The Excretory System in Human Biology
Delve into the intricacies of the excretory system in humans with this comprehensive guide. Explore the functioning and importance of this vital system in maintaining overall health. Gain insights into the various organs involved and their roles in removing waste products from the body. Enhance your knowledge and understanding of human biology through this engaging content.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human 1 Follow-Me iQuiz
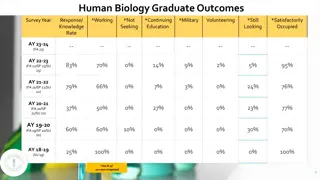
Q. What is meant by the term excretion? Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. State the role of the kidneys in homeostasis. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What tube/structure connects the kidney to the bladder? Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Explain the term plasma. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Explain why red blood cells are normally absent from glomerular filtrate. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Urea is an excretory product. Name a substance from which it is derived. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Where in the human kidney does re-absorption take place? Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name the blood vessel that supplies blood to a kidney. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. In which cavity of the body are the kidneys located? Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name one substance, other than water, excreted in the urine. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Why is glucose normally absent from urine? Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Give a feature of the kidney which indicates that it is an exocrine gland. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Mention one method of excretion in flowering plants. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Name the tube/structure that delivers urine outside the body. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Explain the term glomerular filtrate. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Carbon dioxide is an excretory product. Name a substance from which it is derived. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is the source of the heat that keeps the body at a fairly constant temperature? Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. From which blood vessel does the renal artery arise? Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. The concentration of glucose is the same in plasma and glomerular filtrate. Why is this? Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. State two responses that result when body temperature begins to drop. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. State two ways in which the body is insulated against loss of heat. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Describe the ways in which the body responds when its internal temperature rises above the normal level. Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. Explain briefly how sweating assists in the shedding of excess heat Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question Please CLICK on THIS BOX for the Next Question
Q. What is an endotherm? Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Abdominal; Abdomen Respiration Has ducts; Does not produce hormones Respiration Abdominal; Abdomen Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Film of H2O on body surface, heated by the body; water evaporates with the heat, body left cooler Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Too big to pass into Bowman s capsule Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Animal that produces its own body heat; Body temp independent of environment temp Liquid part of the blood Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Maintaining water/salt balance; Osmoregulation Aorta Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Piloerection; Vasoconstriction; Brain initiates increased metabolic rate Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Carbohydrate; Fat; Fatty acids Urea; Salt; Uric acid Urea; Salt; Uric acid Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Diffusion; Transpiration; Through lenticels or stomata; Leaf fall Plasma that has entered Bowman s capsule Ureter Ureter Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Elimination of waste products of metabolism Protein; Amino acid Urethra Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Fat/Adipose tissue; Trapped air/Hair Proximal convoluted tubule Usually reabsorbed Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery Glucose is small and passes through Vasodilation; Sweat secretion; Hairs lie flat, less air trapped Renal artery
CONGRATULATIONS You re Brilliant
Incorrect Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again Please CLICK on THIS BOX to Try Again