The Impact of Syn-Sedimentary Compaction on Delta Morphodynamics
This study examines the influence of syn-sedimentary compaction on delta development, particularly focusing on how compaction affects delta morphology. It addresses the lack of field measurements by proposing simulation models as an alternative approach to understanding the link between compaction and delta-scale morphodynamics. The research delves into compaction scenarios, formula derivation, modeling results, and validation with laboratory data, offering insights into the complex processes shaping deltas.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
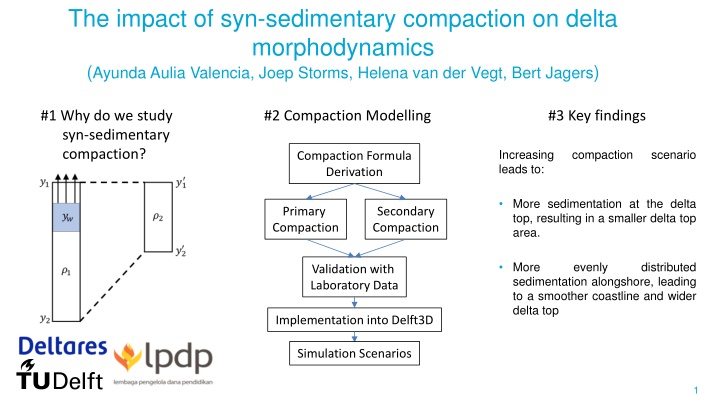
The impact of syn-sedimentary compaction on delta morphodynamics (Ayunda Aulia Valencia, Joep Storms, Helena van der Vegt, Bert Jagers) #1 Why do we study syn-sedimentary compaction? #2 Compaction Modelling #3 Key findings Increasing leads to: compaction scenario Compaction Formula Derivation More sedimentation at the delta top, resulting in a smaller delta top area. Primary Compaction Secondary Compaction More sedimentation alongshore, leading to a smoother coastline and wider delta top evenly distributed Validation with Laboratory Data Implementation into Delft3D Simulation Scenarios 1
The impact of syn- depositional compaction on delta morphodynamics Ayunda Aulia Valencia, Joep Storms, Helena van der Vegt, Bert Jagers A.A.Valencia@tudelft.nl 2
Overview 1.Background 2.Model Design 3.Modelling Results 4.Discussion and Interpretation 3
1. Background Compaction is a natural process, occurring syn- and post-depositional, imposing subsidence to sediment bed. Very little is known about the impact of syn-depositional compaction on the delta development, due to a lack of field measurements and limited possibilities to acquire such measurements considering the spatial (> 103 km2) and temporal (> 103 years) scale of delta evolution The available compaction data from field studies was measured post-deposition in limited spatial and temporal scales. Moreover, laboratory data only provides a first-order approximation of compaction behavior because it does not account for the complexity of various sedimentary environments encountered in deltas, nor does it account for local erosion processes. We propose to study the link between syn-sedimentary compaction and delta-scale morphodynamics by including compaction in simulation models as an alternative to field and laboratory data. 4
2. Model Design #1 Compaction Formula Derivation #2 Compaction Implementation Into Delft3D #3 Delft3D Simulation Primary Compaction Secondary Compaction Compaction Validation with Laboratory Data Initial Model Geometry Delft3D Stratigraphic Layer primary Simulation Scenario: 1. Sediment supply: mud- and sand-rich) 2. Compaction scenario (Cr): 0 0.01 m/yr secondary 5
Modelling Parameters User-Defined Model Parameter Total grid cell of channel in x and y direction Total grid cell of basin in x and y direction Grid cell dimension Initial sediment layer thickness at bed Water discharge Sediment discharge Time interval Total hydrodynamic time Morphological factor Spin-up interval before morphological updating begins Grain Size (sand and two mud fractions) Specific density (sand and mud) Dry bed density (sand and mud) Settling velocity of mud Erosion coefficient mud Critical shear stress of mud Critical shear stress for deposition of mud Value 10x100 281x301 50 4 1600 0.15 0.5 56 120 720 Units - - m m m3 s-1 kg s-1 s day - min m kg s-3 kg s-3 m s-1 kg m-2 s-1 N m-2 N m-2 10E-04, 5E-05, 2E-05 2650 500 and 1600 0.0022, 0.00056 0.0001 0.12, 0.15 1000 6
3.Modelling Results Water Depth Accommodation Delft3D Output Deposited Mass Alongshore Sediment Distribution Deposited Mass at the Delta Top Area Morphology Rugosity Aspect Ratio 9
3.Modelling Results #1 Accommodation #2 Sediment Distribution #3 Morphology Deposited Mass at Delta Top Deposited Mass alongshore Water Depth Aspect Ratio Rugosity Area 10
Interpretation and Discussion The accommodation at the delta top increases over compaction scenarios, driving morphological variability observed in the simulated deltas. The increasing accommodation at the delta top leads to more delta top deposition, resulting in a smaller delta top area. Moreover, sediment distribution occurs more evenly alongshore, leading to a smoother coastline and wider delta top. The change in the delta top geometric characteristics is more apparent in mud-rich deltas, caused by larger accommodation than sand-rich deltas. The impact of compaction on the simulated deltas cannot be validated, as we would require data of millennia-long record of subsidence across the whole delta, which does not exist. The strength of this study is to show that syn-sedimentary compaction does affect delta evolution and that it is essential to be included in simulation studies targeting long- timescale evolution. It is also important to better understand the possible ranges of compaction rates as they impact how delta evolves. 11
Thank you 12