Memory Stack and Variable Scope in Computer Architecture
This content delves into the scope of variables, the stack in memory architecture, automatic and global variables, and the concept of constant types. It explains the functioning of the stack, how function calls are managed, and the allocation of variables within stack frames. The relationship between local variables and stack frames is explored, emphasizing how local variables are temporary and disappear when the function call ends.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CS 240 Lecture 5 Scope of Variables, The Stack, Automatic Variables, Global Variables, Constant Type
Correction to Last Lecture fgets One thing that was left out of last lecture was the return value for fgets. When fgets attempts to read while at the end of input, it will return a zero pointer, NULL Otherwise, it will return the buffer itself on a successful read. This allows us to test whether or not the function received any input at all using control flow. Corrected example usage: char buff[100]; if (fgets(buff, 100, stdin)) printf("%s", buff);
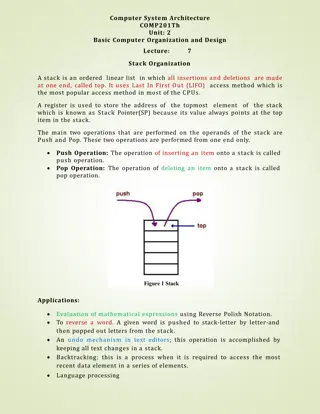
Memory The Stack In the computer's memory architecture, there's a portion of memory dedicated to keeping track of the order of function calls as well as the parameters for them. The stack begins at the higher addresses and is aggregated in the descending direction. Each function call will have a what's called a "stack frame" pushed onto the stack for keeping track of The parameters The future return value (if any) The part of the code the program needs to return to when it's done
Memory Stack Frame Address Data 0x69832efc 0x69832f00 0x69832f04 0x69832f08 0x69832f0c 0x69832f10 0x69832f14 0x69832f18 0x69832f1c 0x69832f20 0x69832f24 0x69832f28 *unused* *unused* *unused* Stack Data Return Address Argument #1 Argument #2 Argument #3 Stack Data Stack Data Stack Data Stack Data Here, we have an example of a stack frame for the function f. int f(int a, int b, int c); Function arguments are pushed onto the stack in reverse order. The blue address indicates where local variables will begin being allocated. Local variables are pushed onto the stack because they will disappear when the function call ends.
Memory Stack Frame Address Data 0x69832efc 0x69832f00 0x69832f04 0x69832f08 0x69832f0c 0x69832f10 0x69832f14 0x69832f18 0x69832f1c 0x69832f20 0x69832f24 0x69832f28 *unused* int e; int d; Stack Data Return Address int a; int b; int c; Stack Data Stack Data Stack Data Stack Data int f(int a, int b, int c) { int d; int e; } When the function ends, the return value is stored in a CPU register. The program then resets the stack and uses the return address to resume running from that last point in the code after the function call. This is not a complete discussion on the stack frame, however this topic will be covered more in depth in CS341.
Variables Local Automatic Local variables are the usual variables declared inside of functions. We should already know these very well. As we discussed in the previous slides, these variables vanish along with the function's stack frame when the function completes. Local variables will be considered to hold junk data unless assigned a value during declaration. We call these variables automatic because they are only there when we can use them. Every time the same function is called, these variables are pushed onto the stack with the stack frame. Even if the same function already has a stack frame on the stack!
Variables Local Static A local static variable declared in a function is given it's own static, unchanging place in memory. Static variables, unlike automatic, are not put onto the stack. static int var; Static variables are guaranteed to be initialized to their zero value. char gets '\0', int gets 0, float and double get 0.0 If the static variable is given a value during declaration, it is done exactly once before any other code has been run. You should only use static local variables if you want to share information with future calls to the same function. "This function ran X times." or "The last time this function ran, it took 3 minutes."
Variables Global / External Global or external variables are variables declared outside of any function inside of a source file. int var; /* won't look any different */ These variables are visible to every block statement in the program. Not just the source file they're declared in, but every other source file used to build the program. This kind of variable is useful for passing information between functions or between source files. Global variables are always initialized to their 0 value.
Variables Global / External Static Global static or external static variables are global variables which are only visible within the source file they are defined in. As a result of being visible only to their source file, they are considered to be a safer option than normal global variables where intra-module communication is needed. We have not yet discussed in-depth programs with multiple source files, that will be for another class. Like normal global variables, they are initialized to 0 instead of junk. Like static local variables, they are initialized once before any other code is executed/
Variables extern variables Extern variables are ways to declaring that you are going to use a global variable from another file. extern int x; This will allow you to write compilable code that uses a variable that a variable will be available later. However, before compiling into a finished executable, some source file of the program must have a non-extern global declaration of this variable. The same can be done for function definitions with the same caveat. extern int func(int a, int b);
Variable Scope Lexical Scoping The scope of a variable is the context in code execution for which its name refers to it. For example, if you have a cousin named Kevin and are at a family gathering with him, you're probably not talking about me. Lexical Scoping is the term used to describe languages whose variable name resolution uses the position in code to determine variable scope. At a certain line of code, you will ALWAYS see the same variables. If multiple variables at different levels of depth have the same name, the deepest variable is the one referenced by that name. Block statements are one layer deeper than the position they were written in.
Examples of Scopes of Variables These examples are from p.342: C Programming for Scientists and Engineers with Applications by Rama Reddy and Carol Ziegler, Jones and Bartlett 2010. Slides on scope courtesy of Professor Cheung
Scope of Variables Example #1 #include <stdio.h> int main(){ int a=10; printf( a=%d\n , a); { int b=5; printf( b=%d\n , b); { int c=40; printf( c=%d\n ,c); } } return 0; } 10 5 40 Scope of a Scope of b Scope of c
Scope of Variables Example #2 #include <stdio.h> int main(){ int x=10; printf( x=%d\n , x); { int x=5; printf( x=%d\n , x); { int x=40; printf( x=%d\n ,x); } x=x+4; printf( x=%d\n ,x); } x=x+15; printf( x=%d\n ,x); return 0; } If the same variable is defined inside and outside the block, the name inside the block will be referenced if the block is being executed. x = 10 x = 5 x = 40 x = 5+4 x = 10+15
Scope of Variables Example #3 int x; void func1(void){ x = 5; printf( In func1 x=%d\n ,x); return; } #include <stdio.h> int main(){ int x = 20; printf( x=%d\n , x); func1(); x = x + 10; printf( x=%d\n , x); func2(); x = x + 40; printf( x=%d\n ,x); func3(); return 0; } Scope of global x void func2(void){ int x = 0; printf( In func2 x=%d\n , x); return; } Scope of x from main Scope of x from func2 void func3(void){ printf( In func3 x=%d\n , x); return ; } Uses global x
Scope of Variables Example #4 #include <stdio.h> int main(){ int x=5; printf( x=%d\n , x); func1(); x=x+5; printf( x=%d\n , x); func2(); x=x+5; printf( x=%d\n ,x); return 0; } int x; void func1(void){ x=6; printf( In func1 x=%d\n ,x); } Uses global x void func2(void){ x=x+10; printf( In func2 x=%d\n , x); } Scope of x from main Uses global x
Scope of Variables Example #5 File 1 File 2 int x; void func1(void){ printf( In func1 x=%d\n ,x); x=5; } void func2(void){ x=x+10; printf( In func2 x=%d\n , x); } #include <stdio.h> Uses global x from File 2 Uses global x from File 2 int main(){ extern int x; x=1; printf( x=%d\n , x); func1(); x=x+6; printf( x=%d\n , x); func2(); x=x+7; printf( x=%d\n ,x); return 0; } Uses global x from File 2
Scope of Variables Example #6 File 1 File 2 int x; void func1(void){ x=5; printf( In func1 x=%d\n ,x); } void func2(void){ int x=10; printf( In func2 x=%d\n , x); } #include <stdio.h> void func1(void); void func2(void); int main(){ extern int x; x=1; printf( x=%d\n , x); func1(); x=x+6; printf( x=%d\n , x); func2(); x=x+7; printf( x=%d\n ,x); return 0; } Uses global x from File 2 Scope of x from func2 Uses global x from File 2