SAMPLING
Non-probability sampling methods like Quota Sampling, Judgemental Sampling, Systematic Sampling, and others offer various ways to select samples without considering probabilities. Learn about these methods and the differences between them to make informed decisions in your research studies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SAMPLING (NON PROBABILITY SAMPLING) DR. PRIYANKA SHUKLA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR & RCI registered Clinical Psychologist Department of Psychology SAHSS & LIFE LONG LEARNING AND EXTENSION CSJM UNIVERSITY, KANPUR
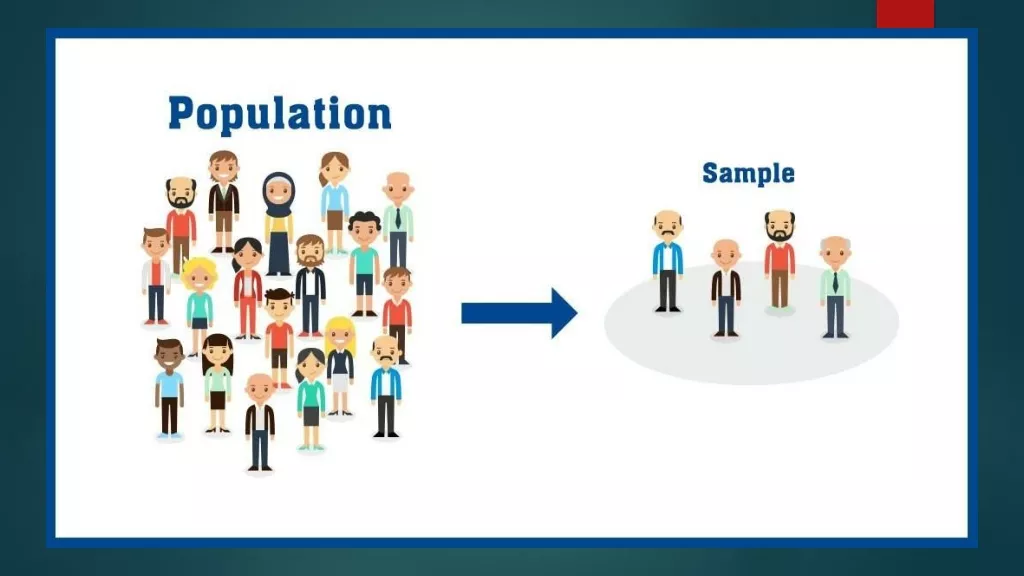
Non Probability Sampling: There is no way of assessing the probability of the elements of the population being included in the sample. Types: Quota Sampling Accidental Sampling Judgemental or Purposive Sampling Systematic Sampling Snowball Sampling Saturation Sampling Dense Sampling
Quota Sampling: This is similar to stratified random sampling, here investigator recognize different strata of population and from each strata he selects the number of individual arbitrarily. (this is only difference between quota and stratified random sampling, in stratified random sampling sample drawn randomly from the strata.)
Purposive and Judgemental Sampling: Here the investigator on the basis of his impression makes a judgement regarding the concerned cases and select them as a sample. Accidental Sampling: The investigator does not care about including the people with some specific or designated traits, rather he is mainly guided by convenience and economy.
Snowball Sampling: Research participates recruit other participants for study. Systematic Sampling: All the items of the universe are systematically arranged and numbered and then sample units are selected at equal intervals. One item of the first selected numbers would be selected at random.
Saturation Sampling & Dense Sampling: Saturation sampling is defined as drawing all elements or individuals having characteristics of interest to the investigator. Drawing all physicians having at least the age of 45 (from a small community), would be called saturation sampling. Dense sampling is a method of sampling which lies somewhere between simple random sampling and saturation sampling.