Understanding Condensation and Associated Phenomena
Condensation is the process of transforming water vapor into liquid or solid forms based on relative humidity and temperature. Dew point marks the saturation temperature, leading to dew, fog, rain, frost, ice, snow, and hail. Ascending air brings moisture, while descending air causes dryness.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CONDENSATION AND ASSOCIATED FORMS
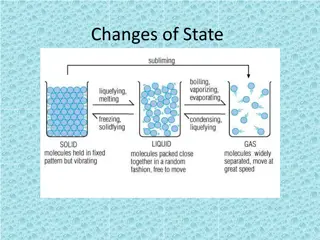
The transformation of gaseous form of water (i.e. water vapour) into solid form (ice) and liquid from (water) is called condensation. In other words, the process of change of water vapour into liquid form is called condensation. The process and mechanism of condensation depends on the amount of relative humidity present in the air. The air having 100% relative humidity is called saturated air. An air may become saturated in two ways e.g.either (1) the absolute humidity at a given temperature is raised to equal the humidity retaining capacity of the air or (2) The temperature of the air is reduced to such an extent that the humidity capacity becomes equal to its absolute humidity.
The temperature at which an air becomes saturated is called dew point. It may be pointed out that condensation will begin only when the air is supersaturated e.g. if the relative humidity exceeds 100 percent, and this can be achieved only when the air is further cooled. If dew point is above freezing point (32 F), condensation will occur in liquid form (e.g., dew, fog, rainfall etc.) but if dew point is below freezing point, condensation occurs in solid form (e.g., frost, ice, snow, hailstorm etc.). It is apparent that condensation depends on (1) the percentage of relative humidity of the air and (2) the degree of cooling of the air. The air becomes cool when it rise while it gets heated when it descends. Thus, the ascending air may bring moist weather while descending air causes dry condition.
Dew point The temperature, at which the given air is saturated e.g. the humidity holding capacity and absolute humidity of a given volume of air at given temperature and point of time become equal is called dew point.
Frost Frost is defined as transformation of gaseous form of water (water vapour) Directly into solid form through the process of sublimation at the ground surface, in the soils, and in the air layer just lying over the ground surface due to condensation occurring below freezing point. Frost point: The temperature at which condensation occurs (always below freezing point, e.g. below 0 C) is called frost point or frost point temperature.