Understanding Fluid Kinematics and Basic Equations in Fluid Mechanics
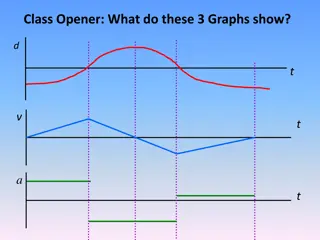
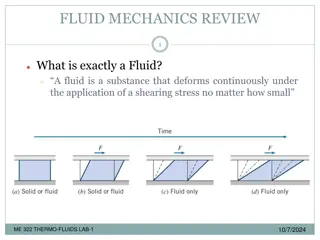
Delve into the concepts of fluid kinematics, including streamlines, pathlines, streaklines, and timelines. Learn the differences between these lines and how they are generated experimentally. Explore the basic equations in fluid mechanics, such as the mass or material balance, energy balance, and momentum equations. Gain insights into the principles governing the behavior of fluids in motion.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Lecture-11 Balance Equations 10/09/2020 Dr V K Sachan UIET CSJMU Kanpur 1
Introduction to Fluid Kinematics Stream lines: A streamline is a curve that is everywhere tangent to the instantaneous local velocity vector. Pathlines: Actual path traversed by fluid particle: 10/09/2020 Dr V K Sachan UIET CSJMU Kanpur 2
Introduction to Fluid Kinematics Streaklines:A line formed by joining the fluid particles that have passed a fixed location over a period of time Streaklines are the most common flow pattern generated in a physical experiment. If you insert a small tube into a flow and introduce a continuous stream of tracer fluid (dye in a water flow or smoke in an airflow), the observed pattern is a streakline. 10/09/2020 Dr V K Sachan UIET CSJMU Kanpur 3
Introduction to Fluid Kinematics Timeline:A timeline is a set of adjacent fluid particles that were marked at the same (earlier) instant in time. Timelines are particularly useful in situations where the uniformity of a flow (or lack thereof) is to be examined. Timelines can be generated experimentally in a water channel through use of a hydrogen bubble wire. 10/09/2020 Dr V K Sachan UIET CSJMU Kanpur 4
Difference: Streamline, Streakline, Pathline and Timeline The streamline is convenient to calculate mathematically, while the other three are easier to generate experimentally. Note that a streamline and a timeline are instantaneous lines, while the pathline and the streakline are generated by the passage of time. The velocity profile are shown forming timeline through experiments of a single discharge of bubbles from the wire. A pathline can be found by a time exposure of a single marked particle moving through the flow. Streamlines are difficult to generate experimentally in unsteady flow unless one marks a great many particles and notes their direction of motion during a very short time interval. In steady flow, where velocity varies only with position, the situation simplies greatly: Streamlines, pathlines, and streaklines are identical in steady flow. 10/09/2020 Dr V K Sachan UIET CSJMU Kanpur 5
Basic Equations in Fluid Mechanics Mass or material balance (continuity equation/continuity principle) Energy balance (First law of Thermodynamics) Momentum (linear and angular) (Newton s law of motion) Second law of Thermodynamics 10/09/2020 Dr V K Sachan UIET CSJMU Kanpur 6
Mass Balance General balance equation: At steady state accumaulation is zero and creation and destruction terms are not present ( , , , ) V V x y z t = = + V x V y V z V t + + dV dx dy dz dt , , y z t , , x y t , , x y z , , x z t Continuity equation: For liquids density is usually constant 10/09/2020 Dr V K Sachan UIET CSJMU Kanpur 7
Steady and Unsteady State (Ref: de Nevers) 10/09/2020 Dr V K Sachan UIET CSJMU Kanpur 8