Food Science and Nutrition: A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the world of food science and nutrition through topics like macronutrients, cooking methods, food safety, influences on food choice, waste management, and health implications. Learn about essential nutrients, food preparation techniques, and factors affecting our dietary decisions. Gain insights into food spoilage, safe storage practices, and the impact of cultural, ethical, and environmental factors on our food choices.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
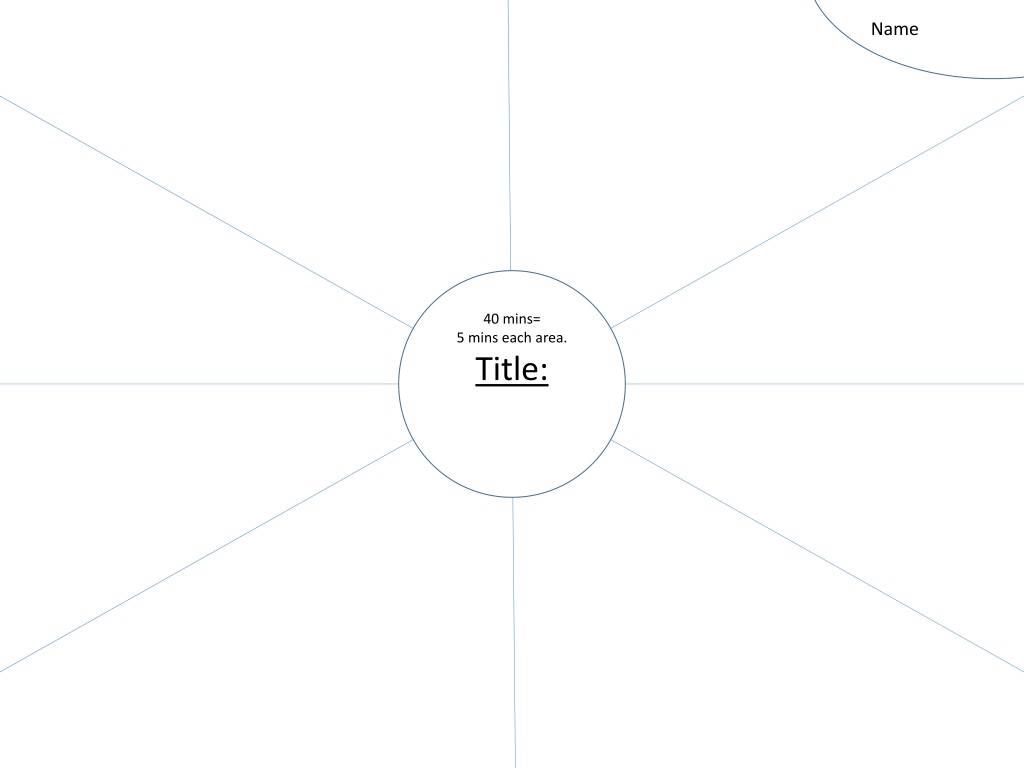
Name 40 mins= 5 mins each area. Title:
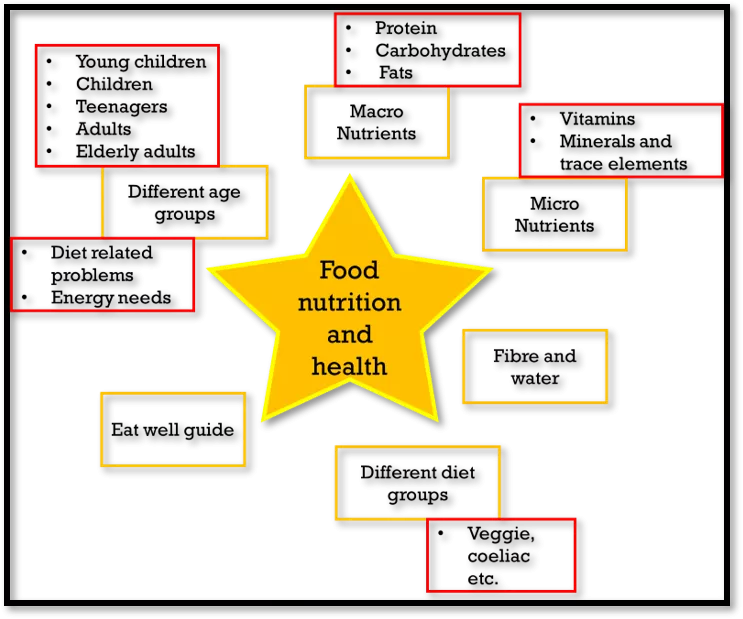
Protein Carbohydrates Fats Young children Children Teenagers Adults Elderly adults Macro Nutrients Vitamins Minerals and trace elements Different age groups Micro Nutrients Diet related problems Energy needs Food nutrition and health Fibre and water Eat well guide Different diet groups Veggie, coeliac etc.
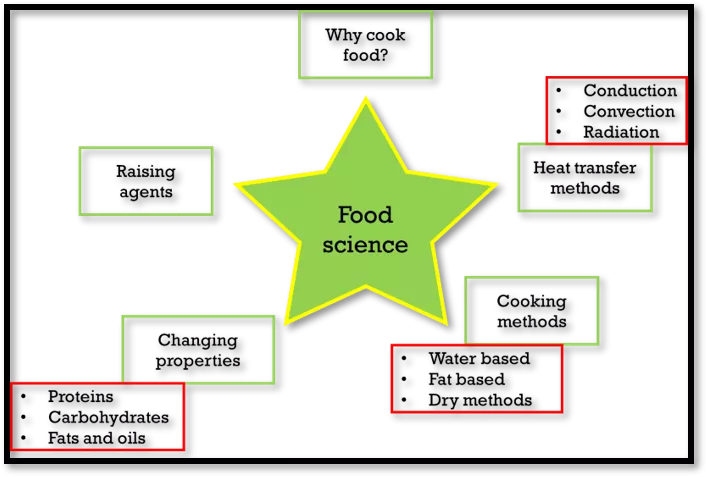
Why cook food? Conduction Convection Radiation Heat transfer methods Raising agents Food science Cooking methods Changing properties Water based Fat based Dry methods Proteins Carbohydrates Fats and oils
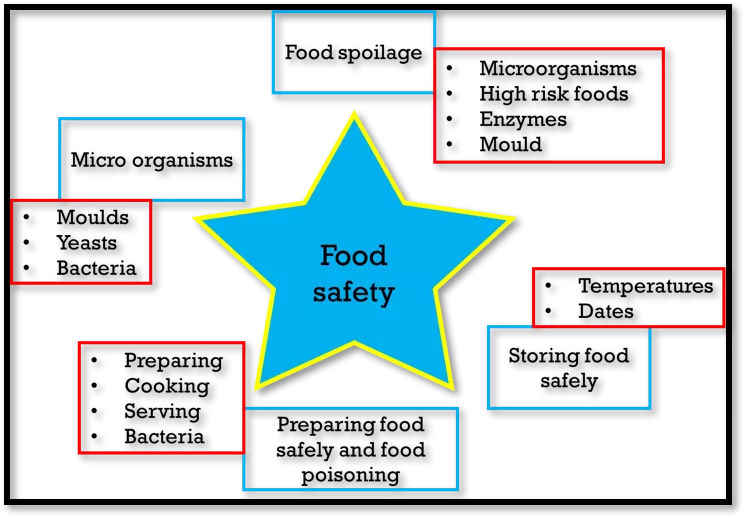
Food spoilage Microorganisms High risk foods Enzymes Mould Micro organisms Moulds Yeasts Bacteria Food safety Temperatures Dates Storing food safely Preparing Cooking Serving Bacteria Preparing food safely and food poisoning
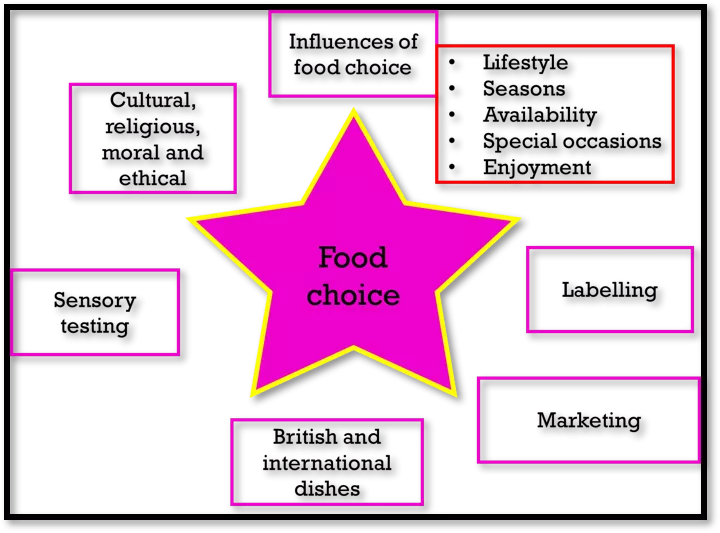
Influences of food choice Lifestyle Seasons Availability Special occasions Enjoyment Cultural, religious, moral and ethical Food choice Labelling Sensory testing Marketing British and international dishes
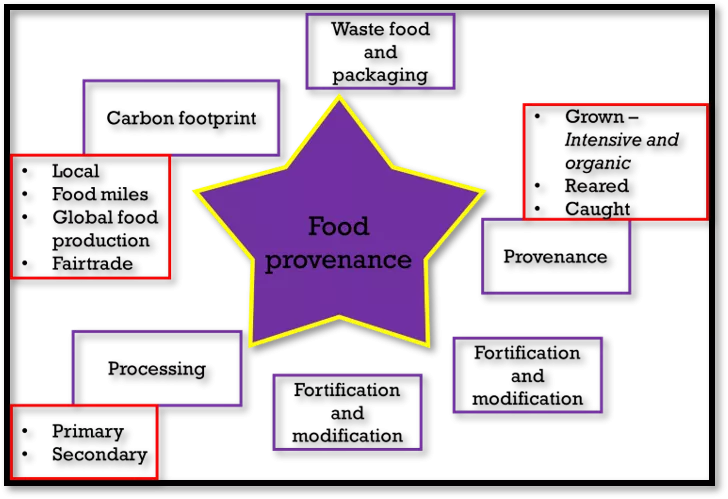
Waste food and packaging Grown Intensive and organic Reared Caught Carbon footprint Local Food miles Global food production Fairtrade Food provenance Provenance Fortification and modification Processing Fortification and modification Primary Secondary
and health Macro and micro nutrients Page 1-10 Needs of different ages 12-13 Health problems 14-16 Different groups Nutrition Why cook? Pg 24 Cooking methods 25-27 Changing properties 28-31 Raising agents 32. Science Food spoilage Pg 34-35 Storing food safely 36-37 Preparing safely and food poisoning 38-39 Micro organisms 40 Safety Influences Pg 42-43 Cultural, Religious and Moral 44-45 Labelling 46-47 Marketing 48 British and international dishes 49-51 Sensory testing 52-53 Choice Grown, reared, caught Pg 55-58 Waste food and packaging 58-60 Carbon footprint and food miles 61 Global food production 62-63 Processing 64-65 Fortification and modification 66-67. Provenance
Food nutrition and health Macro nutrients Proteins Fats Carbohydrates Carbs are needed for energy. Two types: Sugar (simple) Starch (complex). Sugar: glucose and fructose can be found naturally in fruit and V or added to cakes etc. Starch: Potatoes, bread, pasta etc. Contain nutrients: b vitamins, iron and calcium. Simple carbs are digested quickly (sugars) Complex carbs take longer (starch). Glycaemic index: (helps with diabetes) High GI digested quickly Low GI Digested slowly (healthier) 50% of our energy should come from carbs. Too much carbs: Converted to fat if we don't need the energy. Tooth decay Simple carbs shoot blood sugars up, can cause diabetes. Too few carbs: Blood sugar to drop (tiredness, hunger, dizzy). Provide energy, nutrients and insulation. A layer of fat needed to protect organs and bones. Source of fat soluble vitamins. Saturated fats: BAD for health Animal sources. Can increase cholesterol = heart disease. Unsaturated fats: Healthier. Vegetable sources. Replacing saturated fats with unsaturated fats can help to lower blood pressure. Fats should make up less than 35% of daily food energy. Too much fat leads to: Weight gain. High blood pressure and stroke. Too little fat leads to: Less fat soluble vitamins A,D,E and K = vitamin deficiency. Weight loss Less insulation = colder quicker, illness. Needed for growth, repair and maintenance. Different biological values (HBV & LBV) Average male 55g per day/ female 45g per day Too much puts pressure on liver and kidneys. Too little = growth is slowed down, wounds don t heal, growth slows on hair and nails Oedema (fluid filled swelling) Alternative proteins = Soya (beans) Micro protein (Quorn style) TVP (vegetable protein) Tofu (beans).
Food nutrition and health Macro nutrients Proteins Fats Carbohydrates
Food nutrition and health Micro nutrients Vit A Vit D Good eyesight Growth Healthy immune system. Main source: Liver, butter, oily fish, eggs. Too much can weaken bones Too little: night blindness 0.7mg men, 0.6mg women per day. Helps Vit E Vit K
Food nutrition and health Needs of different age groups. BMR Energy needs. PAL Young children (2-5) Children 5-12 Teenagers Adults Elderly adults
Food nutrition and health Diet related health problems. Obesity Coronary heart disease Anaemia Diabetes Skeleton Rickets Osteoporosis Tooth decay.
Food nutrition and health Different groups Lactose intolerance Nut Allergy Coeliac disease Vegetarians
Food Science Why cook food? To make it safe to eat To improve shelf life To develop flavours To improve texture Give variety in the diet.
Food Science Heat transfer Conduction Convection Radiation .
Food Science Cooking methods Water based Fat based Dry based.
Food safety Food spoilage High risk foods Microorganisms love Mould and Yeast Enzymes
Food safety Storing food safely Cooking/ Reheating (75 C) The danger zone (5-63 C) Chilling (0-5 C) Freezing (-18 C) Freeze drying Canning Vacuum packing Using chemicals Use by date Best before date
Food safety Preparing food safely Cross contamination Preparing Cooking Serving Campylobacter E.Coli 0157 Salmonella Staphyloccus Listeria Controlling bacteria
Food safety Micro organisms Moulds Yeasts Bacteria
Food choice Influences Physical activity level (PAL) Healthy eating Cost of food Income Culinary skills Lifestyle Seasonality Availability Special occasions Enjoyment
Food choice Cultural, Religious and Moral Christianity Islam Hinduism Judaism Sikhism Buddhism Rastafarianism