Investigating Impacts of Low Flow on Fountain Darter Reproduction
Research delves into the effects of low flow on Fountain Darter fecundity, highlighting the species' spawning behaviors in response to water flow variations and how it relates to reproductive success. The study aims to refine understanding of year-round spawning patterns, analyze the influence of flow gradients and vegetation types, and evaluate the role of physical, chemical, and biological factors in the reproductive ecology of Fountain Darters.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Effects of low flow on Fountain Darter fecundity
Background Fountain Darters (Schenck and Whiteside 1977) Spawn year round based on presence of ova Two peaks: Aug and Jan Apr Warmer water temperatures (>23)? Decreases in flow (<200 cfs)?
Spring-associated fishes spawning Photoperiod initiates Temperature stops Plenty of unexplained variation
Questions? Effects of low flow on Fountain Darter reproduction? Flow is likely not a proximate cue for spawning However, flow is a master variable Physical, chemical, and biological environments Difficult to test in laboratory setting
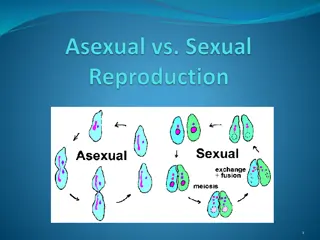
Reproduction: Related to flow? Related to vegetative structure?
Methodology Fish will be collected: monthly from Jan Aug (Dec) from 4 locations (5 to 120 cfs) from three vegetation types (tall, short, no)
Methodology Laboratory: Fish measured (wt, eviscerated wt, TL) Ovary status (I, D, M, S) Oocytes status D. C. Heins, Tulane U.
Analyses and Outcomes ANOVA (cfs, vegetation type) Covariates: time and potentially other factors Refinement of year-round spawning Effects along a flow gradient Effects of vegetation
Effects of predation on fountain darter population size at various flow rates ubparvipinne4.jpg
Piscivorous fishes: Predation varies (Schlosser and Ebel 1989): Temporally, dependent of flow regime Spatially, dependent on habitat Average flows: predation on Fountain Darters is low (BIO-WEST 2002) 3 darters out of 437 potential predators 3 darters out of 126 confirmed predators
San Marcos River (BIO-West 2006) <100 cfs consumption not detected <<100 cfs Increase predation likely, decimation of potential and confirmed fish predators?
Trophic cascade: Rahel and Stein 1988, Taylor and Soucek 2010, Thomas 2011
Questions? Numbers of darters consumed by ? Crayfish only Largemouth Bass only Crayfish & bass Does vegetation mediate the response?
Methods Laboratory setting (FAB) Phase 1: Observational studies Numbers of prey and predators, amount of vegetation, exposure time
Methods Phase 2: Predictions: Consumption (crayfish) > Consumption (bass) > Consumption (bass x crayfish) Consumption (bare) > Consumption (vegetation)
Experimental design Completely randomized design Experimental unit = aquarium with darters TRT: 1: no pred, cray, bass, cray & bass 2: veg/bare
Experimental design Replication: 3 2-factor ANOVA ( = 0.05) with Fisher s LSD