Energy Transfer by Radiation and Infrared Sources
Explore the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation, learn how to measure this transfer, discover sources of infrared radiation, and understand the effects of surface properties on absorption and emission. Find out why dark surfaces absorb more radiation, how objects emit and absorb infrared radiation, and considerations for house color in hot climates.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Heat transfer by radiation * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Hot or cold? ? hot cold * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Heat transfer by radiation Fill a large beaker with hot water Divide between two beakers one with foil and one with dark paper Measure temperature on outside with an IR thermometer dark & dull shiny Dull and dark Shiny Temp inside at start Temp on outside at end * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
All objects emit and absorb infrared radiation. The hotter an object, the more radiation it emits every second. Clipbank: seeing in the dark * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
* ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
* ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
* ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Dull (matt) dark surfaces are better absorbers of infrared radiation than shiny light surfaces. Which metal block will heat up quicker? If you lived in a hot country, would you paint your house a light colour or a dark colour? * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Dull (matt) dark surfaces are better emitters of infrared radiation than shiny light surfaces. Hot tea 62 C Hot tea 62 C Which tea cup will lose heat quicker? If you had a food home delivery business, would you deliver the hot food in dark coloured containers or Aluminium foil? * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation Heat energy from the sun travels to earth by radiation. Since the space between the sun and the earth is a vacuum (no particles present), the heat cannot travel by conduction or convection. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
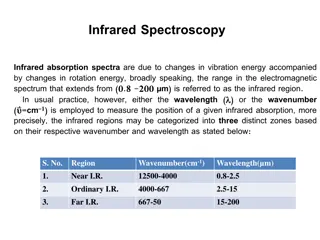
Infrared Radiation pictures Special Infrared cameras can be used to show the Infrared radiation given off by different things. gosublogger.com * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This is a infrared image of a child s hand holding a lizard. Lizards are reptiles and are cold blooded. Notice how the child`s hand is warm compared to the lizard. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This is an infrared image of a person. What area is the hottest? What do you think it is? * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This is an infrared image of two coffee cups containing very hot drinks. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This is a infrared image of a dear in the dark. Since infrared cameras detect heat radiation they can see the heat from warm blooded animals in the dark. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This infrared medical scan shows an injured and healthy leg. The bright white region shows the location of the injury, which is warmer due to the increased blood flow to the injured area. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This is a infrared image of footprints. As this person walks away barefoot the heat left behind her feet stills glows on the ground. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This is an infrared image of a cat. The yellow areas are the warmest and the purple areas are cool. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This is a infrared image of a tyre that has been heated by friction with the road. Notice how the area of the tyre that touches the road glows much more brightly when you look through the infrared camera. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This is a infrared image of a zebra. Notice how the stripes appear on the infrared. Do you think these are the black or white stripes? * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This is an infrared image of a heating element. Even after the stove is turned off, this heating element will glow brightly in the infrared until it reaches room temperature. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Infrared Radiation pictures This is a infrared map of global sea surface temperatures. Infrared satellites are used to measure and track changing ocean surface temperatures to help predict weather patterns. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Radiation Absorbers and Emitters Different surfaces will absorb different amounts of infrared radiation. -Dull, black surfaces are good absorbers of radiation. -Light, shiny surfaces will reflect the radiation. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Vacuum Flask freshpromotions.com.au * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Vacuum Flask A vacuum flask has a double wall of silvered glass with some vacuum between the wall. The silvered surfaces reflect the infrared radiation from the very hot contents back in to the flask. The vacuum between the outer and inner walls prevents heat loss through conduction. * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
* ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)
Properties of heat transfer by radiation You need to write down in your book how heat arrives from the sun by radiation. Be sure to mention the properties of heat transfer by radiation heat transfer radiation sun infrared wave particle reflect absorb shiny dull surfaces equator north pole ice like such as desert space vacuum through night vision * ** *** Explain the characteristics of energy transfer by radiation (L5) Measure energy transfer by radiation (L3) State some sources of infrared radiation (L4)