Mitosis and Meiosis
Explore the fascinating processes of mitosis and meiosis in higher biology. Understand the differences between these two types of cell division - mitosis for somatic cells and meiosis for gametes. Dive into the stages of mitosis - interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase - witnessing the intricate changes that occur at each phase. Discover how chromosomes align and separate during metaphase and anaphase, leading to the formation of two daughter cells in telophase. Uncover the unique characteristics of meiosis, where four daughter cells with half the chromosomes of the parent cell are produced through two rounds of cell division. Visualize the key events in these processes through detailed images and explanations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Mitosis and Meiosis Higher Biology
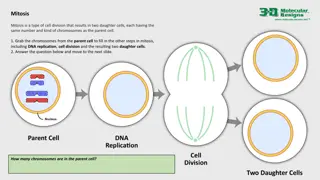
Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis: -division of somatic (body) cells Meiosis -division of gametes (sex cells)
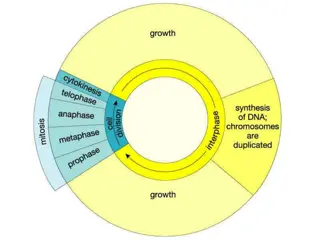
Mitosis Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
Interphase 1. Cell preparing to divide 2. Genetic material doubles Interesting things happen!
Prophase 1. Chromosome pair up! Chromosomes thicken and shorten -become visible -2 chromatids joined by a centromere 2. Centrioles move to the opposite sides of the nucleus 3. Nucleolus disappears 4. Nuclear membrane disintegrate
Metaphase 1. Chromosomes arrange at equator of cell 2. Become attached to spindle fibres by centromeres 3. Homologous chromosomes do not associate Chromosomes meet in the middle!
Anaphase 1. Spindle fibres contract pulling chromatids to the opposite poles of the cell Chromosomes get pulled apart
Telophase 1. Chromosomes uncoil 2. Spindle fibres disintegrate 3. Centrioles replicate 4. Nucleur membrane forms 5. Cell divides Now there are two!
Meiosis 4 daughter cells produced Each daughter cell has half the chromosomes of the parent 2 sets of cell division involved
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.