Gender Equality in Education and Emergencies
This document explores key principles, strategies, and actions for promoting gender equality in education during emergencies. It covers gender-equitable practices, defining key gender terms, and the rationale for gender-sensitive programming. The focus is on enhancing gender equity through inclusive and empowering responses.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
INEE Guidance Note on Gender: Gender Equality in and through Education [Date and location] 1 This document is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0. It is attributed to the Inter-agency Network for Education in Emergencies (INEE).
Objectives By the end of the training, participants will be able to: Explain key gender equity principles and strategies that may be applied in education in emergencies (EiE) programs; Identify gender-equitable EiE programmatic responses across the INEE Minimum Standards (INEE MS) domains; Conduct an EiE appraisal to identify how gender is reflected in existing or future EiE programs; and Describe short- and long-term actions to enhance gender equity in EiE programming.
Self-Assessment and Pair Share: Gender-Equitable EiE Practices Directions: Individually answer statements with yes or no. After answering, share and discuss your responses with a partner. If time allows, discuss further: Are your answers and related experiences similar or different? What is the same or different?
Activity: Defining Key Gender Terms and Concepts Directions: 1. Form the same pairs or small groups from the self-assessment. 1. Use handout 2 in pairs to match terms with their definitions.
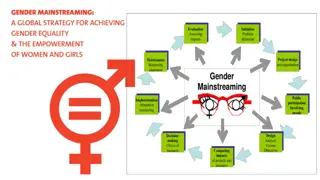
Rationale for Gender Equitable EiE Programming Crises impact girls, boys, women, and men differently because of their differing status and roles in society. These factors can affect their access to the resources and services they need to recover and be resilient Gender inequalities exist before the crisis + Integrating gender considerations into all humanitarian action helps ensure more inclusive, effective, efficient, and empowering responses
Key Principles of Gender Equality Programming for EiE 1. Gender affects everyone. 2. Gender dynamics affect education. 3. Gender-responsive education is protective. 4. Crises present opportunities for transformative change. 5. Promoting gender equality contributes to peaceful and sustainable recovery. 6. Data is disaggregated by sex. 7. Male and female learners are involved in working toward gender equality. 8. Male and female community members are involved in working toward gender equality. 9. Gender is a cross-sectoral issue. 10.Everyone should champion gender equality in education.
Common Arguments related to Key Principles for Gender Equality Programming for EiE 4. Gender is too complex for children to understand we don t have to ask them how gender issues impact them with regards to education and protection. 1. Gender experts only talk about women and girls. Men and boys are just as disadvantaged. 3. Gender-based violence isn t a problem the education sector needs to deal with, especially during crises, because schools protect children. 2. It s too difficult to consider the needs of different learners in emergencies, and everyone is vulnerable and marginalized in an emergency. 5. Gender equality comes from the outside it doesn t apply to us and our culture, our context.
Introduction to INEE Minimum Standards Standards promote a minimum level of access to quality education in emergencies Developed by more than 3,500 educationalists from 52 countries Rights-based: Universal Declaration of Human Rights Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC) Companion standards to Sphere as part of the Humanitarian Standards Partnership: Humanitarian Charter the right to life with dignity
INEE Minimum Standards (cont.) Standards - The why - qualitative, aspirational and universal, applicable in any environment. Key Actions - The what - are suggested actions to be taken in order to reach/meet the standard. Guidance Notes The how - cover points of good practice to consider when applying the minimum standards and adapting the key actions in different situations.
Why should gender equity be reflected across the INEE MS Domains and Standards? A gender-equitable Education in Emergencies (EiE) response: protects equitable education as a fundamental human right. promotes the best possible prospects for sustainable, equitable recovery processes.
Group Activity: Identifying Gender Equitable EiE Strategies Across INEE MS Domains and Standards Directions: 1. Read the case study. 2. Identify the INEE MS Domain and related standards using the INEE MS At- A-Glance Handout. Note: some case studies may include more than 1 Domain and Standard identify the one(s) that stand out the most to you. 3. Brainstorm: What is the gender equitable EiE strategy(ies)/intervention (s) presented in this case study? Why is/are this/these strategy(ies) is important? Note: some case studies may include more than gender equitable EiE strategy related to INEE MS Domains identify the one(s) that stand out the most to you. 4. Check your group s ideas: Find your case study in the INEE GNG. Identify 3 - 4 key points related to the gender equitable EiE strategy(ies) that stand out the most in your case study.
Activity A: Gender Equity Appraisal: Review the South Sudan Multi-Year Resilience Proposal to Identify Gender-Equitable EiE Strategies and Activities Programme Summary Section 1. Situation & Needs Analysis Section 2. Target Population Section 3. Program Results Theory of Change and Strategy Program Results Results Framework Section 4. Implementation Section 5. Multi-Year Budget Section 6. Monitoring and Evaluation and Learning Annexes
Activity: Appraising the INEE GNG with the South Sudan ECW MYRP - EXAMPLE Review the example excerpt handout: Annex on the MYRP development process. Practice using the appraisal template below with the example excerpt: Sections of the South Sudan ECW Proposal Annex 1: MYRP Development Process INEE MS Domains and Standards and INEE GNG Strategies Strategies for Gender-Responsive Participation, Coordination, and Analysis Yes Somewhat Not At All Rationale/Description: If yes, how? If somewhat, what could be strengthened? If not all, what is missing in the proposal? Gender- Responsive Participation
Action Planning: Quick Wins and Long-Term Needs and Opportunities for Enhancing Gender Equitable EiE Approaches in Context Gender Equitable EiE: Quick Wins Strategy and/or related activities or actions Time Needed Human Resources Needed? Financial Resources Needed? 1. 2. Gender Equitable EiE: Longer-Term Needs and Opportunities Strategy and/or related activities or actions Time Needed Human Resources Needed? Financial Resources Needed? 1. 2.
Additional Resources INEE Gender Resource Collection EiE-GenKit Inter-Agency Standing Committee. (2015) Guidelines for Integrating Gender-Based Violence Interventions in Humanitarian Action: Reducing risk, promoting resilience and aiding recovery. UNESCO & UN Women. (2016). Global Guidance on Addressing School- Related Gender-based Violence.
Evaluation Thank you for participating! Please help us improve this orientation by completing the post-orientation evaluation. We welcome your feedback! Please email: gender@inee.org
www.inee.org 17