Risk-Benefit Assessment for Outdoor Play Equipment
This risk-benefit assessment evaluates various outdoor play equipment, including swings, stepping stones, artificial grass, sandpit, trees, basketball net, and doors, by weighing the benefits they offer against the associated risks. Each item is assessed for its benefits such as developing motor skills and balance, alongside potential risks like falls or collisions. Recommendations are provided to manage risks effectively while maximizing positive outcomes for children.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
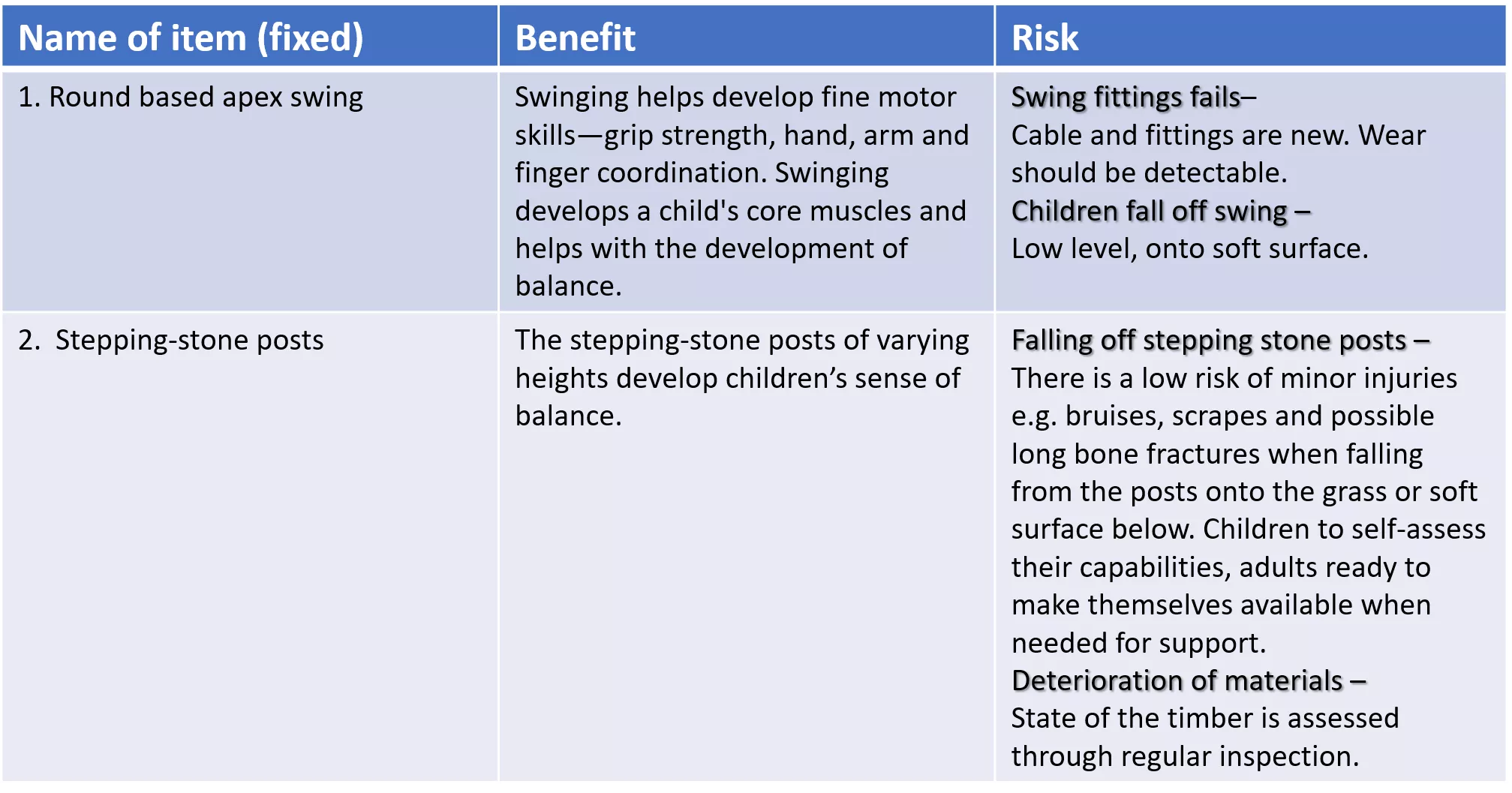
Example of Risk-Benefit Assessment for outdoor play equipment Date of Assessment: Aim: To manage risk to achieve positive outcomes for children Assessed by: Name of item (fixed) Benefit Risk 1. Round based apex swing Swinging helps develop fine motor skills grip strength, hand, arm and finger coordination. Swinging develops a child's core muscles and helps with the development of balance. Swing fittings fails Cable and fittings are new. Wear should be detectable. Children fall off swing Low level, onto soft surface. 2. Stepping-stone posts The stepping-stone posts of varying heights develop children s sense of balance. Falling off stepping stone posts There is a low risk of minor injuries e.g. bruises, scrapes and possible long bone fractures when falling from the posts onto the grass or soft surface below. Children to self-assess their capabilities, adults ready to make themselves available when needed for support. Deterioration of materials State of the timber is assessed through regular inspection.
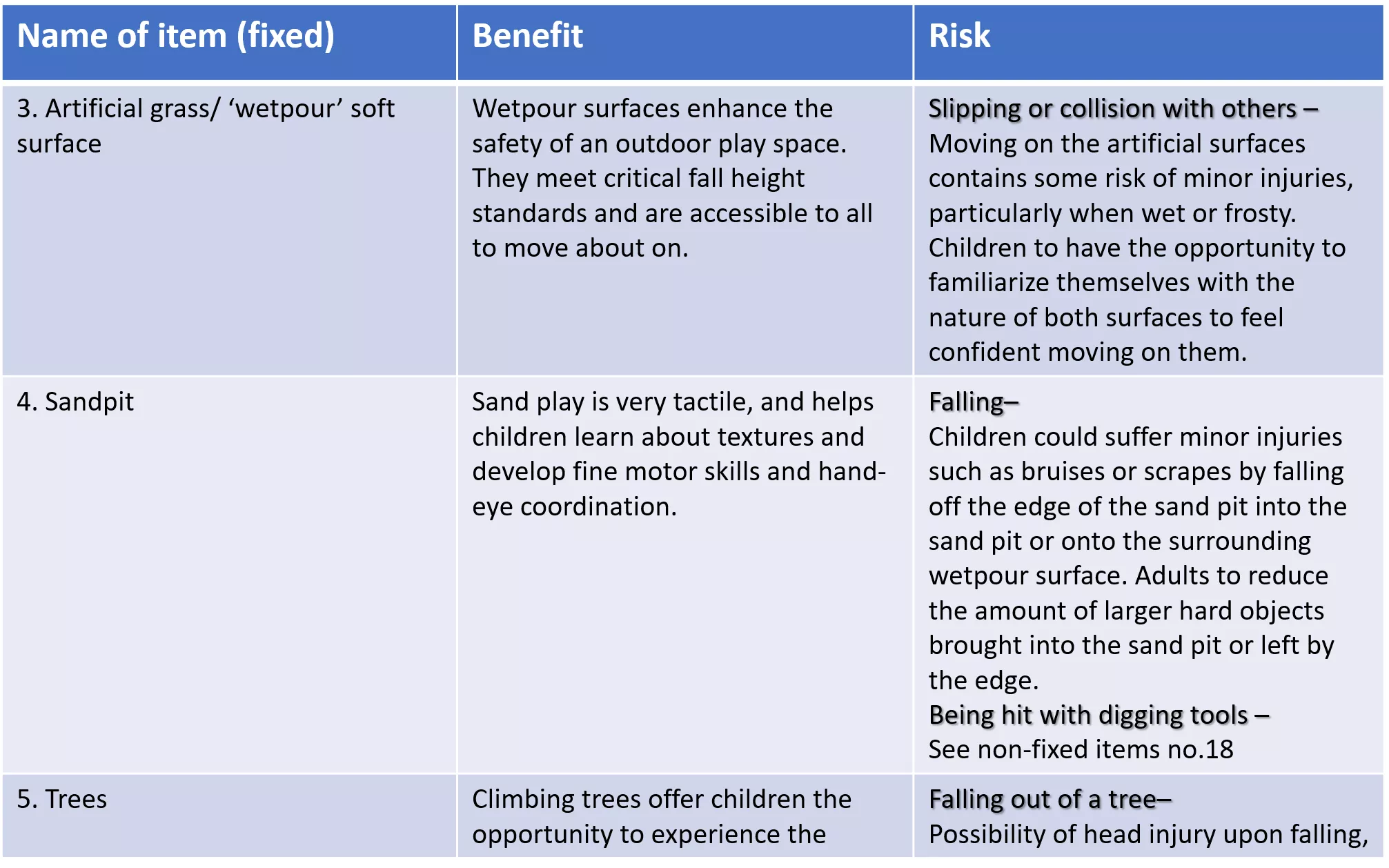
Name of item (fixed) Benefit Risk 3. Artificial grass/ wetpour soft surface Wetpour surfaces enhance the safety of an outdoor play space. They meet critical fall height standards and are accessible to all to move about on. Slipping or collision with others Moving on the artificial surfaces contains some risk of minor injuries, particularly when wet or frosty. Children to have the opportunity to familiarize themselves with the nature of both surfaces to feel confident moving on them. 4. Sandpit Sand play is very tactile, and helps children learn about textures and develop fine motor skills and hand- eye coordination. Falling Children could suffer minor injuries such as bruises or scrapes by falling off the edge of the sand pit into the sand pit or onto the surrounding wetpour surface. Adults to reduce the amount of larger hard objects brought into the sand pit or left by the edge. Being hit with digging tools See non-fixed items no.18 5. Trees Climbing trees offer children the opportunity to experience the Falling out of a tree Possibility of head injury upon falling,
Name of item (fixed) Benefit Risk unpredictability of natural forms, thereby encouraging children to learn how to self-assess risks. though much more likely to be scrapes and bruises. The surface around climbable trees is a mixture of bark and softpour. There are no protruding tree roots or stones. However, objects such as bikes or logs to be distanced from the potential fall area. Collision Tree branches that extend across paths can act as hazardous protrusions, particularly at head height. Regular upkeep of the garden environment will help to prevent this happening. The trees offer significant health benefits to users of the garden space, in terms of wellbeing and offering natural shade in the summer. They also provide micro habitats for wildlife. 6. Basketball net Falling Children may injure themselves by falling from the edge of the basket ball net. This can happen if a child finds a way to climbing up to the net. The risk of the frame breaking
Name of item (fixed) Benefit Risk off its bracket is minimal, given the comparatively low weight of a 2-4 year old child. Children will be discouraged from using the net in this way. 7. Doors opening into garden space Escaping nursery To find the means to escape from nursery by going through open or unlocked exits. When confronted with a child who is known to be motivated by this idea, the child s key person to ensure that this risk is communicated to the staff team, so that doors are closed during the session.
Name of item (non-fixed) Benefit Risk 8. A-frame climbing structure The frame provides challenges for fundamental movement skills, including climbing and sliding, as well as developing upper body strenghth. Slipping, falling off Possible minor scrapes, bumps and collisions. Mitigate against injury through appropriate positioning of the A-frame, moving it round regularly to keep up the challenge, thus heading off inappropriate actions by confident children. 9. Large timber box/climbing frame Placement of box in an appropriate mode that offers positive challenge. Falling off Possible head injury and bone fractures, scrapes and bruises resulting from falls from the top of the box. Children self-assess capabilities in climbing and balancing, resulting in low-risk actions. Adult to support any unsafe behaviour through talk and positive modelling. 10. Horizontal swinging rope Swinging on ropes develop co- ordination, balance and agility. Hanging Low risk in current position, as the rope is suspended with relative tautness between two trees and as such is difficult to knot or loop. Any
Name of item (non- fixed) Benefit Risk re-positioning of swinging rope to ensure there is limited scope for looping. Crashing into the tree While children may hit the supporting tree, this is easily seen and the tree trunk will likely be used for pushing against with their feet. Collision with other child Minor bumps may occur due to a lack of attention from children entering the swinging space and the placement of the swings in a busy area by the mound. As the trees are located there, this issue needs managing through conversation. 11. Garden bench Falling over Children may fall backwards on account of the lack of stability of the bench if the weight is predominately placed on the back. If children are accompanied by an adult, the risk of this happening is
Name of item (non-fixed) Benefit Risk much lower. The bench to be also be situated in front of an upright, to reduce the chance of this happening. Slipping through Children may fall between the back support and the seat of the bench, as the gap is unusually wide. The space between the back support and the seat of the bench makes a good child friendly space. 12. Assorted planks Uneven surfaces for climbing on will develop physical mobility and a sense of balance Falling, turning an ankle Potential minor injuries can occur when climbing on upturned ribbed planks, where feet may become caught in the gaps. 13. Builders trays Children will compensate for the risk of slipping by focusing their attention on remaining on their feet. Slipping There is a danger of slipping when used with children for paddling, possibly resulting in bumps and bruising. 14. Wooden play kitchen unit Adults to encourage its use for role play and exploration. Collapsing the unit If the unit is used for purposes other than role-play, such as for climbing on, there is a chance it will not
Name of item (non- fixed) Benefit Risk support the weight, causing a risk to minor injury. 15. Metal bikes, trikes and scooters Collision with others There is a significant risk of minor injuries e.g. bruises, scrapes and possible long bone fractures if children are hit by a heavy, metal bike or tricycle. This is exacerbated if the bike is being driven at speed or without awareness of others. Limiting the use of bike, trikes and scooter extends the potential for developing engagement in open- ended imaginative play Having a limit to the number of bikes and trikes out at one time reduces the risk of accidents in such a well- used space, while balancing them with alternative wheeled equipment e.g. wheelbarrows, carts offers children alternatives to riding. 16. Piano Open-ended and accessible resource for children s music making outside Trapping fingers Low risk of small fingers getting stuck in exposed wires.
Name of item (non- fixed) Benefit Risk 17. Water hose The use of the hose to water the plants, with adult supervision, gives children responsibility for caring for the garden. Giving children autonomy over how they choose to use outdoor equipment will help to unleash their potential for learning Tripping hazard Unravelling hoses in a busy environment can cause people to trip, leading to minor scrapes and bumps. Adults using hoses to be be mindful about keeping them on the ground as much as is practicable and to store them carefully after use. 18. Metal spades Using authentic garden resources enables children to carry through their intentions in the best way possible. It acknowledges their capacities as gardeners. Impact to body Being hit with the edge of a heavy metal tool such as spade may cause serious injury, particularly to the head. Tools of this nature to be stored safely and used in appropriate contexts with the guidance of an adult e.g. modelling effective usage. 19. Tractor tyres Tractor tyres are very versatile. They can be used differently according to how they are positioned ie. vertically or horizontally. Getting stuck It may be possible for some larger children to get stuck inside the rim of the tyre during play e.g. hide and
Name of item (non- fixed) Benefit Risk seek, although this is a low risk. Adults to maintain engagement and curiosity in children s play. 20. Child sized ladders Giving children autonomy over how they choose to use outdoor equipment will help to unleash their potential for learning. Falling There is a risk of minor scrapes and bruises in the event that a child falls off a ladder. Adults to model appropriate use of ladders, including how to angle them against an upright and keeping away from the base while in use. 21. Ropes and other ligature materials ie. capable of strangulation The open-ended use of a variety of resources allows children to feely create their own play scenarios. Strangulation Any material that can be tied around a neck has the capacity for throttling, with potentially fatal consequences. This includes ropes but also other everyday items such as belts, string, electric cables or fabric. Where children use such materials in their play, adults to have a heightened awareness of this risk, focusing on
Name of item (non- fixed) Benefit Risk the way they are used. Any instances of such materials involving load bearing weights around the body are to be avoided. Loose ropes to be tidied away and secured when not in use. 22. Jumping trestle table The height of the trestle table challenges children to climb higher and jump further than would otherwise be possible Falling and collision Potential head injuries or minor scrapes and sprains resulting from falling off the top, which may also involve colliding with another child. Trestle to be situated in an area of impact-reducing surfacing, such as bark or artificial grass. When being used for jumping off, space to be given to avoid collisions between children.
List of risk-benefit garden items 1. Round apex swing 12. Assorted planks 2. Stepping-stone posts 13. Builders trays 3. Artificial soft surfaces 14. Wooden play kitchen unit 4. Sandpit 15. Metal bikes, trikes and scooters 5. Trees 16. Piano 6. Basketball net 17. Water hose 7. Doors opening into garden space 18. Metal spades 8. A-frame climbing structure 19. Tractor tyres 9. Large timber frame 20. Child sized ladders 10. Horizontal swinging rope 21. Ropes and other ligature materials 11. Garden bench 22. Jumping trestle table This Risk-Benefit Assessment Form was based on a worked example co-authored by David Ball, Tim Gill and Bernard Spiegal on behalf of the Play Safety Forum, 2014