Genetic Inheritance Through Punnett Squares
Explore the fascinating world of genetic inheritance by delving into Punnett Squares, traits, alleles, dominance principles, phenotypes, and genotypes. Discover how characteristics are passed down from one generation to another through genes. Learn about homozygous and heterozygous traits and get ready to predict genetic outcomes using this essential tool. Don't miss out on the Beginner's Guide to Punnett Squares homework due Friday!
Uploaded on Sep 27, 2024 | 1 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Science Fact of the Day: Sheep, goats, and the octopus have almost rectangular-oval pupils in their eyes.
Content Objective: I will understand and predict genetic outcomes using a Punnett Square Language Objective: I willwrite notes. I will answer questions by writing Punnett Squares with a partner.
Homework: Due Friday A Beginner s Guide to Punnett Squares Watch the video and complete the worksheet. There will be consequences for those who do not complete this homework by Friday.
A trait is a specific characteristic that varies from one individual to another. Example
Biological inheritance is determined by factors that are passed from one generation to the next. The chemical factors that determine traits are called genes. The different forms of a gene are called alleles.
The principle of dominance states that some alleles are dominant while others are recessive. The dominant allele will always be expressed. A capital letter is used to represent a dominant allele.
The recessive allele will only be expressed (phenotype) when the dominant allele for the trait is not present. A lower case letter is used to represent a recessive allele.
A phenotype is an organism s physical characteristics. A genotype is an organism s genetic makeup. Two organisms can have the same phenotype but different genotypes. Example
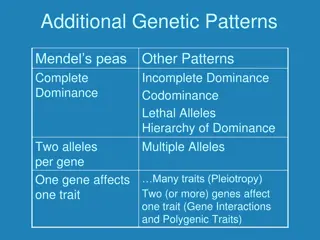
Organisms that have two of the same alleles for a trait are homozygous. Organisms that have two different alleles for a trait are heterozygous. Homozygous organisms are true-breeding for a trait. Heterozygous organisms are hybrid for a trait.
The way in which alleles separate during meiosis is completely random. This is also known as the principle of independent assortment.
The results of genetic crosses can be explained by probability. Probability is the likelihood that a particular event will occur.
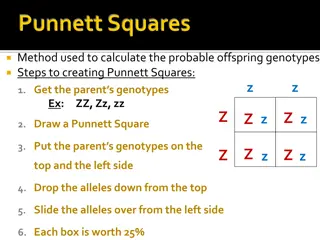
The gene combinations that might result from a genetic cross can be determined by drawing a diagram known as a Punnett square.
The letters in the Punnett square represent alleles. Punnett squares are used to predict and compare the genetic variations that will result from a cross.
Punnett Square practice 1. What would be the possible outcomes for the offspring of a cross between pink flower (PP) and a white flower (pp)?
2. Long fingers are dominant (F) to short fingers (f). Complete the Punnett square for a homozygous recessive mom and a heterozygous dominant dad.
3. In a plant, long stems are dominant (L) to short stems (l). If a homozygous dominant flower and a homozygous recessive plant are crossed, what would be the phenotypic ratio of their offspring?
4. Straight hair (C) is dominant to curly hair (c). What would be the probability that a child would have curly hair if both parents are heterozygous dominant?
5. Having a hitchhiker's thumb is a dominant trait. If a woman with a straight thumb has a child with a man who is heterozygous for the trait, what are the chances their child will have a hitchhiker's thumb?
6. What would the phenotypic and genotypic ratios be for two purple (Pp) flowers that were bred together?
7. If being right handed is a dominant trait, then how many right handed children would two left handed parents have?
Summary: In 35 words summarize your understanding of genetics. Be sure to use the words allele, dominant, phenotype