Observational Research Methods
Observational research methods involve systematic observation of behaviors and can be used in various study designs such as experimental, correlational, and descriptive research. This type of research aims to provide insights into real-world behaviors with a focus on ecological validity. The process includes categorizing behaviors, creating clear definitions, and quantifying observations through techniques like frequency counts and narrative records. Interrater reliability is crucial when multiple observers are involved in the data collection process to ensure accurate and consistent results.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
OBSERVATIONAL METHODS Research Methods
Observation Methods Observational Methods Describe behavior Can be used in many different designs (e.g., experimental, correlational, descriptive) Involves systematic observation Ecological Validity does it generalize to the real world
Observational Method Behavioral categories Categories of behaviors to be observed Clear operational definitions Prior research & preliminary observations
Examples of basic recording sheets Sample Descriptive Coding Form.
Observational Method Quantifying Observations Frequency Behavior count during fixed time Duration Time engaged in behavior during fixed time Intervals Divide observation into intervals, record whether or not behavior occurs during each interval
Examples of basic recording sheets Sample Descriptive Coding Form.
Examples of basic recording sheets Sample Checklist for Coding Child Behavior.
Observational Method Narrative records Video/audio-recording Pick up on missed behaviors Multiple observers watch same event Might be less disruptive Sampling Observations Time Observe-record-observe-record Event Observe one behavior Shift behavior (behavior1-behavior2-behavior3) Individual Shift individuals
Multiple Observers Interrater reliability Agreement between observers Evaluating interrater reliability Percent agreement total # of agreements X 100 total # of observations
Multiple Observers Evaluating interrater reliability Pearson s r (correlation coefficient) +/- 1.00 Note: Scores could be correlated, but very different Observer 1 1 2 3 2 Observer 2 3 5 6 3
Observational Method Undisguised (open/overt) observations Presence of researcher is known Nonparticipant observations Observe, don t get involved Participant observations Observe and participate Disguised (covert) observations Presence of researcher is unknown or minimized Nonparticipant or Participant Issues: Reactivity and Ethics
Observational Methods Reactivity issues Can be reduced Remain hidden Habituation Indirect measures (unobtrusive) Advantages Usually higher external validity (higher ecological validity) Can examine behaviors that can t be manipulated Disadvantages No causal statements (unless the observation is the DV in an experiment) Time consuming & expensive No guarantee that behavior will occur
Example Leo (1996) interested in studying police interrogation practices. Spent 9 months observing122 interrogations involving 45 different detectives. In addition, observed 60 videotaped interrogations. Reactivity Representativeness/generalizability Qualitative & quantitative
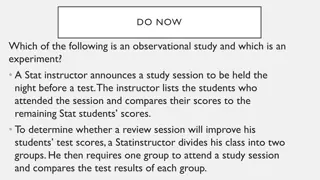
Mini-Review Observational Methods Behavioral categories Operational definitions Quantifying Observations Frequency, duration, intervals Record all observations or sampling observations Sampling: Time, event, individual Role of the researcher Undisguised or Disguised Nonparticipant or Participant Observer

 undefined
undefined