Evolutionary Evidence in Biology
Fossil records, comparative embryology, anatomy, convergent and divergent evolution, cell biology, and serology provide compelling evidence for common ancestry and evolutionary relationships among organisms. Fossils offer a glimpse into the past, while comparative studies highlight similarities in structure and function, supporting the theory of evolution. Language detection: English
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
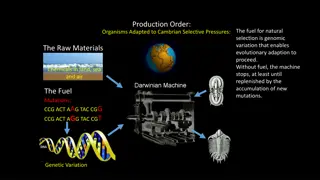
Fossil record What are fossils? Fossils are remains of ancestral forms of organisms that were preserved in naturally occurring materials such as sedimentary rocks over a long period of time. The study of fossils is called paleontology Petrifaction is process by which hard plant/animal parts change in to rock i.e bones, teeth, shells and woody stems They give a direct evidence of what existed at aparticular geological era
Importance of fossil records Give evidence of type of plants and animals that existed long ago. Give evidence of structural changes that have taken over a long period of time. Limitations of fossil records 1. Rapid decomposition of dead organisms cannot fossilize/soft parts cant fossilize/scavenging animals 2. Missing links 3. Distortion of parts during sedimentation 4. Destruction of fossils by geological activates like volcanic eruptions 5. Sudden appearance of new species in absence of intermediate.
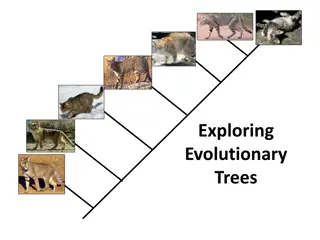
Comparative embryology Vertebrate embryos have similar morphological features during their early developmental stages which suggest a common ancestry. Birds are more closely related to humans since their embryos have a lot of morphological similarities.
Comparative anatomy Members of a phylum show similarities in structural organs performing the same function hence have a common ancestry. Importance of comparative anatomy It gives evidence of a common ancestry of a group of organisms Comparative anatomy is classified into two groups;- Convergent evolution Divergent evolution
What is meant by convergent evolution? Convergent evolution is the process where different structures of different embryonic origin evolve to perform same function. What is divergent evolution? Divergent evolution is a process whereby structures with a common embryonic origin evolve to perform.
Cell biology Organisms having same chemicals such as nucleic acids and organelles such as mitochondria have a common ancestry All vertebrates have a common ancestry since they all contain organelles like mitochondria and ribosome.
Comparative serology Organisms with similar blood proteins/similar antibody antigen reactions have a common ancestry.