2000 m/s while the rabbit runs the first 200.0 m at 2.000 m/s. The rabbit then stops to take a nap for 1.3 hours and awakens to finish the last 800.0 m with an average speed of 3.000 m/s. Who wins the race and by how much time? Tortoise by 47 s
SPEED It is now 10:29 am, but when the bell rings at 10:30 am, Ashley will be late for Science class for the third time this week. She must get from one side of the school to the other by hurrying down three different hallways. She runs down the first hallway, a distance of 35.0 m, at a speed of 3.50 m/s. The second hallway is filled with students, and she covers its 48.0 m length at an average speed of 1.20 m/s. The final hallway is empty, and Ashley sprints its 60.0 m length at a speed of 5.0 m/s. Does Ashley make it to class on time? No, she is 2 seconds late
DISTANCE-TIME GRAPH Draw a distance vs time graph of Ashley's journey to Science class. (Assume constant speed for each hallway.)
AVERAGE SPEED Your drive 200 miles in 3 hours before stopping for 30 minutes for lunch and gas. After lunch, you drive 90 miles in an hour and a half. What was your average speed for the trip? 58 mi/hr
ACCELERATION Explain how an object accelerates. Speeding up, slowing down, changing direction What is acceleration? A change in velocity over time What is the formula to calculate acceleration? a = Vf Vi t
ACCELERATION Chloe got up late and doesn t want to miss her bus. She runs out the door at an impressive 18 m/s, but realizes that the bus is pulling away and that she can t make it. She slows down and stops in 4.5 s. Calculate her acceleration. -4m/s2
ACCELERATION The Lamborghini Diablo sports car can accelerate from 0.0 km/hr to 99.2 km/hr in 4.0 seconds. What is the acceleration of this car? 24.8 km/hr/s
ACCELERATION The cheetah, which is the fastest land mammal, can accelerate from 0.0 mi/hr to 70.0 mi/hr in 3.0 seconds. What is the acceleration of the cheetah? 23.3mi/hr/s
COMPARISON Which has greater acceleration, the cheetah or the Lamborghini Diablo? (To figure this out, you must know that there 1.6 kilometers in 1 mile) 37.3 km/hr/s Cheetah
ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY What is the velocity of a rubber ball dropped from a building roof after 5 seconds? Vf = 49 m/s
ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY If a ball that is freely falling has attained a velocity of 19.6 m/s after two seconds, what is its velocity five seconds later? 68.6 m/s
ACCELERATION DUE TO GRAVITY How long will it take an object that falls from rest to attain a velocity of 147 m/s? 15s
DISTANCE-TIME GRAPH Your leave Science class and walk to the furthest bathroom on campus. Draw a distance- time graph illustrating the distance you traveled.
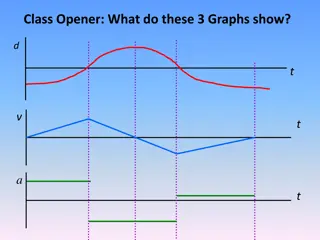
VELOCITY-TIME GRAPH Choose the correct word from the list below to describe the motion taking place in each section. acceleration steady speed stationary
VELOCITY-TIME GRAPH a. At what time during the journey did the bus reach its greatest speed? After 5 sec b. How long was the bus stopped for during its journey? 3 sec c. During which section of the journey did the bus have the greatest acceleration? B-C
VELOCITY-TIME GRAPH d. Calculate the acceleration of the bus during section DE. 1m/s2 e. Which section could be described as a deceleration? B-C
VELOCITY-TIME GRAPH a. What is the distance travelled by the bus during its 25 s journey? 122.5 m b What is the average speed of the bus during its 25 s journey? 4.9 m/s