Sampling Methods in Research
Explore key concepts in sampling such as probability and non-probability methods, sampling error, representativeness, and types of biases. Learn about the importance of sampling in research, theoretical variables, conceptualization, and operationalization. Evaluate different types of sampling processes and their impact on data collection and analysis.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CONCEPTS TO BE INCLUDED Population Quota sampling Sampling frame Representativeness Probability sampling Sampling error Nonprobability sampling Simple random sampling Sampling bias Convenience sample Cluster sampling Purposive (judgmental) Stratified sampling (Item) Non-response sampling Response rate Snowball sampling Weighting 1 9/30/2024 Footer text: to modify choose Insert (or View for office 2003 or earlier) then Header and Footer
SAMPLING HENK VAN DER KOLK
AIM When do we need sampling? What does a sampling process look like? Two different types of sampling Probability sampling Non-probability sampling Criteria: Sampling bias & Sampling error Evaluating different types of sampling 3
TWO ASPECTS OF OBSERVATION Example: how many people in the Netherlands do currently support the EU? Theoretical variable(s) Conceptualization Operationalization Measurement Sampling Unit (s) Data 4
TWO ASPECTS OF OBSERVATION How well do the data reflect my units of analysis? Theoretical variable(s) Conceptualization Operationalization Measurement Sampling Unit (s) Data 5
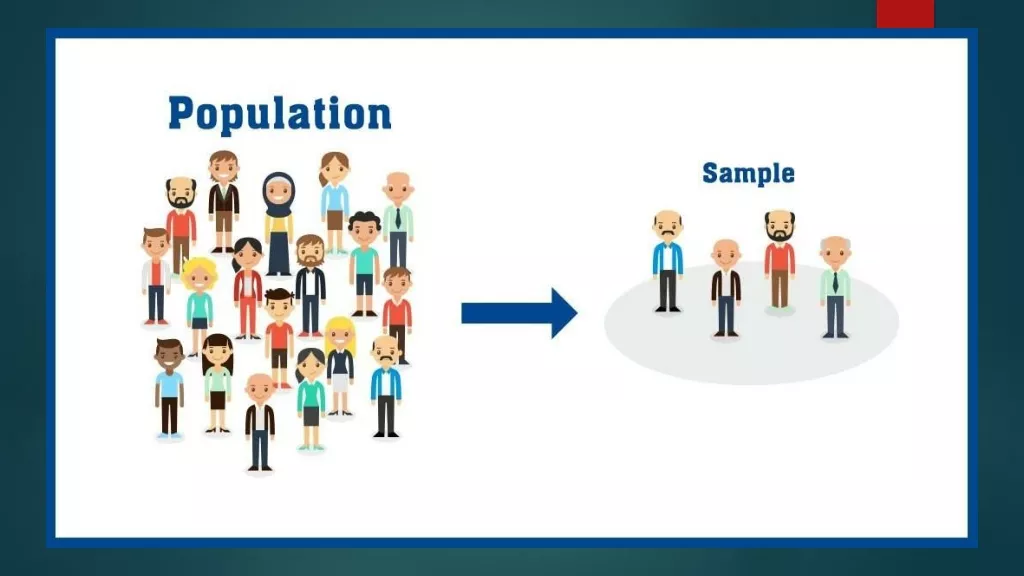
WHEN SAMPLING? If not all units mentioned in our research question can be studied, we need to sample . Studying a smaller set of units with the aim to say something about all units. 6
Dutch people between 18 and 65 in 2015 Population Sampling frame Population registry Sample Every 100thindividual Studied units People participating Data on studied units People answering a specific question 7
WHAT IS SAMPLING? sampling Sampling frame Interviewed sample Population Sample Data 8
DISTORTIONS IN THE PROCESS ??????????? ?????? ???? ?????? ???? = response rate sampling Sampling frame Interviewed sample Population Sample Data Registration errors Sampling error & bias Non-response, refusals 9 Item non-response
FOCUS ON (DISTORTIONS IN) SAMPLING sampling Sampling frame Interviewed sample Population Sample Data Sampling error & bias 10
SAMPLING PROCEDURES Is the chance that a specific unit from the sampling frame is included in the study, known? No: Non-probability sampling Yes: Probability sampling 11
NON-PROBABILITY SAMPLING Convenience Purposive Snowball sampling Quota Example: opt-in survey of some newspaper Selected units do NOT neccessarily reflect the population. The sample is probably biased . 12
PROBABILITY SAMPLING Simple Stratified (multi-stage) cluster sampling Example: Simple random sample from the population registery. Selected units reflect the population. 13
ASSESSING SAMPLING We always make sampling mistakes. Two types of mistakes: Sampling bias (sampling invalidity) Sampling error (sampling unreliability) 14
SAMPLING BIAS Bias: not being typical for the population. Studying the wrong group of people. Example: how many people in the Netherlands currently support the EU? Using snowball sampling. 15
SAMPLING ERROR Sampling error is a consequence of sample size and characteristics of the population. Example: how many people in the Netherlands currently support the EU? sample size 5 and sample size 400 16
EVALUATING SAMPLING PROCEDURES Non-probability sampling: Bias (Sample size relatively unimportant) Probability sampling: No bias Sample size affects sampling error 17
THIS MICRO LECTURE When do we need sampling? Different types of sampling Sampling bias Sampling error Evaluating different types of sampling (sampling bias and sampling error) 18
19 9/30/2024 Footer text: to modify choose Insert (or View for office 2003 or earlier) then Header and Footer
IMAGES USED Slide 16/18: https://pixabay.com/en/europe-european-union-flag-155191/ 20




 undefined
undefined