Understanding Chemical Reactions and Energy Transfer in Biology
Exploring the origin of life, the formation of molecules, and the transition to proteins through amino acids. Definitions of key terms in biology, the role of enzymes, and the significance of chemical reactions in rearranging atoms and transferring energy are discussed. Various forms of energy and the first law of thermodynamics are introduced, emphasizing the rearrangement of atoms and the energy involved in chemical reactions.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
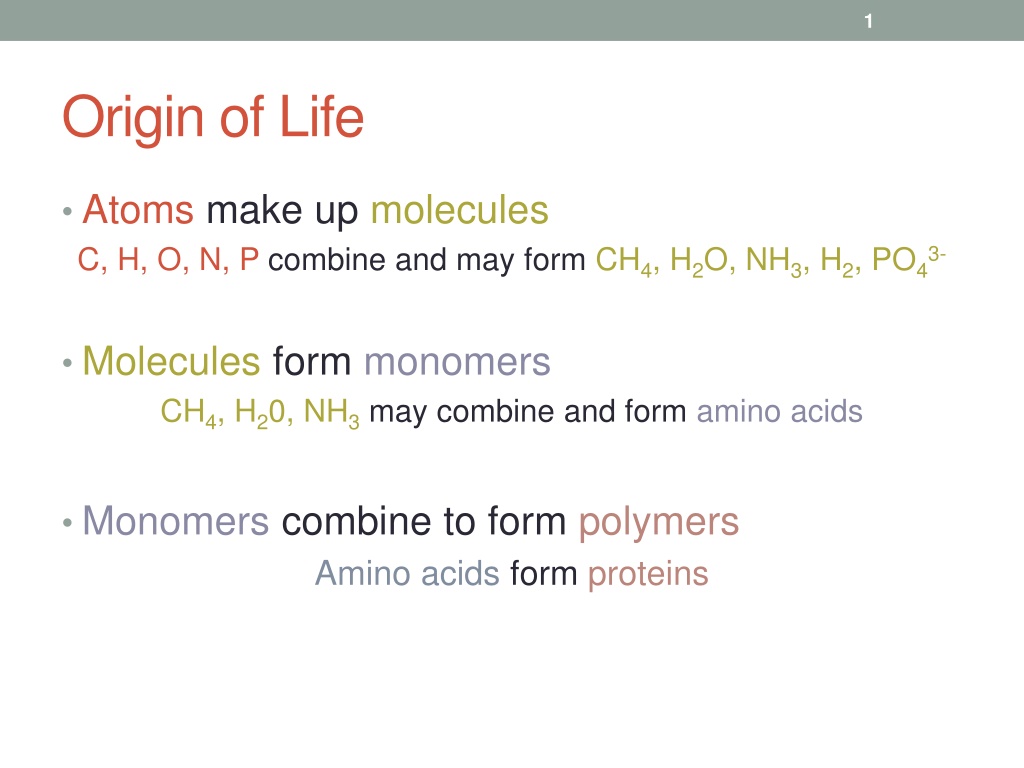
1 Origin of Life Atoms make up molecules C, H, O, N, P combine and may form CH4, H2O, NH3, H2, PO43- Molecules form monomers CH4, H20, NH3may combine and form amino acids Monomers combine to form polymers Amino acids form proteins
2 Definitions ___________: a single unit molecule that may chemically bind to other molecules Ex. ___________________: building blocks of protein ___________: a chain of repeated monomers Ex. _____________: a large molecule formed by linked monomers called amino acids
3 Enzymes: special type of protein __________: a type of ________ that speeds up chemical _________ in living organisms without being _________ or destroyed. Chemical reactions are synonymous with metabolic reactions in biology. Are picky and only work on one molecule Example: catalase only works with H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide)
4 CHEMICAL REACTIONS Transfer of Energy Rearrangement of Atoms
5 Energy Definitions: Ability to do work Ability to move or change matter Energy comes in ______ forms.
6 Forms of energy Light - sun Heat - shivering Mechanical - rub hands together Electrical - shock metal door knob Chemical - combustion
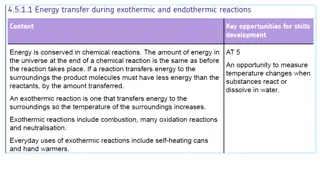
7 Chemical Reactions Energy is transferred Atoms are rearranged
8 Energy is Transferred First Law of Thermodynamics: The total amount of energy in an isolated system is constant (not increasing or decreasing). Energy cannot be created nor destroyed.
9 Rearrangement of Atoms __________: starting materials Product: newly formed substances : changes into A + B C + D Ex. HCl + KOH KCl + H2O
10 Energy in Chemical Reactions Chemical bonds are formed and broken Hydrogen Bonds, Ionic Bonds, Covalent Bonds Products can either _______ or _______ energy Endothermic Reaction Exothermic Reaction -gonic = suffix meaning energy
11 Chemical Bonds and Reactions Are strong bonds easier or harder to break compared to weak bonds? And do they require more or less energy? Therefore, weak bonds are _________ to break and require ________ energy to do so. Do spontaneous reactions break more stable or less stable bonds? Why?
12 RULE OF THUMB The more strong bonds a molecule has, the more stable it is; consequently, more energy is needed to break down the molecule.
13 What is happening in this reaction?
14 How would you graph the diagram to the right? High Energy (heat) Low Time
15 Endergonic Reaction Energy is absorbed Unfavorable or _________________ Products are less stable than reactants Ex 1. Photosynthesis 6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 Ex 2. burning paper
16 What is happening in this reaction?
17 How would you graph the diagram to the right? High Energy (heat) Low Time
18 Exergonic Reaction Energy is released Favorable or spontaneous Products more stable Ex. Respiration C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O
19 Enzymes and Metabolic Reactions Endergonic Reaction Exergonic Reaction Energy is __________ Products have ______ energy than reactants Energy is _________ Products have ______ energy than reactants
20 Starting Chemical Reactions How do endergonic and exergonic reactions begin?
21 Activation Energy Activation energy (EA): the energy needed to ________ a reaction Do spontaneous reactions require EA? Do non-spontaneous reactions require EA?
22 Enzyme and EA (Activation Energy)
23 Role of Enzyme
24 Enzymes protein that speeds up metabolic reactions Catalysts: _______ the activation energy needed to start a chemical reaction How do enzymes speed up chemical reactions?
25 Importance of Enzymes Allow organisms to maintain homeostasis Without enzymes, reactions would occur too slowly for life to exist Enzymes lower the activation energy needed for chemical reactions to occur = quicker reactions
26 Enzyme Specificity Specificity- specific, particular, precise Enzymes only work with certain _____________ or reactants. ____________: substance or molecule which an enzyme acts on Amylase Starch H2O2 glucose 2H2O + O2 Catalase
27 How are enzymes specific?
28 Enzyme Lock and Key Model
29 What effects the performance of enzymes? Two things. Discuss with your table partner for a few moments.
32 THE END