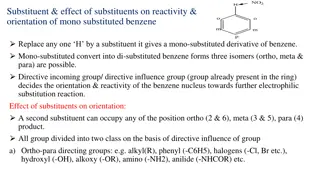
Reactivity of Metals and Non-Metals: A Comprehensive Overview
Metals like potassium and sodium react vigorously with water, while non-metals like phosphorus are highly reactive and stored in water. Metals react with acids to form hydrogen gas, while non-metals generally do not react with acids. Reactivity series explains displacement reactions where more reactive metals displace less reactive ones. Metals find uses in machinery, vehicles, and cooking utensils, while non-metals are essential for fertilizers, water purification, and antiseptics.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
REACTION OF METALS AND NON- METALS WITH WATER Potassium and sodium reacts with water vigorously. Sodium metal reacts vigorously with oxygen and water and lot of heat is generated, hence it s stored in kerosene. Phosphorous is very reactive non-metal therefore stored in water.
REACTION OF METALS AND NON- METALS WITH ACIDS Metals react with acids to form hydrogen gas with a pop sound. Non metals generally do not react with acids. Eg: Copper doesn t react with dilute hydrochloric acid but it reacts with sulphuric acid.
REACTION OF METALS AND NON- METALS WITH BASE Metals react with sodium hydroxide to produce hydrogen gas with a pop sound. Pop sound indicates the presence of Hydrogen gas. The reaction of non-metals with bases is very complex.
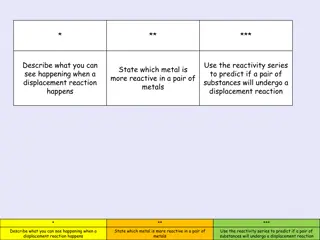
DISPLACEMENT REACTION More reactive metals replace less reactive metals. One metal displaces another metal from its compound in aqueous solution.
DISPLACEMENT REACTION Example 1: Copper sulphate + Zinc ------------- Zinc Sulphate + Copper. Here, Zinc is more reactive than Copper, therefore Zinc displaces Copper.
DISPLACEMENT REACTION Example 2: Copper Sulphate + Iron ------------- Iron Sulphate + Copper. Here, Iron is more reactive than Copper, therefore Iron displaces Copper.
USES OF METALS Making machinery, Automobiles, Airplanes, Trains, Satellites, Industrial gadgets, Cooking utensils
USES OF NON-METALS Fertilizers, Water purification, To manufacture antiseptics, Crackers
SUMMARY Metals are lustrous, malleable, ductile and good conductors. Non-metals are brittle, poor conductors, non lustrous, etc., Metals react with oxygen to form its oxides.
SUMMARY Non metals do not react with water. Metals react with acids to produce hydrogen gas. More reactive metals displace less reactive metals. Metals and non-metals are used widely every day.
THANKYOU End of module III