Mendel's Experiments and Principles of Genetics
Delve into the pioneering work of Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics, as he conducted groundbreaking experiments with pea plants, identified key principles of genetics, and introduced the concept of dominant and recessive traits. Explore how Mendel's work laid the foundation for our understanding of heredity and the passing of traits from parents to offspring.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
BIOLOGY CHAPTER 8 Heredity
8.1 OBJECTIVES Discuss Mendel s experiments and his results. Explain the three principles of genetics Mendel obtained through his experiments. Solve genetics problems using Punnett Squares.
8.1 PRINCIPLES OF GENETICS Discuss Mendel s experiments and results. Explain the three principles of genetics Mendel obtained through his experiments. Solve genetics problems using Punnett squares.
PRINCIPLES OF GENETICS The passing of traits from parents to offspring is termed heredity. Can we predict certain traits? Can we determine what types of genetic information parents have by looking at certain traits of the offspring? We can answer these questions through genetics the science of heredity.
ORIGIN OF GENETICS Father of genetics: Gregor Mendel (1882-1884) Tended to a garden of pea plants in a monastery. Published results from 8 years of research, only to be ignored until 1900.
MENDELS EXPERIMENTS Peas are grown easily and produce large numbers of offspring in a short time. Chose 7 traits to study: Seed Shape Seed Colo r Yello w Green Flowe r Color Purple Flower Position Pod Color Pod Shape Plant Heigh t Long Dominant Trait Recessive Trait Round Axial (side) Green Inflated Wrinkled White Terminal (tips) Yellow Constricted Short
MENDELS PROCESS Mendel crossed pea plants w/ different traits. Offspring of parental cross were called F1 Offspring of F1crosses called F2. He noted for each trait, there was a dominant and recessive form. In his crosses, recessive trait disappeared in F1 generation and then reappeared in F2.
MENDELS HYPOTHESIS He reasoned that for every trait, there must be a pair of factors. He called them characters, but we now know them as genes. One gene came from each parent.
THE TEST OF SEGREGATION He predicted if the F1 purple flowered plants were crossed with white flowered plants, he would get ratios different from any of his previously obtained ratios.
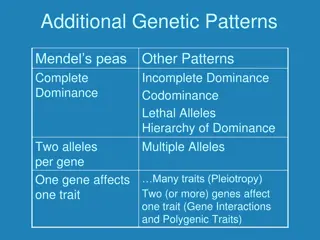
TERMINOLOGY Each alternative form of a gene for a certain trait are called alleles. Combination of genes for a given trait referred to as genotype. Example: WW and Ww The physical appearance of a trait is the phenotype. Example: Blue and brown eyes. Homozygous = two of same alleles: WW or ww (homozygous dominant and homozygous recessive) Heterozygous = two different alleles: Ww
8.2 SOLVING GENETICS PROBLEMS Objectives: Apply the rules of probability to solve genetics problems. Demonstrate the inheritance of traits resulting from incomplete dominance, codominance, and multiple alleles.
PROBABILITY What is the probability of getting heads or tails when you toss a coin? There is a list of steps to follow on page 208 in text, but we have already been doing this. Remember, we can find either genotypic or phenotypic ratios.
INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE: 4 OCLOCK PLANTS AS AN EXAMPLE
8.3 THE CHROMOSOME THEORY OF HEREDITY Walter Sutton s work showed good evidence that genes reside on chromosomes. Some genes appear only on sex chromosomes. XX = female and XY = male in humans. Different combinations for different species. Example: Grasshoppers X = male and YY = female. Sex-linked traits are traits that result from genes on the sex chromosomes.
SEX-LINKED TRAITS IN HUMANS Hemophilia gene is a recessive gene found on the X chromosome. Mostly, males get the disease. Color-blindness is the same way.
MANY GENES ONE EFFECT Height, hair, eye, and skin color all controlled by multiple alleles. Sample genotypes: AABBCCDD AaBbCcDd Aabbccdd Modifier genes can also impact things like eye color. Brown, blue, hazel, green, mixed etc.