The Human Gastrointestinal System
The human gastrointestinal system plays a vital role in digestion and nutrient absorption. Explore the functions of the GI tract, solid organs like the liver and gallbladder, and the importance of sphincters in maintaining digestive health. Learn about bile production, toxin detoxification, and the impact of liver metabolism on drug processing. Enhance your knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the GI system through informative visuals and learning objectives.
Uploaded on Feb 25, 2025 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
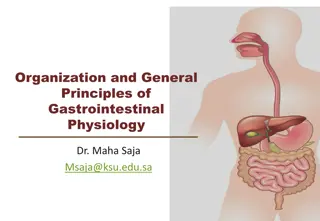
Human Gastro-Intestinal System Part 3 November 2021 Dr. Anna Haro Westside HS
LEARNING Objectives TEKS: 130.231.(c)(1)(A, & B) and 130.231.(c)(2)(A, B, C, F, & G) & (3)(B) Students will apply knowledge of human and cellular biology. Students will develop knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the human gastro-intestinal system (GI). Students will compare the physiology of the solid organs of the GI system. Students will identify the ancillary organs of the GI system.
Objetivos de aprendizaje TEKS: 130.231.(c)(1)(A, & B) and 130.231.(c)(2)(A, B, C, F, & G) & (3)(B) . Los estudiantes aplicar n conocimientos de biolog a humana y celular. Los estudiantes desarrollar n el conocimiento de la anatom a y fisiolog a del sistema gastrointestinal (GI) humano. Los estudiantes comparar n la fisiolog a de los rganos s lidos del sistema GI. Los estudiantes identificar n los rganos auxiliares del sistema GI.
Human gastrointestinal system The main function of the human GI system is the ____________ of food. Digestion begins in the mouth and concludes with waste excretion from the anus. The GI tract consists of seven hollow organs, plus, solid organs and the sphincters.
Human gastrointestinal system GI Tract Solid Organs Sphincters Mouth Liver Pharynx (not a true sphincter), the name is the UES, upper esophageal sphincter (lower) Esophageal sphincter Esophagus Gallbladder Stomach Pancreas Pyloric sphincter Small Intestine Ileocecal sphincter Large intestine (colon) Rectum Internal anal sphincter External anal sphincter Anus
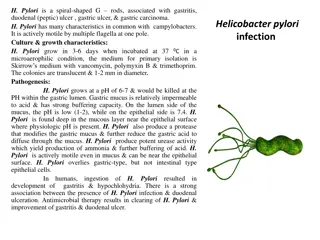
Solid organs Liver: The liver has several functions, but its main job within the digestive system is to metabolize the nutrients absorbed from the small intestine. The liver is your body's chemical "factory" of metabolism. It utilizes digestive materials absorbed by the intestine and builds the various chemicals the body needs to function. Bile is _____________ from the liver into the small intestine and plays an important role in digesting fat and some vitamins. The liver also detoxifies harmful chemicals and substances. It breaks down many drugs that can be toxic to the body, including ___________. Note: metabolic enzymes have a capacity limit; thus, if drug levels exceed the capacity for the liver to metabolize them, then the patient will suffer liver damage and other toxic effects.
Solid organs Gallbladder: The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile from the liver, and then releases it into the duodenum in the small intestine to help absorb and digest fats. Pancreas: The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum that break down protein, fats, and carbohydrates. The pancreas also makes insulin, passing it directly into the bloodstream. Insulin is the key hormone in the body for the utilization of _______________ from carbohydrates (sugar).
The sphincters The function of the sphincters is to prevent the backflow of digestive particles in the GI tract. They function like a one- way trap door. Except for the _________ and _________, the other sphincters are smooth muscle (involuntary). Please, learn the name and location of each sphincter: Name Pharynx (actually, the UES) (lower) Esophageal sphincter Pyloric sphincter Ileocecal sphincter Internal anal sphincter External anal sphincter Location Inferior to the pharynx and superior to the esophagus Inferior to the esophagus and superior to the stomach Inferior to the stomach and superior to the duodenum Inferior to the ileum and superior to the colon Inferior to the rectum and superior to the anus Inferior to the anus and superior to the exit pathway
Human GI tract Image from: https://my.clevelandclinic.o rg/health/articles/7041-the- structure-and-function-of- the-digestive-system Question: What digestive part is not labeled in the image?
https://www.nursingtimes.net/roles/older- people-nurses-roles/anatomy-and-physiology- of-ageing-3-the-digestive-system-27-03-2017/
What are your questions about the GI system? The quiz is Friday! Please ask, email, use Remind, or TEAMS.
Major Grade Group Assignment (posted on the HUB) Email me if you are not working in a group for the individual modified project. Anna.Haro@Houstonisd.org (today is the last day to switch) Due Friday, at the BEGINNING of class.
References https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/7041-the-structure-and- function-of-the-digestive-system http://mcb.berkeley.edu/courses/mcb32/Miller%20notes- %20digestive%20system%20 https://www.britannica.com/science/chyme https://www.chp.edu/our- services/transplant/intestine/education/about-small-large-intestines