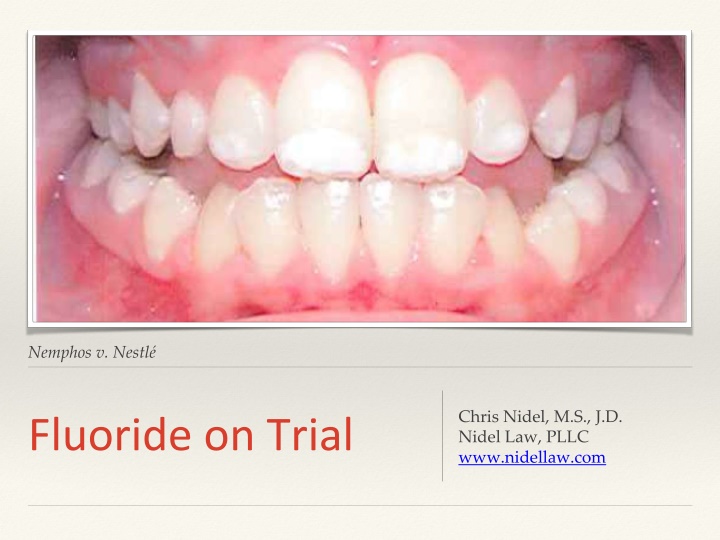
Legal Case: Nemphos v. Nestlé - Claims Regarding Dental Fluorosis
Nestlé and Danon are facing legal action for failing to warn about the risk of dental fluorosis in their bottled waters with added fluoride, marketed as child-friendly. The case involves claims for damages related to dental fluorosis, including cosmetic repair and psychological harm. The issue of federal preemption, especially express preemption under the NLEA, is also highlighted in the context of food regulation standards.
Uploaded on Oct 04, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Nemphos v. Nestl Chris Nidel, M.S., J.D. Nidel Law, PLLC www.nidellaw.com Fluoride on Trial
Claims in Nemphos Case Nestl and Danon failed to warn about the risk of dental fluorosis created by fluoride contained in their products Bottled waters with added fluoride Defendants deceptively marketed their products the one designed with kids in mind 8 oz. bottles, child-friendly sip tops Claims for damages for dental fluorosis cosmetic repair, psychological harm
Federal Preemption In general - where federal law, under the Supremacy Clause, trumps state law (including state common law) conflict preemption implied or field preemption express preemption
Express Preemption under NLEA no State or political subdivision of a State may directly or indirectly establish under any authority or continue in effect as to any food in interstate commerce (1) any requirement for a food which is the subject of a standard of identity established under section 341 of this title that is not identical to such standard of identity or that is not identical to the requirement of section 343(g) of this title, or (4) any requirement for nutrition labeling of food that is not identical to the requirement of section 403(q), except a requirement for nutrition labeling of food which is exempt under subclause (i) or (ii) of section 403(q)(5)(A), or (5) any requirement respecting any claim of the type described in section 343(r)(1) of this title made in the label or labeling of food that is not identical to the requirement of section 343(r) of this title.
Standard of Identity the definition of what it is that you are purchasing e.g. - The name of the food is "bottled water" or "drinking water." FDA also has defined various other types of bottled water, such as "artesian water," "artesian well water," "ground water," "mineral water," "purified water," "sparkling bottled water," and "spring water." Bottled water labeled with any of these terms must meet the appropriate definitions under the standard of identity or it will be considered misbranded under the FD&C Act. canned peas - permits manufacturers to add yellow peas, but only so long as no more than 2% of the peas are yellow. 21 C.F.R. 155.170(b)(1)(i). If a can of peas contains more than 2% yellow peas, the label must state that it is substandard and that it is not high grade or that it contains excessive yellow peas. bottled water with added fluoride
Examples of NLEA Preemption Spring water etc. 0 grams trans fat
Additional Arguments by Ds unapproved nutrient-disease claim (to warn) FDA prohibits unapproved marketing claims for nutrients claimed fluorosis was a disease and therefore they were prohibited from making the claim however - also is a safety exception to labeling requirements for health risks D s claimed it was not a health risk, but merely cosmetic We agreed mild fluorosis was cosmetic but nevertheless still an injury and a damage that is compensable
Express Preemption under NLEA any requirement for a food which is the subject of a standard of identity established under section 341 of this title that is not identical to such standard of identity or that is not identical to the requirement of section 343(g) of this title
Express Preemption under NLEA any requirement for a food which is the subject of a standard of identity established under section 341 of this title that is not identical to such standard of identity or that is not identical to the requirement of section 343(g) of this title
Express Preemption under NLEA any requirement for a food which is the subject of a standard of identity established under section 341 of this title that is not identical to such standard of identity or that is not identical to the requirement of section 343(g) of this title
District Court Interpretation The FDCA expressly preempts state food and bottled water labeling requirements that are non-identical to its own requirements. When the state statute or cause of action would impose a requirement that is not the same as the federal requirement, it is preempted. See, e.g., Mills, 441 F.Supp.2d at 108 09 (finding that requiring a warning on milk products regarding lactose intolerance exceeds the requirements of the NLEA and is preempted); In re PepsiCo, Inc., Bottled Water Mktg. & Sales Practices Litig., 588 F.Supp.2d 527, 536 37 (S.D.N.Y. 2008) (holding that requiring a disclosure that purified water was from tap water rather than other sources went beyond the requirements of disclosure set forth by the NLEA).
District Court Interpretation First, the court concluded that milk was undisputedly subject to a standard of identity under the FDCA. The plaintiffs thus sought to impose a requirement upon a food subject to a standard of identity. Second, the court found that a warning label of the nature requested by [the] plaintiffs would far exceed the labeling requirements mandated by the standard of identity established by the FDA regulations. Id. The court noted that the FDA s standard of identity delineated a detailed list of information required to appear on a product s label, of which a warning label was not included. Because the plaintiffs attempted to impose a non-identical requirement the court held that their claim was expressly preempted by the FDCA. Similarly, Nemphos s claims are preempted by the FDCA because the Defendants bottled water, baby food, and infant formula are subject to FDA regulations, and Nemphos seeks to impose non-identical labeling requirements upon them. essentially - once the food itself (not the requirement) is the subject of a standard of identity - there can be no state requirement related to the label whatsoever compare pharmaceuticals
Arguments on Appeal - 4th Circuit FDCA has limited express preemption - only preempts requirements that are not identical to existing standard of identity requirements the subject of the standard of identity deals only with the identity of the product purchased - in this case bottled water with added fluoride - NOT warnings of any kind, including warnings about fluorosis we are not suing for damages because we were duped into buying a mislabeled product they failed to warn - in the label, in their marketing, anywhere Defendants marketing toward children is not the subject of the nutrition label and is thus not the subject of preemption
Future of Tort Litigation Claims against water utilities Claims against manufacturers Claims against co-conspirators Damages fluorosis other potential injuries and damages Non-tort litigation - agency failure to act, etc.