The Pituitary Gland: Structure, Function, and Hormones
The pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain, comprises two main portions - the anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) and the neurohypophysis. The anterior lobe consists of various cell types that secrete hormones like GH, prolactin, TSH, ACTH, FSH, and LH. GH, also known as STH, plays a crucial role in stimulating cell growth and metabolism. Controlling GH secretion involves substances like GHRH and somatostatin. Insufficient GH secretion can lead to growth limitations and dwarfism.
Uploaded on Oct 03, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
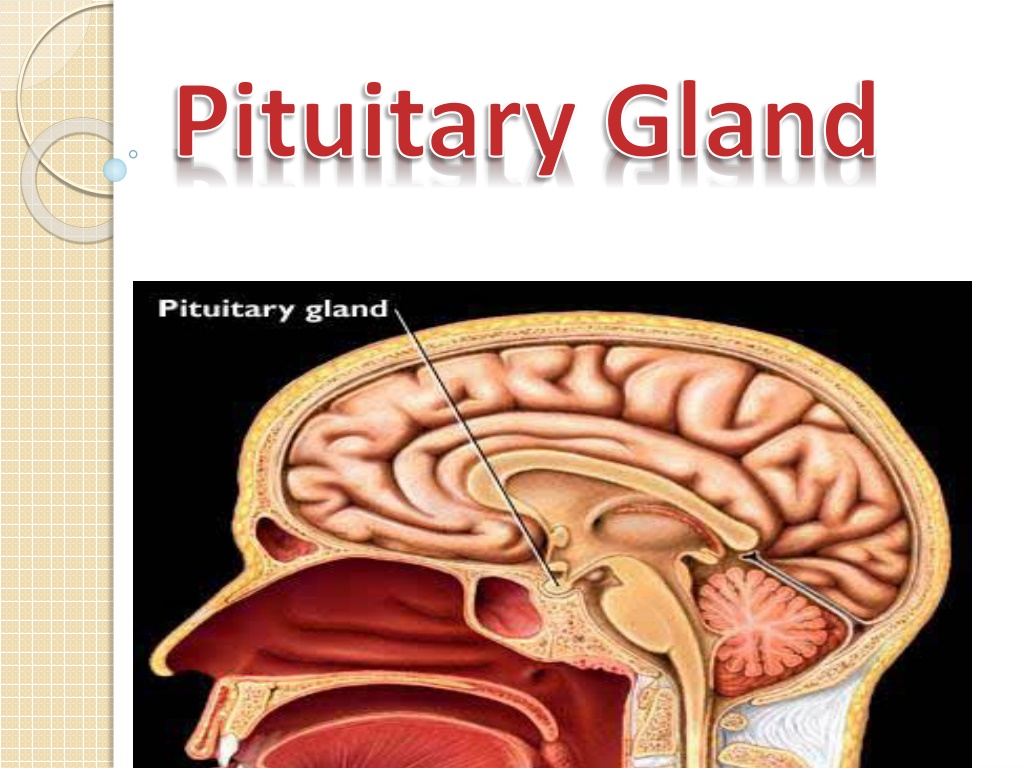
) Pituitary Gland hupophysis) Is located at the base of the brain . It is attached to the hypothalamus by the pituitary stalk or infundibulum and lies in the sellaturcica of the sphenoid bone .
) Pituitary Gland hupophysis) It is composed of 2 distinct portion : 1) An anterior lobe (adenohypophysis )or (parsnervosa ): is formed from an area of the root of the embryonic oral ectoderm called Rathkes pouch . 2) Neurohypophysis : is formed from neural ectoderm of floor of the third ventricle .
) Pituitary Gland hupophysis) An anterior lobe (adenohypophysis )or (parsnervosa ): Depending upon the staining reaction adenohypophysis cells are divides into: 1) Cells without affinity to dye called chromophobes (50%), 2) Cells with affinity to dye called chromophil cells(50%) The chromophil cells are: 1) Eosinophil or A cells (35%) , 2) Basophil or B cells (15%).
) Pituitary Gland hupophysis) The cytologists have classified the cell types as : 1) Somatotropes that secret GH, 2) Mammotropes secrete prolactin , 3) Thyotropes secret TSH , 4) Corticotropes secret ACTH , 5) Gonadotropes secret FSH & LH .
) Pituitary Gland hupophysis) Growth hormone (GH)or (STH) Is protein hormone that stimulate the body cell to increase the size and undergo more rapid cell divisor than usual . It enhances the movement of AA through the cell membrane and causes an increase in the rate at which the cells convert these molecules into proteins . It also causes cells to decrease the rate at which they utilize carbohydrates and to increase the rate at which they use the fat .
) Pituitary Gland Growth hormone The mechanism for controlling GH secretion : hupophysis) Seen to involve 2 substances from the hypothalamus called: 1) GH releasing hormone (GHRH) 2) Somatostatin (ss). It is able to stimulate the elongation of bone tissue directly , its effect on cartilage requires the presence of amediator substance .
) Pituitary Gland Growth hormone hupophysis) This substance called somatomedin (insulin like growth factor ) is released from the liver in response to GH and the somatomedin , in turn , promotes the growth of cartilage . If an insufficient amount of GH is secreted during development (early phase of development , in young stage ) lead to body growth limited and type of dwarfism (hypopituitary dwarfism )result .
) Pituitary Gland Growth hormone hupophysis) 1- over secretion of GH during early growing stage may result in gigantism which the high of the persons may exceed and fact , gigantism is usually compand by a tumor of pituitary gland . 2-GH is secreted excessively in an adult , after epiphyses of the long bone have ossified , the person dose not grow taller , the soft tissue , however , may continue to enlarge and the bone may become thicker affected individual may develop greatly enlarged hand feet and protruding jaw and large tonge and nose
) Pituitary Gland prolactin H hupophysis) It protein H which stimulate and sustains milk production following the birth . It causes decrease in the secretion of the LH , because LH is necessary for the production of male sex hormone (androgens ), Excessive prolactin secretion may causes a male to develop a deficiency of sex hormon become infertility
) Pituitary Gland prolactin H Two substance from the hypothalamus are involved in the regulation of prolactin secretion : hupophysis) 1) Prolactin release inhibiting factor (PIF) act to restrain the secretion of prolactin . 2) Prolactin releasing factor (PRF) Stimulate its secretion .
) Pituitary Gland thyroid stimulating hormone TSH It is also called thyrotropin ,is a glycoprotein ,its major function : hupophysis) is to control the secretion of certain hormones from the thyroid gland . TSH secretion is partially regulated by the hypothalamus ,which secretes thyrotropin releasing hormone(TRH). TSH secretion is also regulated by circulating thyroid hormones that exert an inhibiting effect on the release of TRH &TSH ,
) Pituitary Gland thyroid stimulating hormone TSH As the blood concentration of thyroid h. increases the secretion TRH&TSH are reduced hupophysis) Certain external factors influences the release of TRH &TSH these factors included : 1) Exposure to extreme cold , which is a ccompansed by increased hormonal secretion . 2) Emotional stress , which sometimes triggers increased hormonal secretion and other times causes decrease secretion .
) Pituitary Gland Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Is a peptide h. that controls the manufacture and secretion of certain h. from the cortex of the adrenal gland . hupophysis) The secretion od ACTH may be regulated by corticotropin releasing hormone CRH , which is released from hypothalamus in response to decrease contraction of adrenal cortical hormones . Also as increase TSH , various forms of stress result in increased secretion of ACTH by stimulating the release of CRH .
) Pituitary Gland FSH&LH gonadotropin They exert their action on the gonads or reproductive organs FSH hupophysis) responsible for growth and development of egg cell containing follicles in the female ovaries . It is also stimulate the follicles cells to secrete a group of female sex hormone (estrogen ). In male FSH stimulate the initial production of sperm cell in the testes at puberty .
) Pituitary Gland FSH&LH gonadotropin LH hupophysis) Which in the males is also called interstitial cell stimulating hormone ICSH because it act upon the interstitial cell of the testes. Promotes the secretion of sex hormone in both males and females and essential for the release of egg cells from the female ovaries.
) Pituitary Gland FSH&LH gonadotropin hupophysis) The mechanism that regulate the secretion of gonadotropin is not well understood , its known that the hypothalamus secretesa gonadotropin relesing hormone GnRH .