Exploring the Intricacies of the Human Eye and its Functions
Delve into the fascinating world of the human eye, an extension of the brain, as we explore its proximity to the optic nerve bundle and spinal cord. Understand the crucial role of the retina, lens, cornea, optic nerve, ciliary muscles, and suspensory ligaments in vision. Discover how the retina receives images, the functions of light receptors called rods and cones, and the mechanisms involved in focusing and bending light. Learn about near and distance vision, lens thickness adjustments, and controlling light levels through the iris, all essential for maintaining healthy vision.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
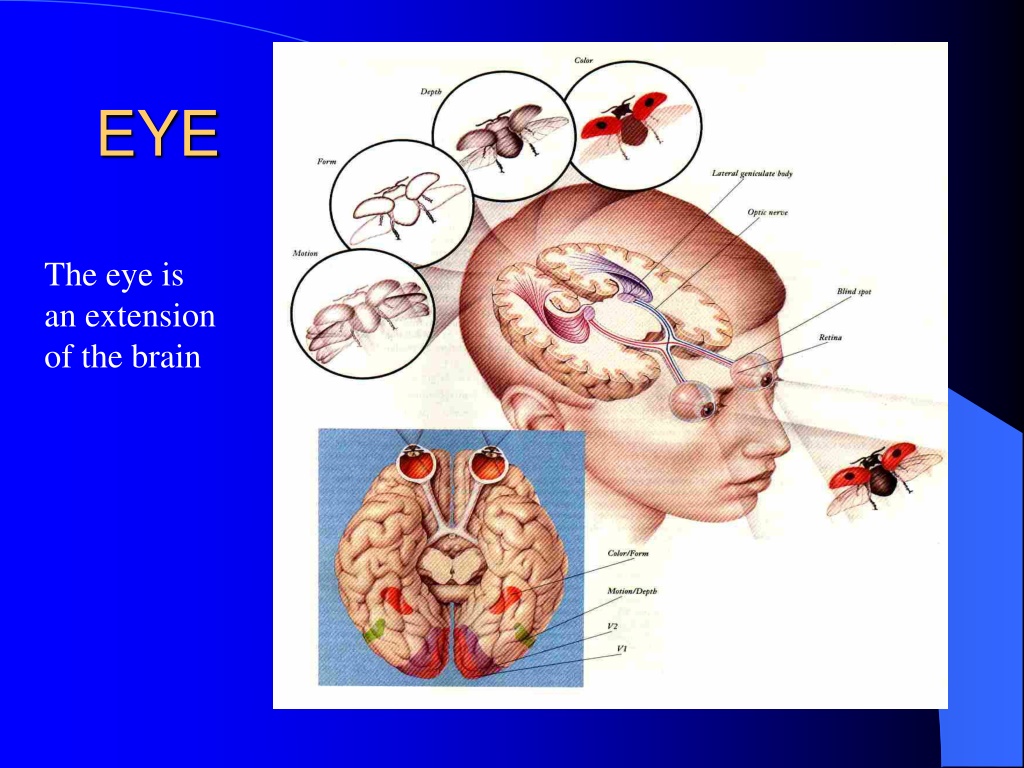
EYE The eye is an extension of the brain
Eye brain proxomity Can you see : the optic nerve bundle? Spinal cord?
Cross section You must know the position of: Retina Lens Cornea Sclerotic Optic nerve Cilary muscles Suspensory ligaments
Retina receives the image Full of light receptors which are sensitive to: Colour Light levels Fovea is the main focal point and has greatest density of light receptors Massive blood supply is also needed
Retina receptors Light receptors are called rods and cone
Focusing on objects The lens and cornea focus the light on the retina
Focusing The lens job is to make the rays hit the same point The red rays will be out of focus
Bending light Light is refracted and bent to focus it as it passes through the lens Lens thickness can be changed so the amount of bending is changed
Near vision to bend the light more to focus it Fat lens needed
Distance vision Rays enter the eye closer together Need less bending Thinner lens needed
Changing lens thickness The lens is slightly elastic, its relaxed state is short and fat. Cilary muscles are attached to the lens, when contracted they pull the lens thin
Controlling light levels Your eye are very sensitive and can be damaged by harsh light. Your iris controls light allowed into the eye by changing the size of the pupil
This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.