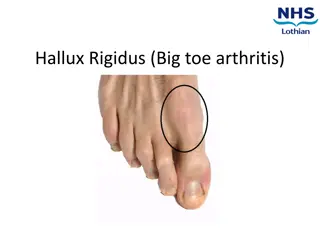
Hammer Toe: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Management
Hammer toe is a flexion deformity of a toe that can cause discomfort and pain, often worsened by ill-fitting footwear or weight-bearing activity. The condition can be caused by factors like bunions, trauma, or toe joint instability. Symptoms may include pain at the joint of the affected toe and secondary pain from calluses. Diagnosis involves a physical examination and possibly an X-ray. Management includes self-care methods like lifestyle changes, padding, and appropriate footwear, along with seeking medical advice for pain relief and podiatry. Lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, weight, and sleep, along with avoiding alcohol and smoking, can help improve outcomes.
Uploaded on Sep 16, 2024 | 2 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Contents 1. What is Hammer Toe? 2. What are the causes? 3. What are the symptoms? 4. How is it diagnosed? 5. What is the management? 6. How can I manage it?
What is Hammer Toe? Hammer toes are a flexion deformity of a toe.
What are the causes What are the causes/risk factors? Bunions Trauma Ill fitting footwear Toe joint instability or dislocation Estimated incidence varies between 2-20% in the population
What are the symptoms? In many cases, hammer toes do not cause any pain. If pain is present, it's typically situated over the joint where the toe flexed or at the end of toe. Secondary pain from callus and/or corns. Aggravated by flexing toe, ill fitting footwear or weight- bearing activity.
How is it diagnosed? An appropriate healthcare professional will discuss your foot symptoms and enquire about your general health. A physical examination of your foot will be carried out to assess your movement, response to particular tests and level of pain. This can be clinically diagnosed. An x-ray might be requested for surgical consideration
What is the management? Many patients are happy to self-manage their symptoms, with painkillers/anti-inflammatory medication or other non-invasive treatments such as: Lifestyle and health changes Activity Modification Padding Wearing appropriate footwear. Podiatry
Lifestyle & Health Changes Maintaining a healthy diet and weight Getting 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night Reducing alcohol intake Quit smoking Not all of these recommendations will be relevant to everyone, but these are important factors to consider to optimise your outcome. Click this link for more information and support options
How can I manage it? Rest/immobilisation/activity modification, as required. Wearing toe sleeves or pads available online or in chemist. Simple pain relief or anti- inflammatory medication - Consult your GP or Pharmacist Appropriate footwear - Avoiding high heeled or narrow footwear. Footwear with support may also help symptoms further. Image result for pain relief
Physiotherapy Podiatry Through a thorough examination, a Podiatrist can : Help you establish what may be causing your pain Provide you with an individualised treatment plan to help and/or resolve symptoms. Advise and arrange further investigation, if required
More Invasive Management Options In some cases symptoms may persist and more invasive treatments may be required/requested by you, as the patient: Surgery
Surgery Surgery is only required if pain is present and symptoms are unable to be controlled by more conservative methods, as described above.