Heart Health and Disease Prevention Through Diet
Heart disease is a prevalent global issue, with cardiovascular diseases leading to millions of deaths annually. Lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes, play a crucial role in managing heart health. Despite being mostly preventable, cardiovascular disease remains a significant cause of mortality worldwide, with key risk factors including aging, sedentary lifestyle, tobacco use, unhealthy diet, and obesity. It is essential to emphasize the importance of adopting a heart-healthy diet to reduce the burden of heart disease.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Diet and our Heart Theme for 2023 World Heart Day USE HEART FOR EVERY HEART Dr R.A. Fakunle (Ph.D Nutrition and Dietetics)
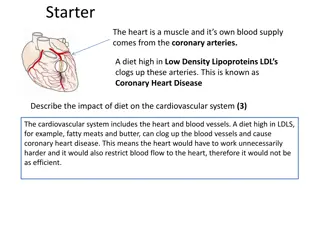
Introduction Introduction Heart disease, also known as cardiovascular disease or coronary heart disease, is a broad term for conditions that result in narrowed or blocked blood vessels that may lead to chest pain,heart attack,or stroke. Common cardiovascular diseases include atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), hypertension (high blood pressure), and heart failure, all of which are related and often coexist. Other conditions such as arrhythmia (irregular heart beat), heart valve problems, or congenital heart defects, also fall under the definition of heart disease (Bellows and Moore,2013).
Introduction Introduction prevalence diseases doubled from 1990 to 2019, and a steady increase in cardiovascular diseases deaths was observed, rising from 12.1 million in 1990 to 18.6 million in 2019. It is anticipated that cardiovascular diseases will remain the leading global cause of mortality, approximately 23 million deaths by 2030 (Roth,2019) The of cardiovascular resulting in
Introduction Introduction Lifestyle modifications including diet changes are the primary approach in managing cardiometabolic risk factors. Thus, understanding different cardiovascular health is important in guiding primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Yet, there are many barriers and limitations to adopting a heart healthy diet (Alaa Diab et al 2023). diets and their impact on
Risk factors of heart diseases Risk factors of heart diseases Despite being a mostly preventable disease, death as a result of cardiovascular disease is a leading killer globally. (World Health Organization, 2014) Age Sedentary lifestyle Tobacco use Unhealthy diet Obesity
Aging and Aging and Heart Diseases Heart Diseases Aging makes blood vessels become less flexible and can develop plaque buildup. This can lead to conditions like high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. Additionally, the heart muscles may weaken over time, increasing the risk of cardiovascular issues. It's important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and regularly monitor heart health as one get older.
Sedentary Lifestyle, Obesity Sedentary Lifestyle, Obesity and Diseases Diseases and Heart Heart A sedentary lifestyle, when a person is not physically active, this can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. When ones doesn't engage in regular exercise or physical activity, it can lead to weight gain, high blood pressure, and unhealthy cholesterol levels. Being inactive also weakens the heart and blood vessels, making them more susceptible to cardiovascular problems. It's important to stay active and incorporate regular exercise into our routine to reduce the risk of heart disease.
Unhealthy Diet, Tobacco Unhealthy Diet, Tobacco and Diseases Diseases and Heart Heart An unhealthy diet, which includes consuming high amounts of saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, sodium, and added sugars, can contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease. These unhealthy food choices can lead to high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, obesity, and diabetes, all of which increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Unhealthy Diet, Tobacco Unhealthy Diet, Tobacco and Diseases Diseases and Heart Heart Smoking damages the blood vessels, reduces oxygen in the blood, and increases the risk of blood clots. These effects can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems. Quitting smoking and adopting a healthy diet are important steps in reducing the risk of heart disease.
The Impact of unhealthy dietary The Impact of unhealthy dietary choices on the heart choices on the heart According to cardiovascular institute (2017), too much salt causes the body to retain water. This increase in fluid in the body increases blood pressure which puts a strain on blood vessels, the heart and kidneys. As a result, people with high blood pressure have an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
The Impact of unhealthy dietary The Impact of unhealthy dietary choices on the heart choices on the heart High blood cholesterol, often from a high fat diet, can lead to plaque formation in vessel walls. Plaque buildup occurs with no symptoms and causes narrowing of the arteries, high blood pressure, and may lead to a heart attack without warning (Bellows and Moore, 2013).
Dietary Recommendations for Dietary Recommendations for Cardiovascular Health Cardiovascular Health Consume a diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole-grains. Limit the amount of saturated fat, trans fat, and cholesterol in the diet. Read the Nutrition Facts on food labels. Choose lean meats and plant-based protein sources. Cook meals that are low in saturated fat, trans fat, and cholesterol. Limit foods and beverages with added sugar. Choose foods with low salt content.
Conclusion Conclusion A healthy diet can help lower cholesterol and blood pressure. It's important to focus on fruits, veggies, whole grains, lean proteins, and limit saturated fats and sodium. Diet plays a major role in managing heart disease.
KEEP YOUR HEART HEALTHY, EAT HEALTHY
THANK YOU FOR LISTENING
References References Alaa Diab, L Nedda Dastmalchi, Martha Gulati,and Erin D Michos A Heart- Healthy Diet for Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: Where Are We Now? Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2023; 19: 237 253. Published online 2023 Apr 21. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S37987 World Health Organization . Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2014. (No. WHO/NMH/NVI/15.1) Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M., Barengo N.C., Beaton A.Z., Benjamin E.J., Benziger C.P., et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990 2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982 3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010.


![READ [PDF] Dash diet Cookbook for beginners: 365 days of simple, healthy, low-s](/thumb/2057/read-pdf-dash-diet-cookbook-for-beginners-365-days-of-simple-healthy-low-s.jpg)