Rebinning: A Data Resampling Technique
Rebinning is a data manipulation technique similar to smoothing, where N points are replaced by 1 point using a functional weighting. This process involves resampling data, linear interpolation, boxcar averaging, and convolution with a kernel function. It is essential to consider boundary effects and always plot the resampled data alongside the original for validation.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
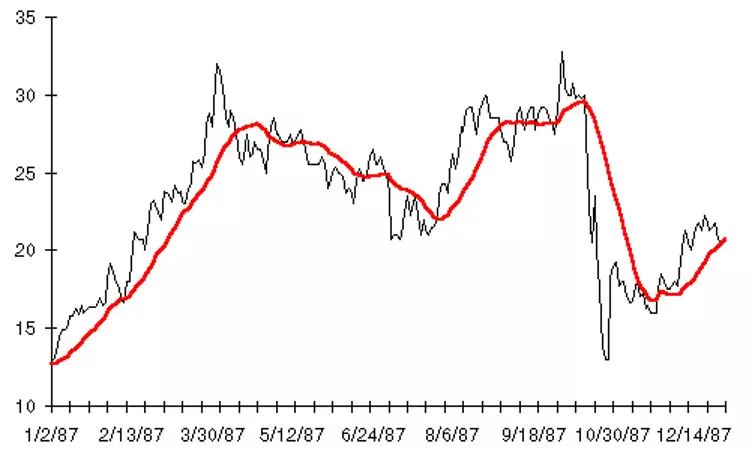
REBINNING Very straight forward but beware the black box
Rebinding of data is quite similar to smoothing You run a filter over N points, and replace those N points by 1 point using some functional weighting of the N-points
RESAMPLING TO REBINNING Linear interpolation (replace N points by 1 point = 5 make a line from N-2 to N+2 and plug and plug the midpoint value in) Simple boxcar averaging of N points in a time series (boxcars do not overlap hence resampling and not smoothing). Kernal rebinning convolve N points with some function (gaussian) You need to worry about boundary effects sometimes always plot the resampled data on the original

 undefined
undefined