Understanding Congenital Hand Abnormalities and Associated Syndromes
Explore congenital hand abnormalities such as macrodactyly, trigger thumb, clasped thumb, preaxial deficiency, and syndromes like Holt-Oram Syndrome and Fanconi Anemia. Learn about assessment, intervention plans, and common treatments provided by experts in reconstructive plastic and hand surgery.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Congenital Hand Abnormalities Nick Sheppard Consultant Reconstructive Plastic and Hand Surgeon Norfolk and Norwich Hospital, UK AO AF / BSSH Hand Trauma Workshop Blantyre, Malawi 16 October 2018
Assessment Assessment Look feel move Function is all-important Plan intervention targeted to specific goals Consider the whole patient
Macrodactyly Macrodactyly Nerve-orientated lipofibromatosis Most commonly occurs in the median nerve distribution Two types of growth Static Progressive Debulking, nerve stripping, amputation
Congenital trigger thumb Congenital trigger thumb Stenosing tenosynovitis Fixed flexion of IPJ Notta node Snapping/popping as the nodule passes beneath A1 pulley Compensatory hyperextension at MCPJ. Frequently bilateral
Congenital clasped thumb Congenital clasped thumb Deficient thumb extensor mechanism. Mild Deficiency of EPB Extension lag at MCPJ Severe Deficiency of EPB & EPL. Associated with arthrogryposis
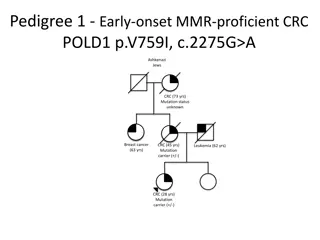
Preaxial deficiency Preaxial deficiency Minor abnormalities to complete absence of thumb Commonly short radius, hypoplasia of the thumb Bilateral almost as common as unilateral Bilateral : part of a syndrome in 77% of patients
Syndromes associated with preaxial deficiency Syndromes associated with preaxial deficiency Holt-Oram Syndrome Heart defects (ASD) Thrombocytopenia-absent radius (TAR) syndrome Thrombocytopenia present at birth VACTERL Vertebral abnormalities, anal atresia, cardiac abnormalities, tracheoesophageal fistula, esophageal atresia, renal defects, radial dysplasia, lower limb abnormalities Fanconi anemia Aplastic anaemia present at birth
Fanconi Fanconi Anaemia Anaemia 1 in 350,000 births Autosomal recessive Ashkenazi Jews , South Africans 20% develop AML 90% develop bone marrow failure by age 40 60-75% have developmental defects Median age of death was 30 years (2000)
Radial Deficiency Radial Deficiency Type Presentation Treatment I Short radius, no radial bowing or deviation No treatment II Hypoplastic radius (rare) No treatment III Partial absence with fibrous anlage (most common) requires centralization procedure IV Total absence second most common; elbow joint usually deficient soft tissue release and centralization O'Rahilly R. Morphological patterns in limb deficiencies and duplications. Am J Anat. Sep 1951;89(2):135-93.
Radial Hypoplasia Radial Hypoplasia
Bayne & Klug classification Bayne & Klug classification
Management Management Conservative Serial splinting Stretching and manipulation Surgical
Polydactyly Polydactyly Polydactyly is one of the most common congenital anomaly of the upper limb. Total duplication of the hand and forearm is ulnar dimelia (rare). Central duplication may be termed polysyndactyly. Isolated postaxial polydactyly has a strong autosomal dominant inheritance pattern and is common in individuals of African descent
Wassel Wassel Classification of Classification of Preaxial Preaxial polydactyly polydactyly Wassel HD. The results of surgery for polydactyly of the thumb. A review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. May-Jun 1969;64:175-93
Thumb Hypoplasia Thumb Hypoplasia
Modified Modified Blauth Blauth Classification Classification Type Findings Treatment 1 Minimal shortening None or augmentation 2 Narrow first web space, thenar weakness, MCP joint instability Opponensplasty, release of first web space, UCL reconstruction 3 Narrow first web space, thenar weakness, MCP joint instability, extrinsic tendon abnormalities 3A Metacarpal hypoplasia with stable CMC joint Reconstruction 3B Metacarpal hypoplasia with unstable CMC joint Pollicisation 4 Rudimentary phalanges, thumb attached by a skin bridge Pollicisation/Amputation 5 Aplasia of thumb Pollicisation/Amputation
Pollicisation Pollicisation Neurovascular components are the most challenging Index MC -> Neo-trapezium EDC -> AbPL EIP -> EPL FDP -> FPL Palmar int. -> Adductor
Syndactyly Syndactyly one of the most common congenital anomalies in the hand 1 in 2000 bilateral, and males are affected more commonly than females third and then fourth web most affected associated with at least 28 syndromes
Classification Classification Completeness Complete skin joined all the way to the finger-tip Incomplete skin is joined part of the distance to the finger tip of the Presence of bony union Simple Complex - bones of adjacent digits are fused Complicated - more than simple side-side bony - adjacent fingers are joined by soft tissue fusion
Congenital Hand Abnormalities Nick Sheppard Consultant Reconstructive Plastic and Hand Surgeon Norfolk and Norwich Hospital, UK AO AF / BSSH Hand Trauma Workshop Blantyre, Malawi 16 October 2018