Study Guide for Neurosciences-II & Psychiatry Module
It is a detailed study guide for the fourth year MBBS students at Liaquat National Medical College and Avicenna Medical College covering neurosciences-II and psychiatry module. The guide includes information on learning methodologies, objectives, resources, assessment methods, examination rules, and regulations. It also introduces the module coordinators, departments involved, and curriculum framework focusing on an integrated curriculum approach. Available resources and schedule details are provided to help students effectively navigate through the module.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
STUDYGUIDE NEUROSCIENCES-II& PSYCHIA TRYMODULE FOURTH YEARMBBS
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE STUDY GUIDE FOR NEUROSCIENES-II & PSYCHIA TRYMODULE Page No. 3 4 5 7 7 8 21 22 23 25 25 28 CONTENTS S.No 1 2 3 4 4.1 4.2 5 5.1 6 7 8 9 Overview Introduction to StudyGuide LearningMethodologies Module 5: NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRY Introduction Objectives and LearningStrategies LearningResources Additional LearningResources AssessmentMethods Modular Examination Rules and Regulations(AVMC) Semester Examination Rules and Regulations of UHS Schedule Page | 2
4th Y E A R MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHI AT RY MODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Module name: Neurosciences-II & Psychiatry Year: Four Duration: 8 weeks Timetable hours: Interactive Lectures, Case-Based Discussion (CBD), Clinical Rotations, Presentations, Demonstrations, Skills, Self-Study MODULE INTEGRA TEDCOMMITTEE MODULECOORDINATOR: CO-COORDINATORS: Professor Dr. Zubair Ahmad(Biochemistry) Professor Dr. Rubina Hafeez (Pathology) Professor Dr.Rehana Shahid(Anatomy) DEPARTMENTS & RESOURCE PERSONS FACILITA TINGLEARNING BASIC HEALTHSCIENCES CLINICAL AND ANCILLARYDEPARTMENTS FAMILYMEDICINE Professor Dr. Muhammad Luqman ANATOMY Professor Dr.Rehana Shahid BIOCHEMISTRY Professor Dr. Zubair Ahmad NEUROLOGY Dr. Aneel Shafi COMMUNITYMEDICINE Professor Dr. Rana Muhammad Akhtar Khan INTERNALMEDICINE Dr. Muhammad Usman Amir PATHOLOGY Endocrinology Prof. Dr. Waheed Ahmed Professor Dr. Rubina Hafeez PHYSIOLOGY Professor Dr. Binyamin Ahmad PEDIATRICS Professor.Dr.Maryam Dr. AneelaZareen PHARMACOLOGY Professor Dr. Rana Tariq Mehmood AVMCMANAGEMENT Professor Dr. Gulfreen Waheed, PrincipalAVMC Brig.Dr. Gul e Rana , Director AVMC Dr. Sadia Awan Dr. Muhammad Muzzammil Sadiq Dr. Usama Bin Ishtiaq STUDY GUIDE COMPILEDBY: Department of Health CareEducation Page | 3
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE INTRODUCTION WHAT IS A STUDYGUIDE? It is an aidto: Inform students how student learning program of the semester-wise module has been organized Helpstudentsorganize andmanagetheirstudiesthroughoutthemodule Guide students on assessment methods, rules andregulations THE STUDYGUIDE: Communicates information on organization and management of themodule. Thiswill helpthestudentto contactthe rightpersonin caseof anydifficulty. Definestheobjectiveswhich areexpectedto beachieved at theendof themodule. Identifies the learning strategies such as lectures, small group teachings, clinical skills, demonstration, tutorial and casebasedlearning that will be implemented to achieve the module objectives. Provides a list of learning resources such as books, computer assisted learning programs, web- links,journals,forstudentsto consultin orderto maximize their learning. Highlights information on the contribution of continuous and semester examinations on the student s overallperformance. Includes information on the assessment methods that will be held to determine every student s achievement ofobjectives. Focuses on information pertaining toexamination policy, rules and regulations. CURRICULUMFRAMEWORK Studentswill experience integratedcurriculumsimilar to previousmodulesof all 7semesters. INTEGRATED CURRICULUM comprises system-based modules such as Eye/ENT, dermatology, genetics, rehabilitation and neurosciences-II & psychiatry modules which links basic science knowledge to clinical problems. Integrated teaching means that subjects are presented as a meaningful whole. Students will be able to have better understanding of basic sciences when they repeatedly learn in relation to clinical examples. LEARNING EXPERIENCES: Case based integrated discussions, Task oriented learning followed by task presentation, skills acquisition in skills lab, computer-based assignments, learning experiences in clinics, wards. Page | 4
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE INTEGRA TING DISCIPLINES OF NEUROSCINCES-II & PSYCHIA TRYMODULE LEARNINGMETHODOLOGIES The following teaching / learning methods are used to promote better understanding: InteractiveLectures Small Group Discussion Case-Based Discussion(CBD) ClinicalExperiences o ClinicalRotations Skillssession INTERACTIVELECTURES:In large group, the lecturer introduces atopic or common clinical conditions and explains the underlying phenomena through questions, pictures, videos of patients interviews, exercises,etc.Studentsareactivelyinvolved in the learningprocess. SMALL GROUP SESSION: This format helps students to clarify concepts, acquire skills or desired attitudes. Sessionsare structured with the help of specific exercisessuchaspatient case,interviews or discussiontopics. Studentsexchangeopinions andapplyknowledge gainedfrom lectures,tutorials and self study. The facilitator role is to ask probing questions, summarize, or rephrase to help clarify concepts. Page | 5
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIA TRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICALCOLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE CASE-BASEDDISUCSSION(CBD): A small group discussion format where learning is focused around a series of questions based on a clinical scenario. Students discuss and answer the questions applying relevant knowledge gained previously in clinical and basic health sciences during the module and construct newknowledge. TheCBDwill beprovided bythe concerndepartment. EXPERIENCES: In small groups, students observe patients with signs and CLINICAL LEARNING symptoms in hospital wards, clinics and outreach centers. This helps students to relate knowledge of basicandclinical sciencesof the module andpreparefor futurepractice. o CLINICAL ROTATIONS: In small groups, students rotate in different wards like Medicine, Pediatrics, Surgery, Obs & Gyne, ENT, Eye, Family Medicine clinics, outreach centers & Community Medicine experiences. Here students observe patients, take histories and perform supervised clinical examinations in outpatient and inpatient settings. They also get an opportunity to observe medical personnel working as a team. These rotations help studentsrelate basicmedicalandclinical knowledgein diverse clinicalareas. SKILLSSESSION:Skills relevant to respective module are observed and practiced where applicable in skillslaboratory. SELF-DIRECTED STUDY: Students assume responsibilities of their own learning through individual study, sharing and discussing with peers, seeking information from Learning ResourceCenter, teachers and resource persons within and outside the college. Students can utilize the time within the college scheduled hoursof self-study. Page | 6
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE SEMESTER 8 MODULE 5 : NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIA TRY INTRODUCTION Neurological disorders jurisdiction starts from Cerebral cortex and moves down through brain stem, spinal cord, cranial nerves, peripheral nerves, nerve roots, autonomic nervous system, neuromuscular junction, and finally involvesmuscles. are diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system. The This module will provide students with a multidisciplinary approach to understanding the etiology of neurological and mental disorders. Neurological problems are the leading cause for disability globally. An estimated 1-billion people around the world have a neurological disorder or disease, which is almost 15-percent of the world s population. According to WHO more than 6 million people die because of stroke each year; over 80% of these deaths take place in low- and middle-income countries. Psychiatric disorders are also major human toll of ill health. According to 2012 WHO data, Neuro-Psychiatric disorders are among 12 leading causes of disability anddeathinPakistan. In this module students will learn about the etiology of common disorders encountered by neurologists and psychiatrists and develop comprehensive understanding of the biological, pathological, psychological and social factors behind these disorders. The basis for pharmacological treatments for conditions such as epilepsy, Parkinson s disease and schizophreniawill alsobediscussed. Page | 7
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIA TRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICALCOLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE COURSE OBJECTIVES ANDSTRA TEGIES By the end ofRehabilitation module students should be able to: COMMUNITYMEDICINE OBJECTIVES I. TEACHINGSTRATEGY List the Neurological disorders, causes and riskfactors Interactivelecture Discuss general methods of prevention ofNeurological disorders Small GroupDiscussion Describeapplication of theprinciples of thepublic health onNeurological Interactivelecture disorders Describethegoalsandfunctions of health systemin provision of the servicesfor Interactivelecture Neurologicaldisorders Discuss the stigma as a threat to individual s psychological and physicalwellbeing Interactivelecture andtherole of educationandtraining in itsprevention 2.NEUROLOGY OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 2.1 Investigation of Neurologicaldisorders Describe various neuroimagingtechniques Discuss uses of various neurophysiological investigations (EMGs, NCS,EEG) Interactivelecture Discuss the indications, contra-indications and process forlumbar puncture Interpret CSF reports of commonconditions 2.2 Lesionlocalization Localizethelikely siteor sites in thenervoussystemwhere alesioncould produce a patient s symptoms andsigns Small GroupDiscussion Formulate a differential diagnosis based on lesionlocalization 2.3 Lesion of cranialnerve Discuss the causes of cranial nervepathologies Diagnosecommoncranialnervelesions thatwould explain lossesof functionin the cranialnerves Skillssession Relatecranialnervedeficits to damageof adjacent,unrelated structures Perform fundoscopicexamination Page | 8
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 2.4 Approach to headache & Primaryheadaches Classifyheadaches Define primary headachesyndrome Differentiate among different patterns ofHeadache Interactivelecture Describetheprocess of historytakingof apatientwith headache Diagnose migraine and tension headache based on written dataprovided Discuss management plans for migraine and tensionheadache 2.5 Secondaryheadaches Discuss differential diagnosis and appropriate diagnostic evaluation forcommon painpresentations Enumerate Red flag signs of secondaryheadache Interactivelecture Describe the classic presentations of trigeminalneuralgia Differentiate between common clinical findings seen in trigeminal neuralgiaand other facial painsyndromes 2.6 Approach tocoma Discuss pathophysiology of coma &altered mental status Assign Glasgow Coma Scale score to a given casescenario Interactivelecture Discuss assessment findings associated with coma &altered mental status Discuss management of coma & alteredmental status 2.7 SeizuresDisorders Classify seizuresclinically Discuss pathophysiology of seizures Discuss assessment findings associated with seizures Describe & differentiatemajortypesof seizures Interactivelecture List most common causes ofseizures Discuss pharmacological treatment ofseizures Define epilepsy & statusepilepticus Describe common side effects ofAEDs Page | 9
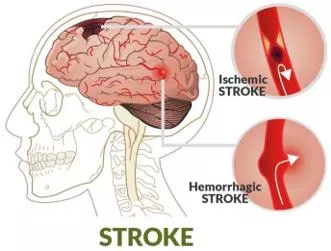
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 2.8 Cerebrovascular Accidents(Stroke) Define the terms stroke/Cerebrovascular Accidents (CVA)&Transient Ischemic Attack(TIA) Describe causes of stroke Differentiate ischemic stroke (cerebral infarct) from hemorrhagicstroke Interactivelecture (intracerebral hemorrhage)in termsof etiologyandpathology Discuss assessment findings associated with stroke,TIA Identifythesigns& symptomsrelatedto TIA Discuss management of stroke &TIA 2.9 Acute CNSInfections Differentiate between acute and chronic CNS infections based on dataprovided Describe the clinical features and investigations of acuteCNS infections Interactivelecture/Small GroupDiscussion Discuss the characteristics of the causativeorganisms Describethepossible complicationsof acuteCNSinfection if left untreated Explain the treatment plan foracute CNS infections 2.10 Chronic CNS Infections Enlist the common chronic CNSinfections Describetheclinical features& investigationsofacuteCNS infections Summarize the characteristics of thecausative organisms InteractiveLecture Describethepossible complicationsof acuteCNSinfection if left untreated Explain the treatment plan foracute CNS infections Approaches to movementdisorders Describe the etiologies and pathogenesis ofmovement disorders (Parkinson s 2.11 disease, essential tremors, Huntington s disease, tics, medicationinduced dyskinesia) InteractiveLecture Describethepresentation of apatientwith movementdisorders Discuss the differential diagnosis of movementdisorders 2.12 Parkinson sDisease Describe the clinical features ofParkinson s disease Discuss approach to a patient withPD Lecture/ SmallGroup Discussion Discuss the differential diagnosis of Parkinson sdisease Outline theprinciples of drugmanagementof Parkinson s disease Page | 10
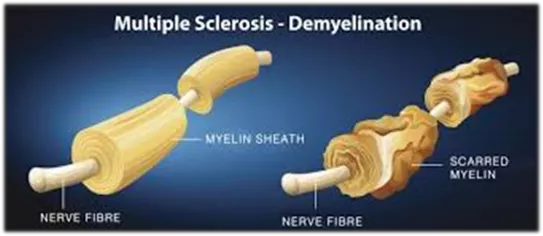
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Multiple sclerosis (MS) and other demyelinatingdiseases List the common CNS and PNS demyelinativediseases 2.13 Describe common anatomical locations of MS plaques, and parts of theCNS that are particularly prone to developinglesions InteractiveLecture Discuss the pathogenesis ofMS InterprettheCSFstudiesareordered in apatientsuspectedof MS Approach to neuropathies and Guillain-Barre syndrome (GBS) Nameat leasttwo laboratorystudiesthatareusefulinthediagnosisof 2.14 peripheral neuropathy List the most common inheritedneuropathies Differentiate between axonal and de-myelinativeneuropathy List the most common causes ofneuropathy Diagnose hereditary peripheral neuropathies based on pathologicalfindings InteractiveLecture Formulate an approach to the evaluation and differential diagnosis ofa patient with peripheralneuropathy Describetheclinical presentation andpathologicalfindingsof theGuillain-Barre syndrome(GBS) Discuss the pathogenesis ofGBS Describe two key laboratory abnormalities in theGBS 2.15 MyastheniaGravis Describe the pathophysiology of Myastheniagravis Explaintheclinical presentation & investigationsforMyastheniaGravis Interactive Lecture + Small GroupDiscussion Discuss the long term management ofMyasthenia Gravis Discuss the management of MyastheniaCrisis 2.16 Dementia Discuss the causes, clinical presentation investigations ofdementia Discuss the differential diagnosis ofdementia InteractiveLecture Describe theprinciples of managementof dementia Page | 11
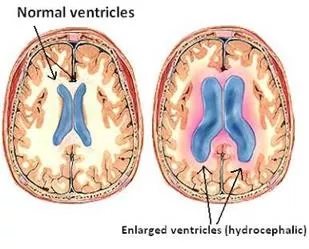
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 3.NEUROSURGERY OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 3.1 Congenital disorders of CNS: Neural tubedefects Diagnose neural tube defects based on writtendata provided InteractiveLecture Describe the management ofMyelomeningocele 3.2 Hydrocephalus & itsManagement Discuss common symptoms and signs of acute hydrocephalus inchildren Discuss common symptoms and signs of normal pressure hydrocephalusin adults InteractiveLecture Define communicating and non-communicatinghydrocephalus Describe the differences in theirtreatments 3.3 Traumatic Braininjury Describetheinitial assessmentof apatientwith headinjury InteractiveLecture Assess Glasgow coma scale in comatose patient Skill session Perform airway prevention in comatosepatient 3.4 Raised Intra Cranial Pressure(ICP) Identify the symptoms and signs of raisedICP Describetheevaluation of apatientwith raisedICPwith referenceto Space InteractiveLecture Occupying Lesion(SOL) 3.5 Traumaticmyelopathies List the causes of traumaticmyelopathies Discuss the clinical presentations, neuro-diagnostic findings, andtherapeutic (nonsurgical vs. surgical) strategies for diagnosing and managing Traumatic InteractiveLecture myelopathies Describe the evaluation of a patient with raised ICP withcompressive myelopathies 4.PATHOLOGY OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 4.1 Reaction of neurons and glial cells to injury, cerebral hypoxia & cerebral edema Describe the pathophysiology of hypoxia and cerebraloedema Discuss the role of microglia in CNS inflammation andrepair. InteractiveLecture Explainall the typesof glialcells,their normal functions,andtheirreactionsto injury Page | 12
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 4.2 Demyelinating diseases of CNS Classify demyelinating diseases of CNS InteractiveLecture Describe pathophysiology and morphology of MultipleSclerosis 4.2 Degenerative diseases of cerebral cortex like Alzheimer sdisease Classify neurodegenerativediseases Interactive Lecture + Small GroupDiscussion Discuss the pathophysiology and morphology ofAlzheimer s and Parkinson diseases 4.3 Braintumors List the genetic conditions associated with braintumors Explaintheinheritance patternandthemostcommontumorsassociatedwith each Interactive Lecture + Small GroupDiscussion Describe the key gross and microscopic differences between differentbrain tumors Describe thepathologicaldiagnosticcriteriaforbrain tumors 4.4 Diseases of skeletalmuscles Describe diseases of the Neuromuscular Junction with special referenceto pathophysiology of Myastheniagravis Describe the Neurogenic and Myopathic Changes in SkeletalMuscle Differentiate among various Inherited Diseases of Skeletal Muscle(includingX- Linked Muscular Dystrophy with Dystrophin Mutation/Duchenne andBecker Interactive Lecture + Small GroupDiscussion Muscular Dystrophy) on the basis ofpathophysiology List various Peripheral Neuropathies including Inflammatory Neuropathies(esp Poliomyelitis) Describe the pathophysiology ofPoliomyelitis 4.5 Common pathogens of nervous system with special references to different age groups List the most common organisms that cause CNS infection in differentage groups Describe the pathogenesis, etiologic agents, cellular reactions, type andlocation of pathologic changes, signs and symptoms (where applicable), age group Interactive Lecture +Lab visit (Microbiology) affected Describe CSF findings of bacterial meningitis, tuberculous meningitis,fungal infections, viral diseases of nervous system andencephalitis Page | 13
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 5. PEDIATRICS OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 5.1 Cerebral Palsy and mental retardation Describe cerebralpalsy List the causes of cerebral Palsy inchildren Describe the topographic classification of cerebralpalsy InteractiveLecture Discuss the associated conditions in cerebralpalsy Explain the management of Children withcerebral palsy 5.2 Common CNS Infections in Children( Meningitis ,Encephalitis and Brian abscess) Identify common pathogens of CNS infections in variousages Recognize common signs and symptoms of CNSinfections InteractiveLecture Investigate and interpret the CSFreports Discuss management of CNS infections and theircomplications 5.3 Upper versus lower motor neuron lesions (Localizing a CNS lesion ) Differentiatebetweenthe symptomsandsignsof upper andlower motorneuron lesions Identify the common conditions associated with AFP.(Polio ,GBS,transverse Case-BasedDiscussion myelitis and traumaticneuritis Identifythecommonconditions associatedwith uppermotorneuronlesions Discussthe importance of Polio eradication programin Pakistan 5.4 Seizures inChildren Identifyvarioustypesof fitsbased ondataprovided List causes of seizures inchildren InteractiveLecture Describe the febrile seizures and childhoodepilepsy Discuss management of acuteseizures 6. PHARMACOLOGY OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 6.1 Sedatives & hypnotics;Benzodiazepines Differentiate among benzodiazepine and barbiturate classes regarding onsetand duration of action, mechanismsof action, routeof administrationand Interactivelecture therapeuticindications Describe advantages and disadvantages of benzodiazepine sedativehypnotics Page | 14
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 6.2 Sedatives & hypnotics;Barbiturates Discussthe classification,onsetandduration of action,mechanisms of action, Interactivelecture route of administration, clinical uses and adverse effects ofBarbiturates 6.3Migraine Discuss the preventative and acute treatment ofmigraine Case-BasedDiscussion 6.4 Drugs of Anesthesia: Generalanesthetics Describe the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic principles ofdrugs Interactivelecture commonly involved in generalanesthesia 6.5 Drugs of Anesthesia: Local anesthetics Discussthemechanismof actionof localanesthetics List the common adverse effects of localanesthetics Interactivelecture Describethecommonroutesof administrationof localanesthetics 6.6 Anti-epilepticdrugs Discussthe Indications& adverseeffectsof anti-epilepticdrugs Case-BasedDiscussion 6.7 Anti-psychoticdrugs Classify antipsychotic drugs List the first and second generationdrugs Interactivelecture Describe the mechanism of action, indications,side effects 6.8 CNS Stimulants andhallucinogens List different classes of CNSstimulants Describe the main pharmacological effects theyproduce Describe the common sideeffects Small GroupDiscussion Explain the mechanism of action and uses of CNS stimulantsdrugs Identify the different types ofhallucinogens Describetheeffectsof hallucinogensonthenervoussystem 6.9 Drugs for Parkinson s Disease(PD) Recommendaninitial treatmentplanforapatientwith PD Describethepharmacology, clinical effect,andsafetyof drugsforthe Case-BasedDiscussion management ofPD 7. SKILLSLAB OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 7.1 SuturingTechniques Identify different suture materials andneedles Demonstrate wound closure techniques by using simple interrupted andsimple continuoussutures Demonstrationand Hands-OnPractice Page | 15
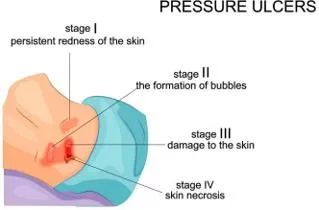
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 8. PLASTICSURGERY OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 8.1 Care of Bed sores (PressureUlcers) Describe the etiology and pathophysiology ofpressure ulcer development Identify risk factors forpressure ulcer development Evaluate pressure ulcer risk assessment methods andprocedures Diagnose and classify pressureulcers Describe the evidence about support surfaces (cushions and mattresses),heel preventive devices, nutrition, and repositioning to prevent and treatpressure ulcers Small groupDiscussion Recommendeffectiveinterventionsforlocaltreatmentof pressureulcers Describe best practices for cleansing, debridement, assessment and treatmentof infection List indications and contra-indications for wound dressings, biologicaldressings, growthfactorsandbiophysical agents forthe treatmentof pressureulcers Describetherole of surgery to treatpressure ulcers 9. PSYCHIATRY OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 9.1 Mood disorders (depression and bipolardisorders) Describe the diagnostic criteria formood disorders (including depression and bipolardisorders) Identify common risk factors for mooddisorders Interactivelecture Discuss the effective management of mooddisorders Statethe epidemiology& aetiologyof mooddisorder 9.2Suicide Discussthe factorstheories of suicidewith referenceto recent advances Explain the process ofrisk assessment and its management Small GroupDiscussion Describe the public health approach forsuicide prevention, including primary, secondary, and tertiary preventionstrategies Page | 16
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 9.3 Anxiety, Panic disorders and Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Distinguish the essential features of generalized anxiety disorder(GAD), panic attacks, and panic disorder, phobias (Specific, Agoraphobia and SocialPhobia Discuss the clinical symptoms, management and differentialdiagnosis Describe the symptoms of Obsessive Compulsive Disorder(OCD) Interactivelecture Define obsessions and compulsions and give examples ofeach Discuss the management ofOCD Discuss the biological, psychodynamic and cognitive-behavioral theories ofOCD 9.4 Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and Acute Stress Response(ASR) Discuss the clinical features and etiology of PTSD andASR Explain the causes of PTSD andASR Small GroupDiscussion Describe the management of theseconditions 9.5Schizophrenia Diagnose schizophrenia based on givencriteria Discussthe principlesof treatmentof schizophrenia Interactivelecture Describetheetiological factorsandprevalenceof thiscondition 9.6 Other PsychoticDisorders Discuss the prevalence of various psychoticillnesses Describe the key features of psychoticillnesses Differentiate among the psychotic disorders based on dataprovided Interactivelecture Select psychopharmacologic treatment for psychoticdisorders Explainthegeneralprinciples onhow to approachapatientwith psychosis 9.7 Disorders Of Addictive Behavior and Alcohol And Substance AbuseDisorders Describe addiction Discuss the behavioral issue related toaddiction List different types of addictivebehaviors Discuss eatingdisorders Discuss the relationship of addiction withOCD Small GroupDiscussion Differentiate between abuse anddependence Explain how different psychological issues pertain to addictivebehavior Differentiate among tolerance, use/ excessive use, abuse/misuse,dependence, excessive withdrawal andintoxication Page | 17
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE List different drugs according to theclassification. Discussbriefly the effectsonthebodyof alcoholandother illicit drugs(cannabis, opioids, cocaine, amphetamines andLSD) Describethemodesof action of alcoholandotherillicit drugs Explain the psychological, emotional, physical and social insults ofthese drugs on humans Describe delirium tremens Small GroupDiscussion Describetheimpact of suddenlystoppingtheuseof addictive drugs Discussthe differenceof harmminimizationanddrugeradication 9.8 Somatic And Medically unexplainedSymptoms Discuss the assessment of medically unexplained symptoms according totheir severity Describe how to make a diagnosis when itis appropriate Small GroupDiscussion Manage these conditions appropriately including a steppedapproach 9.9 Introduction To Childhood Psychiatric Disorders & child abuse Discussthe factorsimpactingchild hoodmental andemotionalhealth. Describe different child hood psychiatricdisorders Diagnose common psychiatric illnesses inchildren Describe theuseof multimodal treatmentin children Describe different kinds of childabuse Discuss the implications of childabuse Interactivelecture Explain the risk and etiological factors forchild abuse Discus the identifying features of childabuse Explain the legal aspects of rights ofa child Explainthemanagementof casesof various typesof child abuse Discussthe role of mentalhealthprofessionalin child abuseapartfromthe management of the any associateddisorder 9.10 Behavioral Disorders Identifybiological and psychosocial riskfactorsof emotionalor behavioral disorders Interactivelecture Describetheclassification,interventionandtreatmentof behavioraland emotionaldisorders Page | 18
4th YEAR MBBS, EUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE Categorize mental health disorders such as emotional disorders,behavior disorders in children andadolescents Identify the symptoms of commonly diagnosed emotionaldisorders, behavior Interactivelecture disorders in children andadolescents Discussthe latestmethodsof treatmentandassessment 9.11 Introduction To Old Age Psychiatric Disorders & Delirium And Dementia Describe the variations in presenting psychiatric symptoms inthis age group Explainthehighlikelihood of co-morbidityin thisagegroup Diagnose common psychiatric illnesses in the geriatricgroup Describe theuseof multimodal treatmentin old agepatients Name standardized assessment tools and their use in measuringcognitive impairment. Interactivelecture Formulatethe differentialdiagnosisof apatientpresentingwith cognitive impairment suggestive ofdementia Compare and contrast features of dementia versusdelirium Formulate the clinical assessment and differential diagnosis of an elderlypatient with delirium 9.12 Psycho-sexualDisorders Discuss different types of psychosexualdisorder Discuss the characteristic features of various psychosexualdisorders Interactivelecture Describe the etiology and prevalence ofvarious psychosexual disorders Explain principles of management of theseconditions 9.13 Introduction ToCounseling Definecounseling Differentiate among counseling, psychotherapy and activelistening Differentiate among various types of psychotherapies/counseling Differentiate among empathy, sympathy andapathy Describe the prerequisites of counseling/psychotherapy Small GroupDiscussion Differentiate between boundary andbarrier Describe the basic rules ofcounseling Discuss the setting, rules and boundaries ofcounseling Identify some basics do s and dont s ofcounseling Page | 19
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 10.RADIOLOGY OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 10.1 CT ScanBrain Describetherole of radiographicimagingstudiesin diagnosisandmanagement of strokepatients Identify thefollowing: i. Normal cranial and neurologicalanatomy ii. Skull fracture iii. Extra-cerebral blood onCT iv. Intracranial blood onCT v. Appearance of both hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes onCT 10.2 MRI Brain Identifytheradiological featuresof normalanddiseasedspineandvertebral column onMRI 10.3 Neuro radiology of brain tumor, head injury andhydrocephalus Describetherole of thediagnostic radiological modalities in theevaluation of patients withbrain tumor, head injury and hydrocephalus Listthe advantages andlimitationsof the following diagnostictoolsusedin the evaluation of braintumors: i. Plain skullradiographs ii. Plain spineradiographs iii. CT scan of head orspine Small GroupDiscussion Small GroupDiscussion Small GroupDiscussion 11.BIOETHICS OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 11.1 Principals ofEthics Apply principles of patientautonomy,equity,justice,beneficence,non- malfeasance in clinicalsettings Small GroupDiscussion 12. FAMILYMEDICINE OBJECTIVES TEACHINGSTRATEGY 12.1 Bio-PsychosocialModel Describetheimportance of bio-psychosocialmodelforcomprehensive assessment, clear communication and targeted treatment of symptoms in patients with chronic neurological disorders (dementia, alzheimers,parkinsons disease) Small GroupDiscussion Apart from attending daily scheduled sessions, students too should engage in self-study to ensure that all the objectives arecovered Page | 20
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LEARNINGRESOURCES Discipline Resources TEXTBOOKS 1. Preventive and Social Medicine by KPark 2. Community Medicine by M.llyas 3. Basic Statistics for the Health Sciences by Jan WKuzma 4. Textbook of Community Medicine and Public Health, 2018. Saira Afzal, SabeenaJalal COMMUNITYMEDICINE TEXTBOOKS 1. Davidson's Principles and Practice ofMedicine 2. Kumar and Clark's Clinical Medicine, Edited by ParveenKumar, 9thEdition NEUROLOGY TEXTBOOK 1. Bailey & Love's Short Practice of Surgery , 26thEdition NEUROSURGERY TEXTBOOKS 1. Robbins & Cotran, Pathologic Basis of Disease,9thedition. 2. Rapid Review Pathology,4th edition by Edward F. GoljanMD PATHOLOGY WEBSITES: http://library.med.utah.edu/WebPath/webpath.html http://www.pathologyatlas.ro/ TEXTBOOKS 1. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics, 19thEdition 2. Textbook of Pediatrics by PPA, preface written by S. M.Haneef 3. Clinical Pediatrics by Lakshmanaswamy Aruchamy, 3rdEdition PEDIATRICS TEXTBOOKS 1. Lippincot IllustratedPharmacology 2. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology byKatzung PHARMACOLOGY TEXTBOOK 1. Oxford textbook of psychiatry by Michael G. Gelder, 2ndEdition PSYCHIATRY TEXTBOOK 1. Bailey & Love's Short Practice of Surgery , 26thEdition PLASTICSURGERY Page | 21
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIA TRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICALCOLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE ADDITIONAL LEARNINGRESOURCES Hands-on Activities/PracticalStudents will be involved in Practical sessions and hands-on activitiesthat link with the Neurosciences-II and Psychiatry Module toenhance learning. Models available in the museum are a rich learning resource forquick Museum review of anatomy and relatededucational activities Skills acquisition in a simulated environment in theskills lab involving experiential learning will ensurepatientsafety andwill alsohelp to build SkillsLab confidence in approaching thepatients Videos and podcasts will familiarize the student withthe procedures and protocolwhich theycanwatch andlistento atanytimeandwherever they Videos/Podcasts are, as part of task orientedlearning Students will use easily accessible internet resources with added time InternetResources flexibilityto enrichandupdatetheirknowledge anditsapplication Page | 22
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE ASSESSMENTMETHODS: Theory: Best Choice Questions (BCQs) also known as MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions) are used to asses objectives covered in eachmodule. A BCQ has a statement or clinical scenario followed by four options (likelyanswer). Students after reading the statement/scenario select ONE, the most appropriate response from the given list ofoptions. Correct answer carries one mark, and incorrect zero mark . There is no negative marking. Studentsmarktheirresponseson specifiedcomputer-based/OMRsheet designedforAVMC EMQs: An EMQhas: An option list of5-15 which may be nerve supply, functions, diagnosis, investigations o etc A Lead In Statement/Question o Two to four Stems or ClinicalScenarios Foreachstemorclinical scenario,the studentshouldchoosethemostappropriateoption o from the optionlist. Asingle option canbeusedonce,morethanonceornot at all. Correct answer carries one mark and incorrect zero mark . There is NO negativemarking. Student mark their responses on a specified computer-based sheet forEMQs. OSPE/OSCE: Objective Structured Practical/ClinicalExamination: o Eachstudentwill beassessedonthesamecontentandhavesametimeto completethe task. Comprise of 12-25stations. Each station may assess a variety of clinical tasks, these tasks may include history taking, physical examination, skills and application of skills andknowledge Stations are observed, unobserved, interactive and reststations. Observed and Interactive Stations: o Theywill be assessedbyinternal orexternalexaminers throughstructuredvivaortasks. Unobserved Stations: It will be static stations in which there may be an X-ray, Labs reports,pictures, clinical scenarios with related questions for students to answer on the provided o answercopy. Page | 23
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Rest station o I t is a station where there is no task given and in this time student can organize his/her thoughts. AVMC nternal EvaluationPolicy Students will beassessedto determine achievement of moduleobjectivesthroughthe following: Module Examination: will be scheduled on completion of each module. The method of o examination comprises theory exam which includes BCQs and OSPE (Objective Structured PracticalExamination). Graded Assessmentof studentsbyIndividual Department: Quiz, viva, practical, assignment, o small group activities such asCBL,TBL,TOL,online assessment, ward activities, examination, andlogbook. Marksof bothmodular examinationandgradedassessmentwill constitute20%weightage. As per UHS policy, this 20% will be added by UHS to SemesterExamination. Example : Number of JSMU Marks allocated for Semester Theory and Internal Evaluation InternalEvaluation (Task Presentation + Assignments + Modular Exam 20% Semester Examination TheoryMarks Total(Theory) Semester 80% 100% FormativeAssessment Individual department may hold quiz or short answer questions to help students assess their own learning. The marks obtained are not included in the internalevaluation More than 75%attendance is neededto sitforthe modular andsemesterexaminations Page | 24
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIA TRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICALCOLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE MODULAR EXAMINATION RULES & REGULATIONS(AVMC) Studentmustreportto examinationhall/venue, 30 minutesbeforetheexam. Exam will begin sharp at the giventime. No student will be allowed to enter the examination hall after 15 minutes of scheduled examinationtime. Studentsmust sitaccordingto theirroll numbersmentioned ontheseats. Cell phones are strictly not allowed in examinationhall. If anystudentisfoundwith cell phonein anymode(silent, switchedoffor on)he/shewill benot be allowed to continue theirexam. No students will be allowed to sit in exam without University Admit Card, AVMCCollege ID Card and LabCoat Student must bring the following stationary items for the exam: Pen, Pencil, Eraser, and Sharpener. Indiscipline in the exam hall/venue is not acceptable. Students must not possess any written materialorcommunicatewith theirfellowstudents. Page | 25
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE ExaminationProtocols: In each semester, module will be assessed by theory paper comprising MCQs and EMQs. For example semester 8 will have separate theory paper of EYE, Dermatology, Plastic Surgery & Burns, Neuro-Sciences-II & Psychiatry, Genetics-II and Rehabilitation modules. There will be one OSPE (Objective Structured Practical Examination)/OSCE (Objective Structured Clinical Examinations) which will cover all modules ofsemester eight. 1. Theory Theory paper will comprise of80 one best type MCQs and 20 EMQs. Timeduration fortheorypaperwill be120minutes. Students will mark their responses on UHS specified response sheets assessed by computer software. It will carryout 80%contributionintheoryresultsof the Semester. There is no negativemarking. 2. OSPE/OSCE: It maycomprisebetween12-25stations.Eachstationwill carry10marks. 3. UHS GradingSystem It will be based on GPA 4system Marks obtained in Percentagerange NumericalGrade AlphabeticalGrade 80-100 4.0 A+ 75-79 4.0 A 70-74 3.7 A- 67-69 3.3 B+ 63-66 3.0 B 60-62 2.7 B- 56-59 2.3 C+ 50-55 2.0 C <50 Un-grade-able 0 U A candidate obtaining GPA less than 2.00 (50%) is declared un-graded(fail). Cumulativetranscriptisissuedat the endof clearance of all modules. Page | 26
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE 4. Retake Examination Retake examinations are for those students who fail in semester examinations, and those who have passed semester examinations with GPA less than 3.0 may reappear in respective retake examination to improvegrades. The format of the retake examination is exactly thesame as in semester examinations. Retakeexaminationwill beconducted3weeksafterdeclarationof results. 5. Promotion to nextclass Studentswho passboth semesterexaminations arepromotedfromfirstyearto secondyear. Students who fail the MBBS first year semester retake examination will be promoted to second year. Students will be promoted from second year to third year and onward only if they have passed the semester examinations of thatyear. Clearance of all modules and their components of semester one to four are mandatory for promotion from second year tothird year (as per PMDC rules). As per PMDC rules any candidate failing to clear a module or its component in four (1+3) attemptsisNOTallowed to carryout furthermedicaleducation. Clearance of all modules and their components of semester/s are mandatory for promotion from third yearonward. Page | 27
4th YEAR MBBS, NEUROSCIENCES-II & PSYCHIATRYMODULE LIAQUAT NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE AVICENNA MEDICAL COLLEGE SCHEDULE: 4th Year SEMESTER8 WEEKS WEEK1 WEEK2 WEEK3 MONTH 23rd April2018 OPHTHALMOLOGY 12th May2018 14th May2018 15th May2018 26th May2018 28th May 2nd June2018 4th June2018 14th 18th June2018 20th June2018 21st & 22nd June2018 25th June2018 MODULAREXAM WEEK1 WEEK2 WEEK1 WEEK1 Eid-Ul-Fitr WEEK2 DERMATOLOGY GENETICS REHABILITATION DERMATOLOGY, GENETICS & REHABILITATION MODULAREXAM** WEEK1 WEEK2 WEEK3 WEEK4 WEEK5 WEEK6 WEEK7 WEEK8 NEUROSCIENCES-II &PSYCHIATRY 11th Aug2018* 13th & 16th Aug2018* 17th Aug2018* MODULAREXAM ENT & EYEOSPE PREPARATORYLEAVE SEMESTEREXAM Sept2018* *Final dates will be announcedlater ** There will be combined module exam for Dermatology, Genetics and Rehabilitation modules Page | 28
 undefined
undefined