Mathematics Fundamentals - Matrices and Determinants
Fundamentals of matrices and determinants, including types of matrices like square matrices, column matrices, identity matrices, zero matrices, and more. Learn about operations on matrices, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication by constants, and transpose. Discover how matrices are used in representing linear equations and solving mathematical problems step by step. Dive into the world of linear algebra with this comprehensive guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
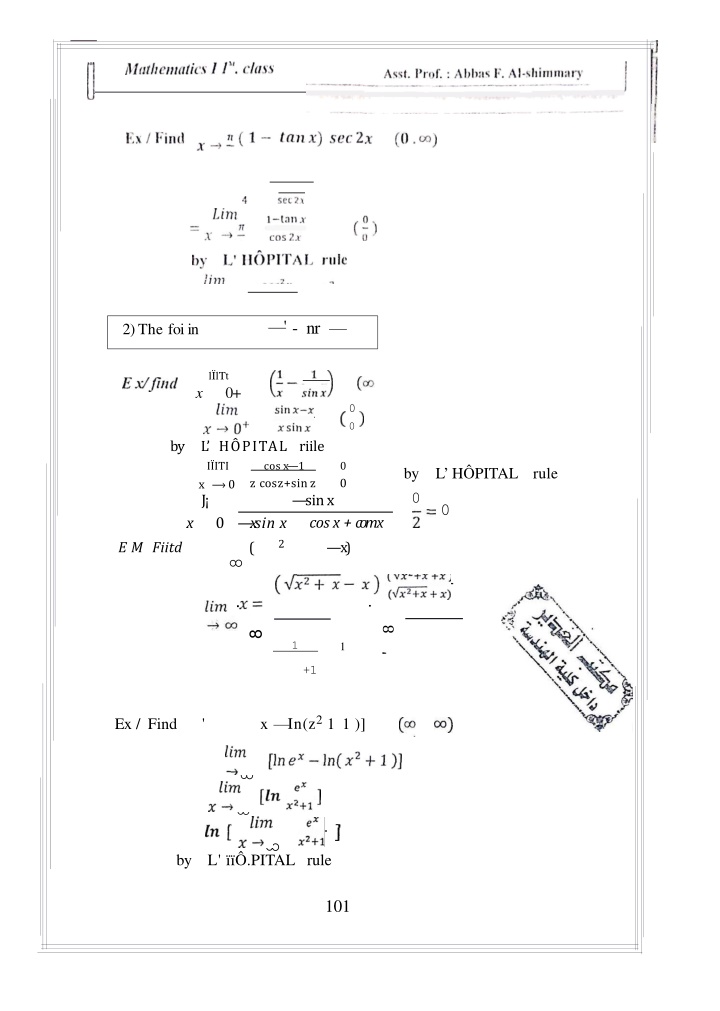
' - nr 2) The foiin l lTt 0+ x 0 0 by L H PITAL riile I ITI x 0 z cosz+sinz J 0 x sin x ( cos x 1 0 0 by 0 L H PITAL rule sinx cos x + comx x) 0 x 2 E M Fiitd 8 . . 8 8 1 1 ' +1 x In(z21 1 )] Ex / Find ' 8 8 8 by L' .PITAL rule 101
by L' I4OI'ITAL rule = In = Inm 0, \ 3) The form ( 00 , ) ex/ Find g , (1 + z)'' (1 ) Let y = ( 1 -I-x )'* take in for both sides let y lit ( 1 -J-x) him (0 . In (1 + z) Iny =g ' 0 x ffm In (1 -+sj 0 (o o by L' HOPIT AL rule lim f 1 tak *e for bothsides In )1 ieC y (e -P Iny =1 z) In(e lvi ( e^+ x ) ( 0 .m ) x" + by fny = L' HOPITAL rule 102
lien+ y fn 2 M atrices and Oeterminants ll ef: any ari angcmciii of die elements in the fo1 lowi s !^ ^ no app 1- Addition & subtraction : 3 0 1 0 1 2 7 0 1 1 4 cal Let [A - 2 2x3 1 0 7 2 6 2x3 2 5 0 7 0 0'2 3 JA] and {B must Note: be of the same order . 2-Multiplication by a constant. 1 5 A (2 ) find 2fi ex/ Let 0 2 84) 4 2 ( o io 2 0 1 5 2 A 2 2) 103
ct Then Ex / Let 1 '2x2 3 7 2 A 3A -t 4 ? Ex / Let A Then find 2A 3B + 4t? = 2 ( 3 7 / 6 \ 21 / 6 \14 6 6+ 4 14 + 21 8 12 16 0 + 3+ 8 12 16 27 36 Jind A.B Yx / Let A - 3x3 3 X1 1 1 i 26 3 x1 104
Asst. Prof. : Ahh:is F. AU-sliimm $t , .. . . .. . . .. . -- .. --- -. . . .... ...-. .. - -. -. .- - - - Types of Matrices: - squzrc *i ztrix : if x = r matrix . thcn [N) i exlled square 3 . ls a sq uzYC Htalrix of orJcr 4 3 , r. o 1 ( ) 2- lt v ri a rix : if m = I Km - 3 - Calumn matrix : if 1 2 7l1x4 - 1 (A) 0 1 33,i 4 Identity matrix : it is asquare matrix with unity main diagonal . 1 o 0 ex I 0 1 0 0 0 1 5 ZePO lfl tfiix : i is a matri with Zeroentries 0 0 0 0 ex [A] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Note : In general A .B B . A 2 0 3j 1 3j [ 2 0 10 A.B [ 2 Then 11 2 2 + 3 (0 1)(2) + (0)(0) (2)(3)+ (3) 1 (1)(3) + (0 4 ) 2 (2) ) 3-(3)(1) (0)(2) + (l)(1 (1)(3) + (3)(0) (0)(3) + (l)(0) 6) 0J ' 1 1 Hence A .B x B .A 105
M themnli-s I I.rlass 'mntct ic n ltri1 : is t squ:mc mili ix lltcl r/,/ 2 3 S ex/ [dj = 3 1 2 5 2 1 7- Skew sy nletric nt lrix : isa squi rc matrix Ann t y = rt , \f; 0 3 Ii ex/ [ A ]= 3 0 5 2 8- Upper triangular matrix : isasquarc matrix with *lc''ncnta fi ' below the main diagonal . 1 4 6 ex/ [ A] 0 2 1 0 0 3 *- *fj, /.j issy n etric i l t the mil*n tl*nP "' 1 n.ain tliagoni l : rc Ktr 2 0 9- Lower triangular atrix: is a square matrix with elen enls 7ero above the main diagonal. 3 0 2 0 0 Ex / [A] = 7 10- Tru spose of a matrix : thetranspose of amatrix [A] is denoted by [A] 3 5 Ex / Let ,[jj = 6 4 2 l 3*2 Rbpr sentation of a set of linear equations by Matrices : Ex: Write the following equation in matrixform z + y + 2z =1 z + 5 z = 7 2 x y + 4z = 3 then [A]T i 1 2 i 0 z 5 x y z i 7 3 1 4 Or ( A ] [ X J = [ B ] 106
r 4fnJli'matics I I . cliiss IJcterminsnts: Sf A is calctlfated from a sqtiarc mali ix then dcl d or ]d} A and found as follows . (n b) I c dJ S y)r*'g l I is anuivber then ad - h I^l (/ ( *J (i)(*) *< ex/ Let ] A Min ors : is a c ctciiuirinnt of oidei aher deleling tlle i tll row and j th coluivln rt 1 nbtaincd fr iu Ex / et the minor of 7( Cofactor : the factor 5 6 ( 1)1-F1 Hence Art A \, -j a kA y det any row or any column that hasmaximum Zero and malt andsum note : for n = 3 only quick oalcufation of det A tofind det A , find the cofactor of 1 2 5 3 6 ex:if 4 then \AJ A - 4S -F84 - 96 105 ( 48) ( 72) = 240 +- 2 3 1 1 3 0 2 1 0 1 5 0 4 0 3 0 Ex/ find det(A) if A - 3 2 0 det Z - 3( i)"' 1 2 3 3(3)( )243 3 5 4 = 9(12 10) = 18 0 107
Propcities rif meter Itt in ii nts: 1- If two rows (or columns) are identical then 1 2 3 clef 2 3 2 ! f\ 0 S 1 2 = 0 1 2- interchanging any two rows (or columns) changes the sign of the determinant. 2 -1 ex/ 3 2 3- \A*\ = \A\ 4 - if arrow (or columns) is multiplied by k (sector) then the determinantmultiplied by k. 3 0 7 3 1 0 3 7 1 5 = 2 1 5 2 2 4 18 0 1 1 2 1 5 .. 3 2 0 9 6 = (2)(3) 1 3 Al B 1 2 3 2 1 Ex 1 1 6 3 = 2 0 0 5 1 AB = 5 1 1 3 1 2 0 3 Ex/evaluate thoosing = i ) ( i ) ' ) $ ]+ 3 ( * "' = 4 + (3) ( 1)( 2 9) = 29 i- 3 1 3 II + I 1 3 Crammed s rule method. for solving system of Linearequations ex/SoIve the following system of Linear eqs. using crammed srule: 2s + 3y z = x + 2z z - 4 2t y + z -3 1 108
= 2 x 0 Det Let[A]be nxn matrix, then the adjoint of matrix A is defined by 11 21 odj (A) -- Ai2 Az2 A2g A or ad j (A) [cof A]T 1 2 3 find adj A. exf tet A An A32 Az A12 A i fi22 ad j A 23 A 33 109
= (--1),+, -2 I' 0 --18 17 --6 --t3 --10 --2 --10 --1 --28 .. md j A--- Inverse of n squirm iitulr tv. [ t]1-- - find \A\=h0 (ind cof A [ind adj A ---- [cof A) !- S ex3' find A if A -- S 6 0 2 1 ' --3 check ) AJ -- --94 T 0 --18 --6 --to 17 --10 -- --6 -- p cof A -- --18 -- - 0 j i adj A ---- [cof AJT = 17 --6 --6 --10 --2 --10 --2 --10 --1 28 --1 28 -18 17 -6 - 1 ad j A I A) A-1- - 9 4 Tocheck A.A = A-* .A ----I 3 -2 5 1 1 2 --18 17 --6 --6 -10 --z --10 -1 8 1 0 o 0 1 6 0 ' = 0 1 --3