Hepatitis C Surveillance Report: Trends and Risk Factors
The CDC National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System data reveals hepatitis C trends, reported cases per 100,000 population across age groups, gender, and ethnicity. Risk factors such as injection drug use, sexual contact, multiple sex partners, and occupation exposures are identified and discussed. Cases among men who have sex with men, injection drug users, dialysis patients, and those with occupational exposures indicate potential areas for intervention and prevention strategies.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
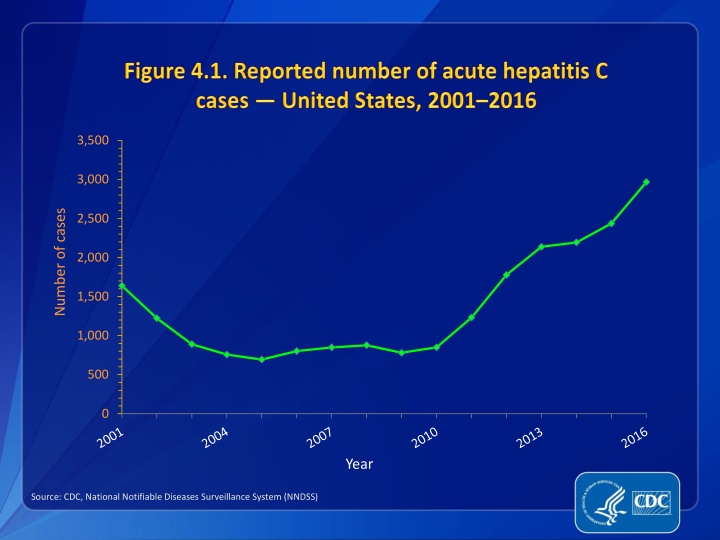
3,500 3,000 Number of cases 2,500 2,000 1,500 1,000 500 0 Year Source: CDC, National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS)
Reported cases/100,000 population 3 0-19 yrs 2.5 20-29 yrs 30-39 yrs 2 40-49 yrs 50-59 yrs 1.5 > 60 yrs 1 0.5 0 Year Source: CDC, National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS)
1.2 Reported cases/100,000 population Male 1.0 Female 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 Year Source: CDC, National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS)
Reported cases/100,000 population 3.5 American Indian/Alaska Native 3 Asian/Pacific Islander Black, Non-Hispanic 2.5 White, Non-Hispanic 2 Hispanic 1.5 1 0.5 0 Year Source: CDC, National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS)
958 32% Risk identified* No risk identified Risk data missing 1557 53% 452 15% Source: CDC, National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS) *Includes case reports indicating the presence of at least one of the following risks 2 weeks to 6 months prior to onset of acute, symptomatic hepatitis C: 1) using injection drugs; 2) having sexual contact with suspected/confirmed hepatitis C patient; 3) being a man who has sex with men; 4) having multiple sex partners concurrently; 5) having household contact with suspected/confirmed hepatitis C patient; 6) having had occupational exposure to blood; 7) being a hemodialysis patient; 8) having received a blood transfusion; 9) having sustained a percutaneous injury; and 10) having undergone surgery.
767 351 Yes Injection-drug use No 1,849 Missing 26 233 Men who have sex with men 1,368 4 5 Sexual contact 2,958 176 298 Multiple sex partners 2,493 0 300 600 900 1,200 1,500 1,800 2,100 2,400 2,700 3,000 3,300 Number of cases Source: CDC, National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS) *A total of 2,967 case reports of acute hepatitis C were received in 2016. More than one risk exposure/behavior may be indicated on each case report. No risk data reported. A total of 1,627 acute hepatitis C cases were reported among males in 2016.
5 967 Occupation 1,995 Yes 7 Dialysis patient No 991 Missing 1,969 96 746 Surgery 2,125 64 654 Needle stick 2,249 0 200 400 600 800 1,000 1,200 1,400 1,600 1,800 2,000 2,200 2,400 Number of cases Source: CDC, National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS) *A total of 2,967 case reports of acute hepatitis C were received in 2016. More than one risk exposure/behavior may be indicated on each case report. No risk data reported.