Genetics: Concepts of Heredity, Mitosis, Meiosis, and DNA
Genetics is the study of heredity and genetic variations, involving terms like genotype, phenotype, homozygous, heterozygous, dominant, and recessive. Mitosis and meiosis are key processes in cell division, each with specific phases and functions. DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, stores and transmits genetic information through nucleotides composed of sugar, phosphate, and nitrogen bases. Learn more about these fundamental concepts in genetics and cellular biology.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Genetics Jessica Garr, Amanda Melair, Ashley Regan, Jake Young, Giovanni Marrero
What is Genetics? What are terms associated with Genetics? Genetics is the study of heredity, or the branch of biology that deals with heredity and genetic variations. Genotype: What is genetically expressed in an organis Phenotype:What is physically expressed in an organism Homozygous: Identical pairs of genes for any given characteristic Heterozygous: Different pairs of genes for any given characteristic Dominant: The trait that is physically expressed Recessive: The trait that is present but not shown
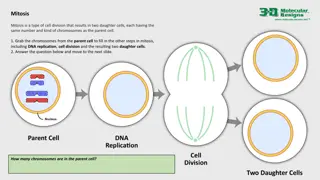
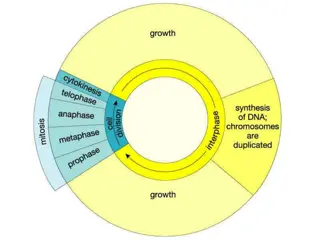
Mitosis & Meiosis Mitosis has 4 phases: Prophase Meiosis goes through 2 processes: Prophase l Crossing over Protiens of chromatids break off and attach to the adjacent chromosomes on the homologous chromosomes Metaphase l Anaphase l Homologous chromosomes seperate Telophase l Prophase ll Mertaphase ll Anaphase ll Sister chromatids seperate Telophase ll 4 haploid cells result They are similar cells Sex cells Haploid cells PREPARE Chromosomes are visible Lose nucleus Metaphase MIDDLE Chromosomes line up in the middle Anaphase AWAY Chromosomes move towards the poles Telophase TWO NUCLEUS Nucleus split and reappears They are identical cells Body cells Diploid cells
Stages of Meiosis l and ll http://thumb7.shutterstock.com/display _pic_with_logo/848740/116607409/stock -vector-vector-diagram-of-the-meiosis- phases-116607409.jpg STages of Mitosis http://www.google.com/search?q=mitosis&safe=active&source=lnms&tbm=isch&sa=X&ei=XgubU9GfEJGOyAS2_ IKYDA&sqi=2&ved=0CAYQ_AUoAQ&biw=1301&bih=620#facrc=_&imgdii=_&imgrc=nhZ- bmMsNUC3FM%253A%3BUhqCAF-wnFwS9M%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fdiffervs.com%252Fwp- content%252Fuploads%252F2013%252F08%252Fmitosis-vs- meiosis.jpeg%3Bhttp%253A%252F%252Fdiffervs.com%252Fdiscover-difference-mitosis- meiosis%252F%3B495%3B420\
Mitosis Video http://video.mit.edu/watch/lego-animation-of-mitosis-with-descriptive- titles-3077/
DNA Stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid Primary Function: to store and transmit the genetic information that tells cells whcih protiens to make and when to make them DNA is an organic compound made up or repeating subunits called nucleotides. Nucleotides have 3 parts: Sugar molecule Deoxyribose Phosphate Group Phosphorus Oxygen Nitrogen Bases Adenine (A) Cytosine (C) Guanine (G) Thymine(T) 2 types of Nitrogen Bases Purines Have 2 rings Adenine(A) Guanine(G) Pyrimdines Have 1 ring Cytosine(C) Thymine(T) VIdeo: https://answersingenesis.org/genetics//
en.wikipedia.org DNA Cont. Base Pairings: Cytosine bonds with Guaning (C-G) Adenine bonds with Thymine (A-T) James Watson and Francis Crick built the 3D model or the double helix 2 nucleotide strands wrap around eachother to form a double spiral Enzymes involved in DNA replication: DNA Helicase Unwind and unzip the DNA Binding Proteins Hold open the replication fork DNA Primase Lay down the start and stop primers for the new strand DNA Polymerase Lays down one new nucleotide at a time DNA Ligase The glue that holds the new DNA strand together The Enzymes involved in DNA replictation
RNA Stands for Ribonucleic Acid Responsible forthe movement of genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the site of protien synthesis in the cytosol A single sranded nucleic acid made up of repeating units Sugar molecule is ribose Thymine(T) relaced with URACIL(U) A strand of RNA http://chemistry.tutorvista.com/bio chemistry/nucleic-acids.html
RNA cont. 3 Forms of RNA Messenger RNA (mRNA) Function: Carries genetic info from the nucleus to the ribosome Transfer RNA (tRNA) Function: Binds to specific amino acids and helps form polypeptide chains (proteins) Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Function: Makes up the ribosomes where proteins are made
Protein synthesis Protein Synthesis- The production of proteins The amount and kind of proteins produced in a cell determines the structure and function of the cell 2 Steps in Protein Synthesis Transcription: Makes mRNA from DNA Transcribe- to copy Translation: mRNA leaves the nucleus through pores in the nuclear membrane mRNA then migrates to a ribosome in the cytosol, the site of protein synthesis http://sciencevogel.wikispaces.com/file/ view/Protein%20Synthesis%20diagram. png/493016480/390x301/Protein%20Syn thesis%20diagram.png
Mutations/Disorders Genetic Disorders: Genetic Traits and Disorders- Genes that control human traits can be mutated and then inherited by offspring Mutations- Definition- A change in DNA sequence that affects genetic info The result of some mutations are gentic disorders Inheritance- There are 4 main ways genetic disorders are passed.... Single Gene Disorder The problem traits controlled by a single gene and are passed in a dominant/recessive manner Multifactoral Disorders These disorders result from mutations in multiple genes These disorders are difficult to study and treat EX. Alzheimer's Disease, Hypothyroidism Karyotype showing the genetic disorder of Down Syndrome http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/d isorders/chromosomal/down/images/tris omy21_karyotype.jpg
Mutations/Disorders continued Inheritance cont. Chromosomal Abnormality Entire chromosomes or large segments of chromosomes are missing, duplicated, or otherwise altered Nondisjunction- Failure of a chromosome to seperate from its homologue during meiosis One gamete receives an extra copy of a chromosome and the other gamete lacks the chromosome entirely Scientisits can use karyotypes to identify disorders caused by chromosomal abnormalities X-Linked Disorders Disorders in which the mutations or errors are in genes found on the X chromosomes Ex.- Hemophilia, Muscular Dystrophy
Review Questions What is the full name for DNA? Deoxyribonucleic Acid What two organelles can DNA be found in? Nucleus, Mitochandria What is the shape of DNA? Double Helix What is a Gene? A sequence of DNA passed on to offspring What are the two purines found in DNA? Adenine, Guanine What are the two phases of protein synthesis? Transcription, Translation What are the four types of chromosomal mutations? What is the gene that is expressed called? What is a mutation?
Answers What is the full name for DNA? Deoxyribonucleic Acid What two organelles can DNA be found in? Nucleus, Mitochandria What is the shape of DNA? Double Helix What is a Gene? A sequence of DNA passed on to offspring What are the two purines found in DNA? Adenine, Guanine What are the two phases of protein synthesis? Transcription, Translation What are the four types of chromosomal mutations? Deletions, Duplication, Insertion, Translocation What is the gene that is expressed called? Dominant What is a mutation? A change in the DNA sequence that effects genetic info