Understanding Brain Cisterns and Meninges in Radiology
Explore the intricate structures of brain cisterns and meninges as seen in radiology images. Learn about the layers of meninges - Dura mater, Arachnoid mater, and Pia mater. Discover the various cisterns in the brain, such as Cisterna Magna, Pontine Cistern, and others, each with its unique characteristics and functions within the central nervous system.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
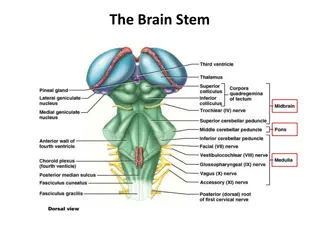
Brain Cisterns Dr. Yaser Abdulghani AlQasimi, MBBS Radiology Demonstrator, KAU
Brain Meninges 3 layer system of membranes which envelops the central nervous system. Layers are: Dura mater Arachnoid mater Pia mater
Cisterns Cisterns are openings in the subarachnoid space of the brain created by a separation of the arachnoid and pia mater. These spaces are filled with CSF.
Brain Cisterns There are many cisterns in the brain, but the notable ones include: Cisterna magna (cerebellomedullary). Cisterna pontis (pontine cistern). Interpeduncular cistern. Quadrigeminal cistern (superior cistern). Ambient cistern. Cistern of the velum interpositum. Suprasellar/Chiasmatic cistern. Cistern of lamina terminalis. Supracallosal cistern. Sylvian cistern.
Cisterna Magna Lies behind the medulla and below the cerebellar hemispheres. Continuos with 4thventricle through median aperture of Magendie. Its lateral part contains the vertebral artery and its posterior inferior cerebellar branch.
Pontine Cistern Lies between the pons and the clivus. Receives CSF from lateral apertures of 4th ventricle (Luschka). Continuous above with the interpeduncular cistern. It contains the basilar artery and its pontine and labyrinthine branches.
Interpeduncular Cistern Lies between the cerebral peduncles. Continuous below with the pontine cistern, laterally with the ambient cisterns, and superiorly with the suprasellar cistern. It contains the posterior part of the arterial circle of Willis.
Quadrigeminal Cistern lies posterior to qudrigeminal plate of the midbrain and between the splenium above and the vermis below. It is continuous with the interpeduncular cistern anteriorly through the ambient cisterns. Contains the great cerebral vein of Galen.
Ambient Cistern sheet like cistern that extend around both sides of midbrain between the interpeduncular cistern anteriorly and the qudrigeminal cistern posteriorly. the posterior cerebral artery and the basal vein lie in the anterior part of each ambient cistern.
Suprasellar / Chiasmatic Cisterns Suprasellar cistern lies above the pituitary fossa and is continuous posteriorly with the interpeduncular cistern and laterally with the sylvian cistern. It contains the anterior part of the circle of Willis and the optic nerve as it passes to the chiasm. Chiasmatic cistern is the part of suprasellar cistern that is anterior to the optic nerve.
Sylvian Cistern This is the area of sylvian fissure.
Cistern of lamina terminalis / Pericallosal Cistern The cistern of lamina terminalis is the superior extension of suprasellar and chiasmatic cisterns that extend to the superior surface of corpus callosum as the pericallosal (supracallosal) cistern. Pericallosal cistern is continuous posteriorly with the quadrigeminal cistern. It contains branches of the anterior cerebral artery.