Understanding Monohybrid Crosses: Incomplete Dominance and Codominance
Explore the concepts of incomplete dominance and codominance through monohybrid crosses. Learn how alleles interact to produce unique phenotypes in plants and horses. Discover the outcomes of crosses between homozygous dominant, heterozygous, and homozygous recessive individuals. Gain insights into genetic inheritance patterns and allele expression in different organisms.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MONOHYBRID CROSSES Looking at incomplete and codominance
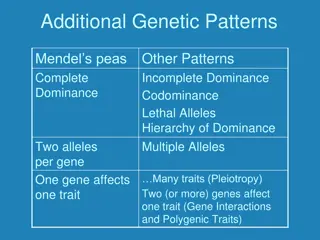
INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE The dominant allele can t completely hide the recessive allele, so a heterozygous genotype results in a phenotype that is a mix of the other 2 phenotypes
EXAMPLE 1 In some plants, red (R) flower color is incompletely dominant over white (r) color. Show the cross between two plants heterozygous for flower color. R r RR Rr R Rr rr r G = RR, Rr, rr P = red, pink, white PR = 1:2:1 GR = 1:2:1
EXAMPLE 2 Show the cross between a homozygous dominant and a heterozygous plant. R R RR RR R Rr Rr r G = RR, Rr GR = 2:2:0 P = red, pink PR = 2:2:0
CODOMINANCE Occurs when both alleles for a gene are expressed in a heterozygous offspring No allele is dominant or recessive
EXAMPLE 1 In horses, red coat is codominant with white coat. Show the cross between a red (R) horse and a white horse (R ). R R RR RR R RR RR R G = RR P = Roan GR = 0 (RR): 4 (RR ): 0 (R R ) PR = 0:4:0
EXAMPLE 2 Show the cross between a white horse and a roan horse. R R RR RR R R R R R R G = RR , R R P = roan, white GR = 0:2:2 PR = 0:2:2