Guide to Conducting Effective Stage-1 Audit Training for TNV
This guide provides insights on conducting an effective Stage-1 Audit Training for TNV. It covers essential training agenda points such as document review, gap analysis, opening and closing meeting agenda points, report writing, and more. It emphasizes the importance of Stage-1 audit in preparing for the subsequent stages and understanding standard requirements.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
How to conduct Effective How to conduct Effective Stage Stage- -1 Audit 1 Audit Training document of TNV Training document of TNV
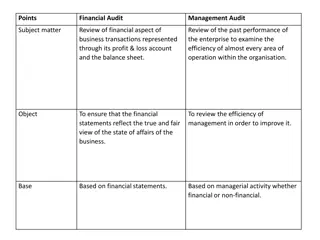
Training Agenda Points : A. B. check the preparedness of documents & Records as per the Context Understanding of Mandatory documents and records required as per context for any management system. Understanding the gap analysis. C. Opening & Closing Meeting Agenda points. D. Report Writing Understanding of Audit Techniques. Understanding of covering all elements as per the stage-01 requirements. Understanding of Report audit results including conclusions and recommendations Validation of Critical Points How to conduct effective stage-01 Audit objective of Audit Documentation review. Location evaluation Employee interviews Audit planning
Use of Stage Use of Stage- -1 Audit 1 Audit Stage 1 aims to establish that you understand the requirements of the standard, and that you ve got systems and procedures in place to comply with it. We ll review any relevant documentation that you ve produced. We ll leave you with a report and an audit schedule for stage 2. The report will identify any actions you re advised to take before the next stage. Stage 1 is an important part of the process as it ensures you re properly ready for the more detailed stage 2. It also gets you used to being audited and provides an opportunity to get to know your auditor.
common activities performed during a Stage 1 common activities performed during a Stage 1 Audit Audit Documentation review. The auditor reviews a company s documentation to establish whether it is in line with the requirements of the standard. Examples can include Procedures, Work Instructions, Invoices, Purchase Orders, Drawings and Travelers. Location evaluation. The auditor will review the company location to ensure that resources are properly allocated for the Stage 2 audit. This can include confirming the number of employees, number of shifts, and square footage of the facility. Employee interviews. The auditor will interview employees to evaluate the effectiveness of and assess conformity to documented Procedures and Work Instructions, and ensure that they understand the standard requirements. The auditor will also use these interviews to determine the preparedness of the company for the Stage 2 audit.
common activities performed during a Stage 1 common activities performed during a Stage 1 Audit Audit Audit planning. The auditor will provide a focus for planning the stage 2 audit by gaining a sufficient understanding of the company s management system and operations. The auditor will also determine what resources are needed and confirm the date of the Stage 2 audit. Continuous improvement The auditor will point out any areas of nonconformity and potential improvements of the management system. By including it in their audit report, the company has an opportunity to rectify the identified deficiencies prior to the Stage 2 audit.
Checking the Preparedness of Documents as per the Checking the Preparedness of Documents as per the Context: Context: 1. Awareness of Mandatory documents for Management Systems : Quality Management System Here are the documents you need to produce if you want to be compliant with Standard Requirements . (Please note that some of the documents will not be mandatory if the company does not perform relevant processes.): Scope Quality policy Quality objectives Criteria for evaluation and selection of suppliers Operating Procedures Work Instruction
Mandatory Record Mandatory Record Monitoring and measuring equipment calibration records Records of training, skills, experience and qualifications Product/service requirements review records Record about design and development outputs review Records about design and development inputs Records of design and development controls Records of design and development outputs Design and development changes records Characteristics of product to be produced and service to be provided Records about customer property
Mandatory Record Mandatory Record Production/service provision change control records Record of conformity of product/service with acceptance criteria Record of nonconforming outputs Monitoring and measurement results Internal audit program Results of internal audits Results of the management review Results of corrective actions
Environmental Management System Environmental Management System Here are the documents you need with Standard Requirements Scope of the EMS Environmental policy Risk and opportunities to be addressed and processes needed Criteria for evaluation of significant environmental aspects Environmental aspects with associated environmental impacts Significant environmental aspects Environmental objectives and plans for achieving them Operational control Emergency preparedness and response
Mandatory Records Mandatory Records: Compliance obligations record (clause 6.1.3) Records of training, skills, experience and qualifications (clause 7.2) Evidence of communication (clause 7.4) Monitoring and measurement results (clause 9.1.1) Internal audit program (clause 9.2) Results of internal audits (clause 9.2) Results of the management review (clause 9.3) Results of corrective actions (clause 10.1)
Occupational health and safety management systems Occupational health and safety management systems Here are the documents you need Scope of the OH&S management system (clause 4.3) OH&S policy (clause 5.2) Responsibilities and authorities within OH&SMS (clause 5.3) OH&S process for addressing risks and opportunities (clause 6.1.1) Methodology and criteria for assessment of OH&S risks (clause 6.1.2.2) OH&S objectives and plans for achieving them (clause 6.2.2) Emergency preparedness and response process (clause 8.2)
Mandatory Records: Mandatory Records: OH&S risks and opportunities and actions for addressing them (clause 6.1.1) Legal and other requirements (clause 6.1.3) Evidence of competence (clause 7.2) Evidence of communications (clause 7.4.1) Plans for responding to potential emergency situations (clause 8.2) Results on monitoring, measurements, analysis and performance evaluation (clause 9.1.1) Maintenance, calibration or verification of monitoring equipment (clause 9.1.1) Compliance evaluation results (clause 9.1.2) Internal audit program (clause 9.2.2) Internal audit report (clause 9.2.2)
Mandatory Records: Mandatory Records: Results of management review (clause 9.3) Nature of incidents or nonconformities and any subsequent action taken (clause 10.2) Results of any action and corrective action, including their effectiveness (clause 10.2) Evidence of the results of continual improvement (clause 10.3)
Understand the gap analysis. A Gap Analysis is used to assess an organizations scope, readiness, and its resources for building the system. It also provides us with the data to develop a project plan for ISO implementation. The auditor (person conducting the Gap Analysis) will use this list to compare the QMS that is in place with the requirements of the ISO 9001 Standard. Where there is a shortfall, it is called a gap
Opening & Closing Meeting Opening & Closing Meeting Opening meeting agenda points The purpose of the opening meeting is to: Confirm Scope and Objectives of the Assessment. Confirm communications, resources and escorts. confirm the agreement of all parties(e.g. auditee, audit team) to the audit plan; Current Number of Employees. Confirm auditor confidentiality. Explain the audit program and the reporting process for deficiencies. ... Confirm time and place for closing meeting. Appeals process.
closing meeting The purpose of the closing meeting is to: A closing meeting, facilitated by the audit team leader, should be held to present the audit findings and conclusions. Participants in the closing meeting should include the management of the auditee and, where appropriate, those responsible for the functions or processes which have been audited, and may also include the audit client and other parties. If applicable, the audit team leader should advise the auditee of situations encountered during the audit that may decrease the confidence that can be placed in the audit conclusions. If defined in the management system or by agreement with the audit client, the participants should agree on the time frame for an action plan to address audit findings.
Understanding of Audit Techniques. Understanding of Audit Techniques. Audit techniques stand for the methods that are adopted by an auditor to obtain evidence. 1. Inspection a. Documents and records: b. Physical Verification 2. Observation . The auditor makes his observations to evaluate the efficiency and effectiveness of the system followed by the organization. 3. Computation An auditor makes appropriate calculations and verifies the accuracy of the records. 4. Analytical analysis The purpose of analysis is to ensure consistency of Management methods and also to evaluate the efficiency of the management by comparing the results of several years
Understanding of covering all elements as per the stage-01 requirements Preparedness of Documents Documentation review. Location evaluation Employee interviews Audit planning Understanding of Mandatory documents and records required as per context for any management system Understanding of availability of resources Understanding of legal & compliance issue as per the Scope. Understanding of Audit techniques for collecting evidences.
Understanding of Report audit results including conclusions and recommendations Report audit results: Results of the evaluation of the collected audit evidence against audit criteria . conclusions : outcome of an audit after consideration of the audit objectives and all audit findings. audit evidence: records, statements of fact or other information which are relevant to the audit criteria and verifiable Categories of non conformities : Audit findings can indicate conformity or nonconformity with audit criteria.- two types Major & Minor. Recommendations : If specified by the audit objectives, recommendations for improvements may be presented. It should be emphasized that recommendations are not binding RECOMMENDATION Recommended for Proceeding to Stage 2 Not Recommend proceeding to stage 2 until objective evidence has been submitted to CB showing that the concerns raised by the auditor (s) have been rectified. A date for stage 2 will then be agreed. (within 60 days from this audit date) Not Recommend proceeding without a further stage 1 Audit due to the severity of the concerns raised by the audit team
Validation of Critical Points Recommendation for Stage-2 Audit: I have checked, examined and discussed and confirm the following: Mark X where applicable. Sl. Validation of Critical Points Yes No Not Applicable Comment of the Auditor 1 Relevance of the QMS documentation with activities of the client Scope applied are justified with the present activities of the Clients Does the organisation have availed Exclusions? 2 3 4 5 6 Are Exclusion justified? Temporary Site? will it requires Considerable Travel Time to visit site is there any Seasonality Factor Suitability of Audit Timing (Activities at Site) 7 8 9 Process and element of the Management system in Stage-1 audit addresses?