Understanding Gene Regulation and Mutation
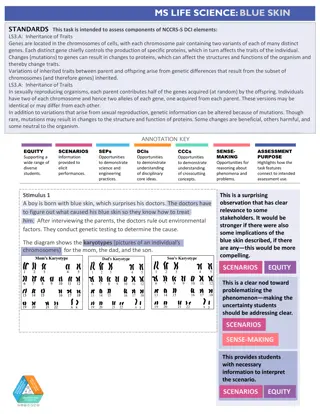
Gene regulation refers to an organism's ability to control gene transcription in response to environmental cues, while mutations are permanent changes in a cell's DNA that can range from single base pair alterations to large chromosomal deletions. Point mutations involve chemical changes in single base pairs, leading to substitutions that can impact amino acid coding. Insertion and deletion mutations alter DNA sequences by adding or removing nucleotides, respectively, often causing frameshift mutations. Duplication mutations result in the repetition of codons. Learning about these genetic processes is crucial for understanding how organisms adapt to their surroundings and evolve.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
GENE REGULATION Gene regulation: The ability of an organism to control which genes are transcribed in response to the environment.
MUTATION Mutation: a permanent change that occurs in a cell s DNA. Can range from changes in a single base pair (Ex: An A instead of a C) in the coding sequence of DNA to the deletion of large pieces of chromosomes. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=efstlgoynlk
POINT MUTATION Involve a chemical change in just one base pair. A point mutation is exchanged for another is called a substitution.
POINT MUTATION Missense mutation: codes for the wrong amino acid. Nonsense mutation: change the codon for an amino acid to a stop codon. Silent mutation: a substitution that does not change the amino acid. Normal Sentence: THE BIG FAT CAT ATE THE WET RAT Missense Mutation: THE BIZ FAT CAT ATE THE WET RAT Nonsense Mutation: THE BIG RAT.
INSERTION MUTATIONS Insertions are additions of a nucleotide to the DNA sequence. This changes the multiples of three in the DNA sequence from the point of the insertion.
DELETION MUTATIONS Deletion mutations remove a nucleotide from the DNA sequence. This changes the multiples of three in the DNA sequence from the point of the insertion.
INSERTION & DELETION MUTATIONS Normal Sentence: THE BIG FAT CAT ATE THE WET RAT INSERTION: THE BIG ZFA TCA TAT ETH EWE TRA DELETION: THB IGF ATC ATA TET HEW ETR AT These mutations are called frameshift mutations because they change the frame of the amino acid sequence.
DUPLICATION MUTATION A duplication mutation is the repeat of one or more codons.
DUPLICATION MUTATION Normal Sentence: THE BIG FAT CAT ATE THE WET RAT Duplication: THE BIG FAT FAT CAT ATE THE WET RAT
Original DNA Sequence:T A C A C C T T G G C G A C G A C T mRNA Sequence: A U G, U G G, A A C, C G C, U G C, U G A Amino Acid Sequence: Met Try Asp Arg Cys Stop
Mutated DNA Sequence #1 What s the mRNA sequence? A U G, U A G, A A C, C G C, U G C, U G A(Circle the change) What will be the amino acid sequence? Stop.... Will there likely be effects? YES What type of mutation is this? Base substitution of T for C causing a NONSENSE mutation. T A C A T C T T G G C G A C G A C T Met STOP Asp Arg Cys