Expectancy Theory of Motivation in the Workplace
Explore the Expectancy Theory of Motivation, its development, Vroom's theory, and how it explains the link between performance and rewards. Learn why rewards sometimes fail to motivate employees despite expectations. Discover the key elements of the theory and its implications for managerial practices.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Objective Learning Objectives Explain what are Motives Explain why Rewards Often Fail to Motivate Describe Vroom s Expectancy Theory Explain the Expectancy Theory Equation Describe the Managerial Implications of Expectancy Theory
Introduction Helios Software recently announced a new set of rewards for its employees who exceed the expected performance levels. The HR expected such a reward system to boost employee morale and to motivate them. However, after six months, when an audit was conducted, it was found that there was not much change in the performance levels of the employees.
Introduction So, why do rewards fail to motivate? Is there a link between performance and rewards which is individual based? Such questions can be answered by Expectancy Theory which was proposed by Vroom. Let us learn about Expectancy Theory of Motivation in detail. Helios Software recently announced a new set of rewards for its employees who exceed the expected performance levels. The HR expected such a reward system to boost employee morale and to motivate them. However, after six months, when an audit was conducted, it was found that there was not much change in the performance levels of the employees.
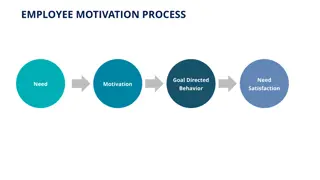
Development of Expectancy Theory Motivation was defined as a goal directed behavior involving an active process of evaluating the valence of outcomes and the expectancy of goal attainment. The early research work done by Tolman (1936) and Lewin (1938) paved the way for the development of the Expectancy Theory. Their research works provided a relationship between stimulus and response.
Vrooms Expectancy Theory This theory focuses on three relationships or key elements of expectancy theory: Let us see, how these components are linked:
Expectancy Model of Motivation Motivation Inputs Behavior Motivational Outputs Needs (Internal Stimuli) Satisfaction Perception EP* PI* IN* Abilities and Traits Perceived and Equitable Reward Motivation Incentive (External Stimuli) Performance * EP: Effort Performance * PI: Performance Incentive * IN: Incentive - Needs Productivity
How Expectancy Theory Works Your manager offers you 1 billion dollars if you memorise the company handbook in one night. Expectancy Instrumentality Valence Effort - Performance Link Performance - Reward Link Reward - Personal Goals Link No matter how much effort you put in, probably not possible to memorise the text in 24 hours Your manager does not look like someone who has $1 billion There are a lot of wonderful things you could do with $1 billion I = 0 V = 1 E = 0 Conclusion: Though you value the reward, you will not be motivated to do this task.
ManagementStudyGuide.com This is a DEMO Course On Expectancy Theory of Motivation. Join MSG Premium Membership and Get Access to around 120 Courses + New courses added every week. What You Get: 1. View All Courses Online. 2. Download Powerpoint Presentation for Each Course. 3. Do the Knowledge Checks for Each Course.