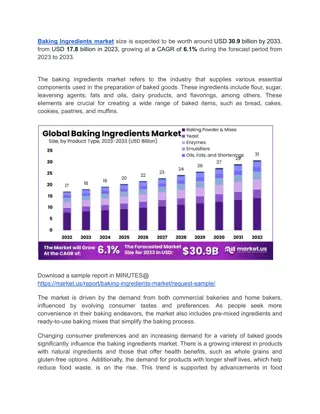
Leavening Agents in Baking
This content delves into the importance of leavening agents in baked goods, discussing natural leavening agents, the chemical processes of baking soda and baking powder, the role of yeast leavening, and the differences between quick breads and other baked products. It also covers the leavening agents used in various types of cakes, such as baking powder, baking soda, and fermentation. Additionally, it explains how air and steam can act as leavening agents, as well as the use of carbon dioxide in baking soda and baking powder to create lift in baked goods.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Leavening Agents Chapter 21
Objectives Vocabulary Explain the purpose of leavening agents in baked goods Identify natural leavening agents and describe how they work Explain the chemical process by which baking soda and baking powder leaven baked goods Describe the role in yeast leavening Explain how quick breads are different from other baked products Compare the leavening agents used in different types of cakes Baking powder Baking soda Double acting baking powder Quick breads Fermentation Single acting baking powder
Leavening Agents Air Steam Air Gives baked goods a lift Air is added by: Sifting dry ingredients Beating fat with sugar Whipping batter Steam used in some recipes as a primary leavening agent. Requires a very hot oven convert the liquid into steam Steam forms and the batter expands around it. Baking coagulates the protein, setting the structure.
Leavening Agents using Carbon Dioxide Baking Soda + Acid = Baked Goods Baking Soda Chemical Compound sodium bicarbonate Releases sodium carbonate and carbon dioxide when heated Baking soda always needs to be used with an acid, to alter the chemical reaction to prevent sodium carbonate from forming
Leavening Agents using Carbon Dioxide Baking Powder Chemical Compound that contains baking soda, dry acids, and starch or some other filler. Single-acting starts reacting as soon as liquid is added Double-acting contains two acids one that reacts with old liquid and one that reacts with heat http://video.about.com/chemistry/Differentiatin g-Baking-Soda-and-Baking-Powder.htm
Making Leavened Products Batters Dough's Soft dough's three parts flour, one part liquid Yeast breads Pizza crusts Biscuits Pour batters made with a nearly equal ratio of flour to liquid Range from thin to hard to pour Funnel cake pancakes Stiff dough's six to eight times as much flour as liquid Scones Pie crusts Drop batters two parts flour, one part liquid Quick bread loaves Some cookies muffins
Yeast as a Leavening Agent Yeast microscopic organism that produces carbon dioxide through fermentation Fermentation a biological reaction that slowly splits compounds into simpler substances http://www.edtechlens.com/wp-content/uploads/Yeast-Rising-Bread-3.jpg
Making Yeast Products Ingredient Purposes Flour provides structure Liquid provides medium that dissolves other ingredients and transports them to the yeast cells. Salt prevents enzymes from breaking down protein Sugar - helps the crust brown and adds flavor Fat - makes bread tender Eggs - makes bread rich in texture and flavor
Quick Breads Quick Breads are NOTmade with yeast, they don t need time to rise. Made with steam or carbon dioxide that is produced with baking powder or baking soda. Examples: Muffins Coffee cakes Cake-like breads Popovers Biscuits The History of Bread - The Chemistry of Baking Soda and Yeast (4:28) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qylxpwNhFYI