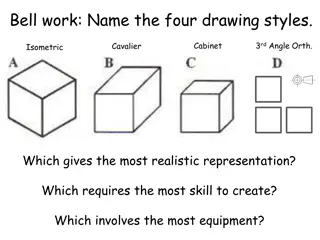
House Styles: A Brief Overview
House styles encompass a variety of architectural designs, with buildings classified based on shared characteristics like roof shape, window placement, and construction materials. Early American house styles, such as American Colonial, reflect the diverse origins of settlers in North America. Colonial homes are known for features like symmetrical facades, gable roofs, and six-over-six windows. Explore the rich history and distinctive traits of different house styles to better appreciate the evolution of residential architecture.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
DO YOU KNOW YOUR HOUSE STYLES?
STANDARD Students will identify components related to the design process. A. Demonstrate an understanding of different house styles.
WHAT IS HOUSE STYLE? Style" is a vague and confusing term Architects, home builders, and real estate professionals often don't agree on what they mean when they describe a style. Most buildings are actually a combination of several styles Modern-day homes are often called Neo-eclectic An eclectic mix of details borrowed from many times, places, and building traditions
Buildings are said to belong to the same classification (or style) when they share many of the same characteristics Roof shape and pitch Building size and number of stories Window size, shape, and placement Door shape and placement Decorative details Construction materials such as brick, stucco, or wood Footprint and floor plan Historic period
EARLY AMERICAN HOUSE STYLES
AMERICAN COLONIAL 1600s 1800 When North America was colonized, settlers brought building traditions from many different countries. Colonial architecture includes: New England Colonial Cape Cod German Colonial Georgian Spanish Colonial Southern Colonial American Federal/Adam French Colonial Dutch Colonial
AMERICAN COLONIAL One of the country's most prevalent home styles The term "Colonial" covers a broad spectrum of homes
COLONIAL Colonial homes typically share the following characteristics: Large entryway Symmetrical fa ade Six-over-six windows Gable or gambrel roof Often have dormers
Gable Roof A double sloping roof with a ridge and gables at each end
Gambrel Roof A gable roof with two pitches. The lower section of the roof slopes gently up. Then, the roofline angles in form a steeper pitch. Gambrel roofs are often called barn-shaped because the this roofing style is so often used on American barns.
An Enduring Design This home dates back to the pre-Revolutionary era, but still remains a popular architectural choice for many Americans.
NEW ENGLAND COLONIAL 1600 s - 1740 British who settled in the New England colonies built rustic, square homes with details drawn from medieval Europe. Massive chimney placed at the center Diamond-paned windows
NEW ENGLAND COLONIAL GARRISON Diamond window panes Second story protrudes SALTBOX Two story in front Roof slopes to create one story in back
GERMAN COLONIAL 1600s mid- 1800s German Settlers in the American colonies used local materials to recreate building styles from their homeland. Reinforced stone arches above the first floor windows and doors
GERMAN COLONIAL Two-feet thick sandstone walls Hand-hewn beams with wooden pegs Exposed half-timbering Flared eaves Massive wishbone-shaped chimney
SPANISH COLONIAL 1600 - 1900 Settling in Florida, California, and the American Southwest, settlers from Spain and Mexico built homes with many of these features: One story Flat roof, or roof with a low pitch Earth, thatch, or clay tile roof covering Interior shutters Several exterior doors Small windows, originally without glass Wooden or wrought iron bars across the windows Thick walls made with rocks, coquina, adobe brick coated with stucco
SPANISH COLONIAL Later Spanish Colonial homes had more elaborate features, such as: Second story with recessed porches and balconies Interior courtyards Carved wooden brackets and balustrades Double hung sashed windows Dentil moldings and other Greek Revival details
Balustrades A row of repeating balusters - small posts that support the upper rail of a railing. Staircases and porches often have balustrades. Double Hung Window
DUTCH COLONIAL 1625 - mid-1800s Settling along the Hudson River in the land that became New York, Dutch colonists built brick and stone homes like those found in the Netherlands. Stone or brick construction Wide, slightly flared eaves Gambrel roof or gambrel roof with flared eaves Two matching chimneys Or a massive wishbone-shaped chimney at front Dutch doors (upper and lower halves can be opened independently) Built in 1740, the Dutch Colonial Home shown has a gambrel roof and a salt-box shaped lean-to addition.
DUTCH COLONIAL Dutch Colonial turned on its side to fit a narrow lot with: Gambrel roof Full shed dormer Later Dutch style buildings became known for elaborately shaped gables, dormers, and parapets
1690 mid 1800s CAPE COD The classic Cape Cod features: One-story symmetrical cottage (sometimes 1.5 story) Exteriors are typically clapboard, stucco or brick Exterior siding originally left unpainted Steep pitched, narrow roof overhang with side gable
CAPE COD Large, central, single chimney Rectangular shape Center front door Multi-paned, double- hung windows Dormers
Dormer A window that is set vertically on a sloping roof. Dormers have their own roof, which may be flat, arched, or pointed.

 undefined
undefined