The Anatomy of the Eye: Organs and Structures
Explore the intricate anatomy of the eye, including the organs like Oculus, Auris, and Cutis, and the internal structures such as the lens, vitreous body, and various eye chambers. Discover anatomical terms and visual elements essential for grasping the complex structure of the eye.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
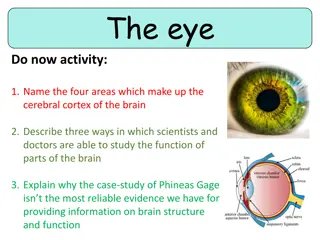
Organa sensoria 1. Oculus. 2. Auris. 3. Cutis M. Petrova
1. Oculus. Organum visus
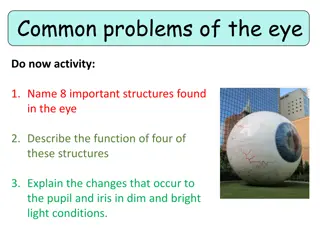
Oculus. Anatomical terms. 1. Coats of the eye bulbus oculi -the globe of the eye; eyeball tunica fibrosa bulbi -fibrous (outer) coat a. tunica sclera= sclera, ae, f * gr. scleros -hard sclera; the white of the eye b. cornea, ae, f -cornea; front part covering iris, pupil tunica vasculosa bulbi -vascular (middle) tunic= uvea, ae, f * lat. uva -grape;because it has grape-like appearance when stripped intact from a cadaveric eye a. iris, idis, f -iris * Iris -from the Greek goddess of the rainbow, because of the many colours of the iris b. pupilla, ae, f -pupil; from Latin pupilla, originally "little girl-doll," diminutive of pupa "girl; doll" , so called from the tiny image one sees of oneself reflected in the eye of another c. corpus ciliare -ciliary body d. choroidea,ae, f -choroid; vascular layer tunica interna bulbi -inner coat = retina, ae, f *lat. rete -net, literally "net-like tunic a. macula lutea -macula; literally yellow spot b. discus (papilla) nervi optici -optic disc c. punctum caecum -blind spot 1. 2. 3. 4.
Oculus= gr. -OPHTHALM- Term-elements 1. Eye coats 1. 2. -BULB-= OPHTHALM-(o) - a. -SCLER- (o) b. -CORNE- (o) / gr. -KERAT- *gr. keras,atos - horn -UVE-(o) a. -IRID-(o) b. -PUPILL-/ gr. -COR- (o) 1. bulbus oculi 2. tunica fibrosa bulbi a. tunica sclera = sclera, ae, f b. cornea, ae, f 3. tunica vasculosa bulbi = uvea, ae, f a. iris, idis, f b. pupilla, ae, f c. corpus ciliare d. chorioidea,ae, f 4. tunica interna bulbi = retina, ae, f 3. *gr. kore -Greek used the same word as in Latin, kor (literally "girl;" see Kore), to mean both "doll" and "pupil of the eye;", source of 17c. colloquial expression to look babies "stare lovingly into another's eyes."etymology a. b. -CYCL- (o) * gr. k/cyklos -circle, wheel, ring -CHORIOID-(o) *gr. chorio+ides -membranous 1. -RETIN-(o)
Anatomical terms. 2. Internal structures 1. camerae bulbi oculi -eye chambers a. camera anterior bulbi -anterior chamber b. camera posterior bulbi -posterior chamber c. humor aquosus -aqueous humor, occupies the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye 2. lens, lentis, f -eye lens * from Latin lens (genitive lentis) "a lentil," on analogy of the double-convex shape 3. corpus vitreum -vitreous body (Lat. glass-like ) the clear gel that fills the space between the lens and the retina of the eyeball
Term-elements 2. Internal structures 1. camerae bulbi oculi a. camera anterior bulbi b. camera posterior bulbi c. humor aquosus 2. lens, lentis, f 3. corpus vitreum a. humor vitreus 1. - fluids (humor aquosus, humor vitreus) -PHAK-(o) / -PHAKIA *phakos - lentil, eye lens, lens -VITRE-/ -HYAL-(o) c. -END-OPHTHALM-used for the intraocular 2. 3. * hyal- word-forming element in scientific compounds meaning "of glass; glass-like, transparent," from Greek hyalos "glass, clear alabaster, crystal lens used as a burning glass," apparently a non-Greek word, said to be of Egyptian origin (glass was first made in Egypt). Hence terms as hyaline mean transparent, glass-like
Anatomical terms. 3. Additional, protecting structures 1. 2. 3. musculi externi bulbi oculi -7 extraocular muscles supercilium, i, n pl. supercilia -eyebrow/s palpebra, ae, f (superior/inferior) -upper / lower eyelid a. angulus oculi -the angle formed by the union of the upper and lower eyelids b. cilia pl. -eyelashes tunica conjunctiva -the delicate membrane lining the eyelids (palpebral conjunctiva) and covering the eyeball (ocular conjunctiva). apparatus lacrimalis -lacrimal apparatus * lacrima -tear a. glandula lacrimalis -lacrimal gland, gland that secretes tears b. ductus nasolacrimalis -nasal duct; the downward continuation of the lacrimal sac c. punctum lacrimale -* Lat. punctum -dot; an opening of a lacrimal duct on the edge of the eyelid d. saccus lacrimalis -lacrimal sac 4. 5.
Term-elements 3. Additional structures 1. - 2. - 3. -BLEPHAR- (o) / -BLEPHARON 4. -CONJUNCTIV- 5. -DACRY- * gr. dacryon - tear 1. musculi externi bulbi oculi 2. supercilium, i, n pl. supercilia 3. palpebra, ae, f 4. tunica conjunctiva 5. apparatus lacrimalis * lacrima - a. glandula lacrimalis b. ductus nasolacrimalis c. punctum lacrimale d. saccus lacrimalis a. DACRY-o-ADEN- b. - c. - d. DACRY-o-CYST-
Term-elements. Eye[s]; sight; vision lat. visus, us, m = gr. -OP-(o), ...-OPIA/ -OPT-, OPTIC-(o) / -OPS-, -OPSI-, ...-OPSIA ambly-opia *gr. ambly-dulled+ ops -eye; weakening of the eyesight without any apparent defect in the eyes, calles also lazy eye click a-sthen-opia *gr. sthen-strenght; a fatigue/tiring of the eyes, usually characterized by discomfort, dimness of vision, and headache my-opia - nearsightedness, short sight ; hyper-metr-opia = hyper-opia - farsightedness, ; dipl-opia *gr. dipl- double; double vision, a single object appears double presby-opia*gr. presby- old, farsightedness, associated with aging hemeral-opia* gr. hemera - day; inability to see as clearly in bright light as in dim light; day blindness an-opsia= an-opia = a-bleps-ia-lat. caecitas -blindness amaurosis - blindness, esp. when occurring without observable damage to the eye: amaurosis fugax - (Lat. fugax meaning fleeting, Gr. amaurosis meaning darkening, dark, or obscure) is a painless temporary loss of vision in one or both eyes. hemi-an-opsia= hemi-an-opia-loss of vision in either the whole left or the whole right half of the field of vision.; scotoma -gr. skot- dark; an area of diminished vision within the visual field. dys-chromat-opsia- color blindness mono-chromat-ismus = a-chromat-opsia- condition of being completely colorblind. di-chromat-ismus -only two of the three fundamental colors can be distinguished
Ophthalmology. General terms - conditions entropion/ectropion palpebrae -the turning inwards / outwards of the edge of the eyelid click horde-olum -medical name for a stye of the eye; hordeolum externum/internum click miosis - constriction of the pupil of the eye (both normal and pathol.); mydriasis - dilation of the eye pupil click phot-o-phobia *phot- light *phobia -fear; abnormal sensitivity to or intolerance of light cor-ectopia- displacement of the eye's pupil from its normal, central position nystagmus - *gr. nystagm-nodding, drowsiness; involuntary eye movement; dancing eye ex-ophthalm-us /en-ophthalm-us - protrusion/ retrodisplacement of the eyeball from/within the orbit, caused by disease or injury. ophthalm-o-plegia-paralysis or weakness of the eye muscles epiphora = dacry-o-rrhoea- excessive flow of tears a-stigmat-ismus - type of refractive error caused by the irregularities in the shape of a person's cornea click cataracta - *gr. kataraktes- waterfall, broken water; a kind of portcullis - opacity/clouding of the lens of the eye or its capsule glauc-oma- * gr.-"cataract, opacity of the lens," perhaps from glaukommatos "gray-eyed," cataracts and glaucoma not distinguished until c. 1705. In the Hippocratic Aphorisms the term glaucoma was used to describe blindness coming on in advancing years associated with a glazed appearance of the pupil. Modern term glaucoma means a group of degenerative eye diseases characterized by damage to the optic nerve usually due to excessively high intraocular pressure - hypertensio intraocularis
Pathological conditions. glaucoma primarium / secundarium: diabeticum - Open-angle glaucoma, also called primary or chronic glaucoma/ Secondary glaucoma - may be caused by an eye injury, inflammation, certain drugs such as steroids and advanced cases of cataract or diabetes (sub) luxatiolentis traumatica (=ectopialentis)-(partial) dislocation of eye lens due to trauma ablatioretinae (traumatica) - detachment of the retina cataracta congenita: hereditaria / acquisita: senilis - congenital form of cataract / acquired for of cataract: senile (in old age) etc. strabismus - strabism; squint eye - condition in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object strabismus convergens = esotropia- the eyes are crossed ("cross eyed") strabismus divergens = exotropia the eyes diverge ("lazy eyed" or "wall eyed") click episcleritis syphilitica / tuberculosainflammation of the layer on top of the sclera caused by syphilis / tuberculosis iridocyclitis acuta / subacuta acute / subacute inflammation of the iris and of the ciliary body degeneratio maculae luteae senilis senile type degeneration of the macula (yellow spot) ophthalmoplegia externa progressivaprogressive external ophthalmoplegia; syndrome of diverse causes and is often accompanied by disorders of other tissues other than extraocular muscles