MODEL DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
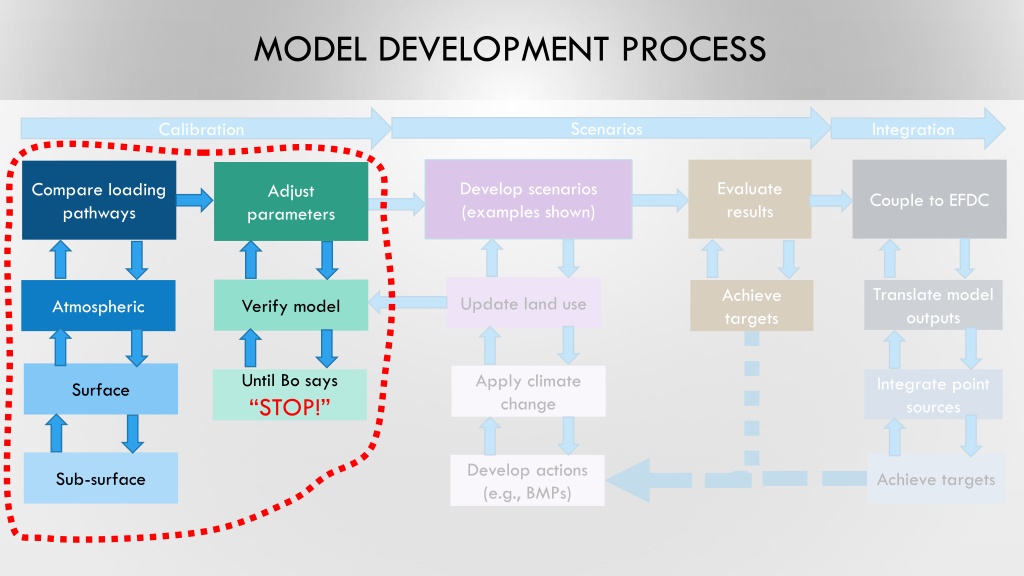
Explore the iterative steps involved in model development, from developing scenarios and comparing loading pathways to updating land use and integrating point sources. Learn how to adjust parameters, couple to EFDC, and apply climate change considerations until reaching desired targets. The process involves translating model outputs, verifying results, and incorporating atmospheric feedback. Stop only when the model achieves the set objectives, ensuring accuracy through evaluation.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MODEL DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Scenarios Integration Calibration Evaluate results Develop scenarios (examples shown) Compare loading pathways Adjust parameters Couple to EFDC Translate model outputs Achieve targets Update land use Verify model Atmospheric Until Bo says STOP! Apply climate change Integrate point sources Surface Develop actions (e.g., BMPs) Sub-surface Achieve targets
RAINFALL ZONES Original (83 zones) Revised (30 zones)
HYDROLOGIC RESPONSE UNITS (HRUS) Pervious Surfaces Impervious Surfaces wetlands EIA-Roofs EIA-Res EIA-Com EIA-Rds Land Use Grass Barren Pasture Forest water Shrub Agri Water LD Residential HD Residential Commercial Barren Shrub Forest Grassland Agriculture King Co. Wetlands Roads 30 Slope Sewer Development Age Soil Permeability Low Moderate Separated Partially Combined Pre 1980 Post 1980 Low High Saturated Land Use Water LD Residential HD Residential Commercial Barren Shrub Forest Grassland Agriculture King Co. Wetlands Roads
COMPARE AND ADJUST HRU ASSUMPTIONS Study Area Pervious Surfaces Impervious Surfaces 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% 15% 10% 5% 0% Existing Revised*
MODEL DEVELOPMENT PROCESS Scenarios Integration Calibration Evaluate results Develop scenarios (examples shown) Compare loading pathways Adjust parameters Couple to EFDC Translate model outputs Achieve targets Update land use Verify model Atmospheric Until Bo says STOP! Apply climate change? Integrate point sources Surface Develop actions (e.g., BMPs) Sub-surface Achieve targets