Salmonella: A Zoonotic Pathogen
Salmonella, a genus of bacteria, includes species causing various diseases in humans, cattle, sheep, goats, and poultry. The pathogen can be transmitted through contaminated food and is classified into typhoidal and nontyphoidal serovars. Nontyphoidal serovars are common and typically lead to self-limiting gastrointestinal issues. Salmonella's Gram-negative morphology, including pleomorphic forms, and its incubation period in different environments contribute to its pathogenic nature.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Salmonella Dr. Ban sahib abed al-nabi zoonotic disease unit post graduate lecture
Species In human Diseases 1. S. typhi Causes typhoid fever 2. S. para typhi causes para typhoid fever 3. S. enteritidis causes food poisoning 4. S. typhimurium causes food poisoning In cattle & sheep Diseases 1. S. dublin Enteritis & septicaemia 2. S. typhimurium Enteritis & septicaemia
Species in goat Disease 1. S. typhimurium 2. S. enteritidis 3. S. hadar Species in poultry & bird Disease 1. S. pullorum 2. S. gallinarum 3. S. arizonae causes enteritis = = causes white diarrhoea causes fowl typhoid causes enteritis,septicaemia = = 4. S. enteritidis 5. S. typhimurium
Salmonella as pathogens Salmonella species are facultative intracellular pathogens .Many infections are due to ingestion of contaminated food. Salmonella serovars can be divided into two main groups typhoidal and nontyphoidal Salmonella.
Nontyphoidal serovars are more common, and usually cause self- limiting gastrointestinal disease. They can infect a range of animals, and are zoonotic, meaning they can be transferred between humans and other animals.
Morphology & S taining : It is a Gram negative bacteria , cocco bacilli or straight rod with rounded ends . some times they develop into pleomorphic forms or very short coccobacilli after prolonged culture on media .
Micro scopic appearance & Incubation period : G ram stain Negative Morphology cocco bacilli or straight rod with rounded end Motility by peritrichous flagella (actively motile) except S. pullorum & S. gallinarum Capsule observed with mucoid strains Spore Non Temperature 37 c on media without any addition Time 16- 24 hours Atmosphere Aerobic & facultative an aerobic
Natural Habitat Salmonellae live in the intestinal tracts of warm and cold blooded animals. Some species are ubiquitous. Other species are specifically adapted to a particular host. In humans, Salmonella are the cause of two diseases called salmonellosis: enteric fever (typhoid), resulting from bacterial invasion of the bloodstream acute gastroenteritis, resulting from a foodborne infection . The majority of infected animals become subclinical excretors . Salmonella can survive for 9 months or more in the environment such as moist soil , water , faecal & animal feeds .
Isolation & Identification of salmonella : 1.Enrichment broth Mannitol Selenite broth & Tetera thionate broth & Soy peptone broth for salmonella isolation from stool specimen . These fluid a useful medium which allows the growth of salmonella but inhibits other enteric organisms .
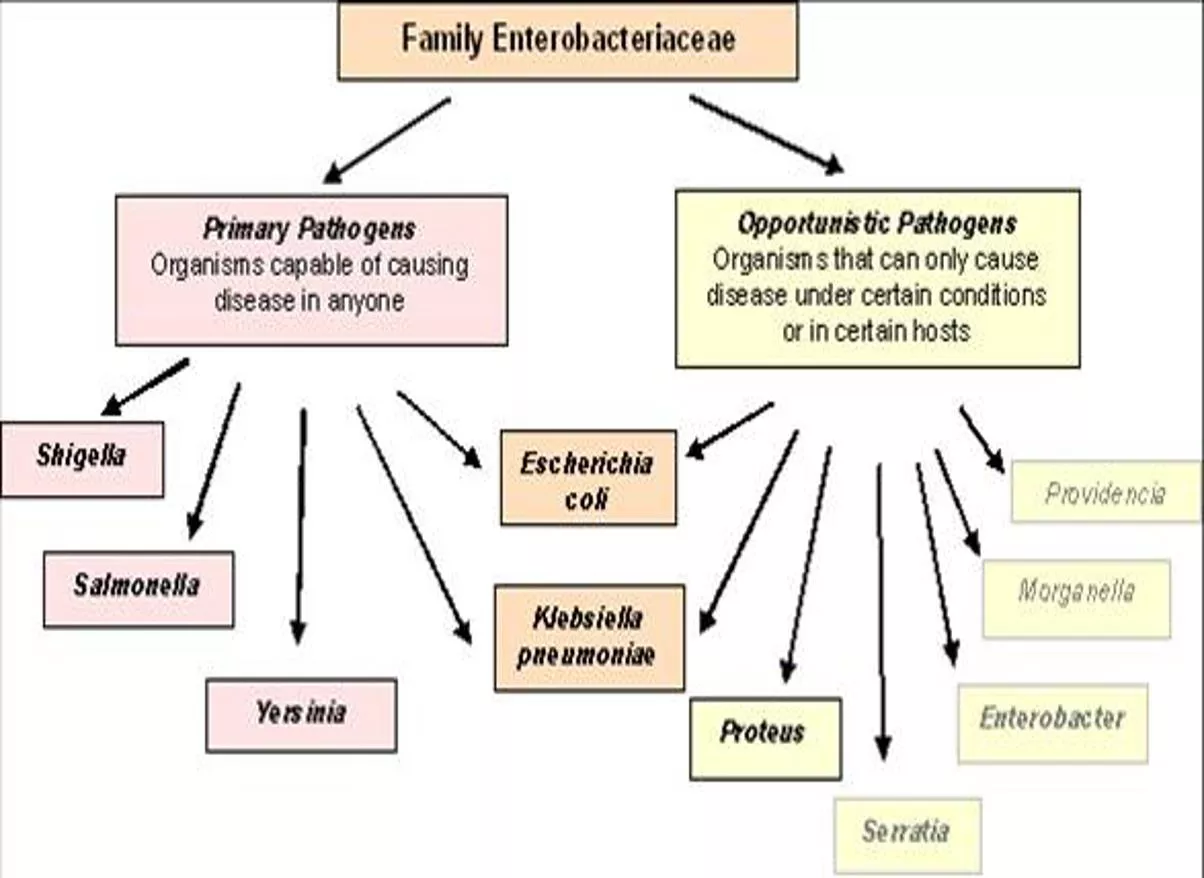
1. MacConkey agar & desoxy cholate citrate agar : (DCA) The medium & colonies are pale yellow- straw smooth & non lactose Ferment . lactose fermenting Non lactose Fermenting Escherichia coli Salmonella spp Klebsiella pneumoniae Shigella proteus
2. Salmonella- Shigella agar (ss agar) : Its selective for salmonella . Colonies are colorless with black center . Non lactose ferment .
3. Xylose lysine desoxy cholate (XLD) : Red colonies with black centers of H2S producing . Non lactose ferment .
4. Brilliant green agar : Red colonies & medium . Non lactose ferment . Smooth circular entire edges .
5. Bismuth sulfite agar : Is highly selective for salmonella & one of the most sensitive media to detect H2S production. Colonies are black surrounding by metallic sheen on the surface.
6. Hektoen enteric agar (HE) : Colonies are blue-Green with black due to H2S production. Non lactose ferment .
Biochemicals test : salmonella don t ferment lactose, sucrose but ferment glucose, maltose , mannitol . positive Negative
TSI/ p/y +H2S simmon citrate + Motility test/ motil +H2S
MR/ positive VP/ Negative Negative urease test -