Understanding BJT and FET Transistors in Electronics
Learn about the differences between BJT (NPN, PNP) and FET transistors like JFET and MOSFET. Explore characteristics such as voltage gain, current gain, input/output impedance, noise generation, and switching time. Discover when each type is best suited for specific applications.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
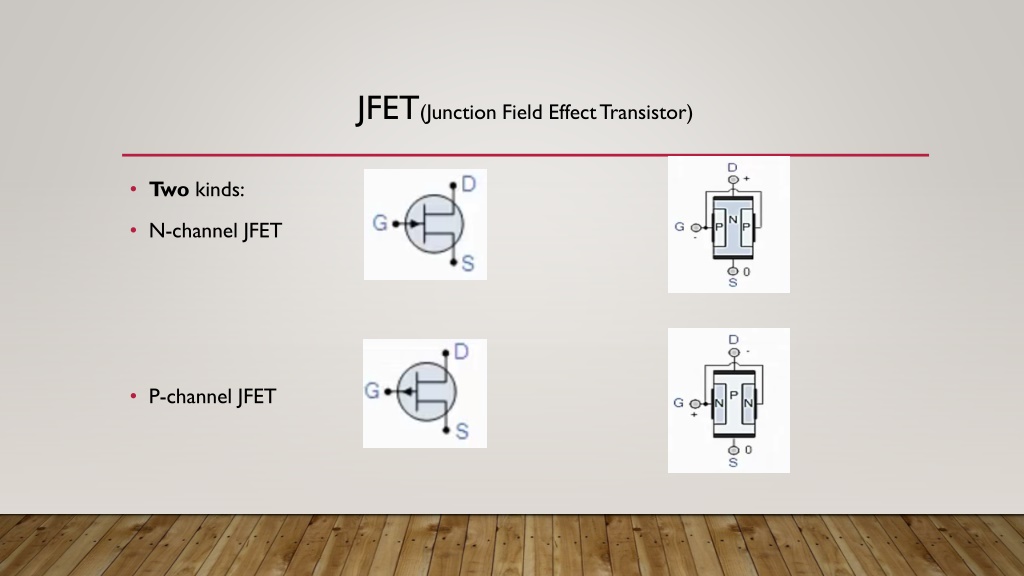
JFET(Junction Field Effect Transistor) Two kinds: N-channel JFET P-channel JFET
BJT VS FET BJT FET High voltage gain Low current gain Low input impedance Low output impedance Medium Noise Generation Medium switching time Robust Requires zero input to turn it "OFF" Low voltage gain High current gain Very high input impedance High output impedance Low Noise generation Fast switching time Easily damaged Some need an input to turn it "OFF"