Energy Sector Challenges and Solutions in Pakistan
The Energy Research Centre at COMSATS Institute of Information Technology, Lahore Campus, highlights major challenges in Pakistan's energy sector, including demand-supply gaps, high fuel costs, investment declines, and distribution losses. The table comparison of distribution losses in different countries underscores the need for sustainable tariff reforms.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Khalid Saeed Head Energy Research Centre COMSATS Institute of Information Technology, Lahore Campus
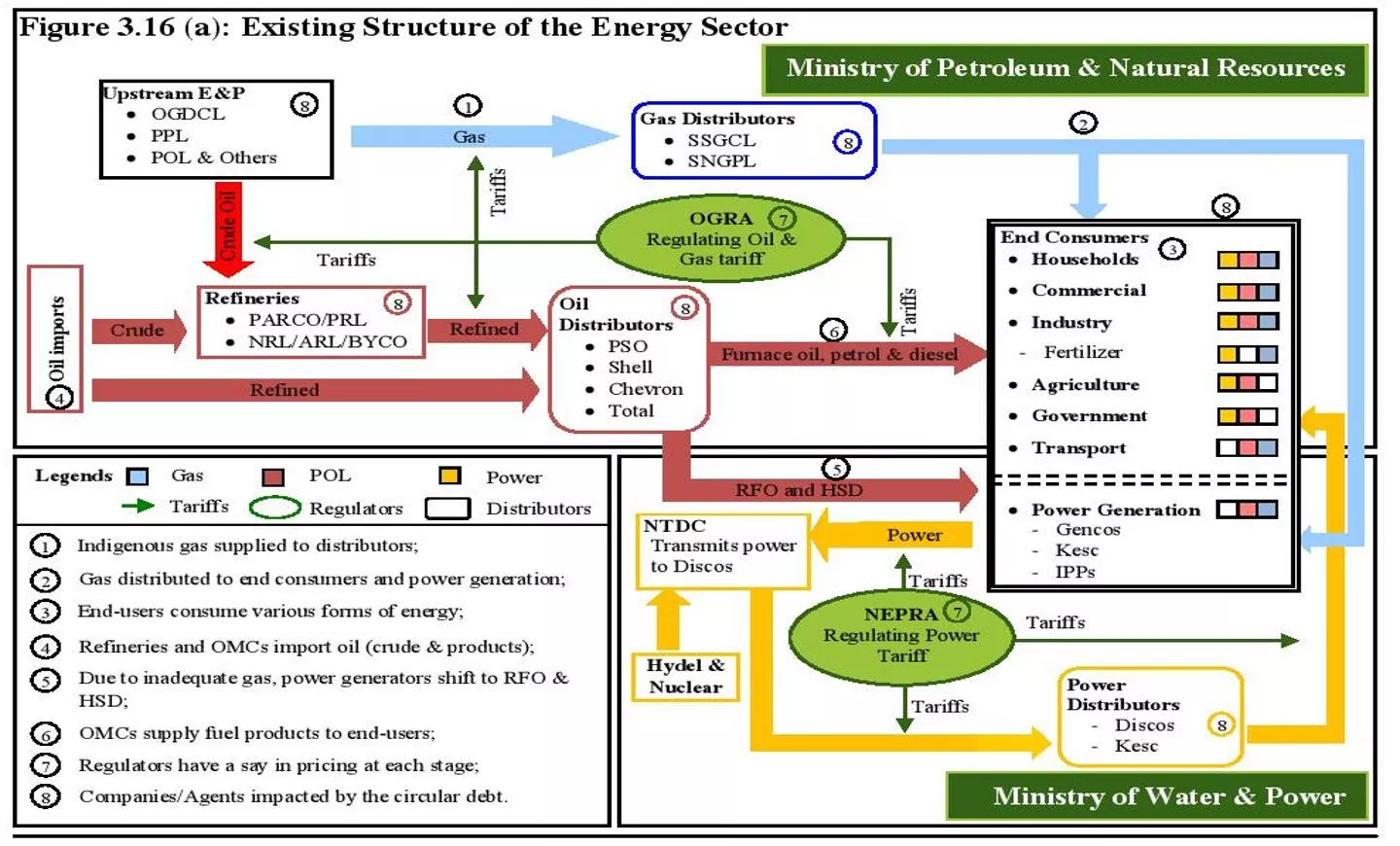
Introduction Existing Structure of Energy Sector 2
Major Challenges Demand and Supply Gap: 6000-7000MW (1/3rd of total demand) 3
Major Challenges High cost fuel mix for power generation Sources: Overseas Investors Chamber of Commerce & Investments (OICCI) Pakistan, Energy Sub Committee, NEPRA s State of Industry Report 2013 4
Major Challenges High cost fuel mix for power generation Low hydel share; decrease in gas allocation for power sector 5
Major Challenges Fall in share of investments in Energy Sector: While in mid 90 s, 26% of total and 51% of public sector investments, the share of energy (including power) dropped to 4% and 26% by 2009-10. Trust Deficit a reason for inability to undertake large hydel projects over last 25 years (except Ghazi- Barotha) 6
Major Challenges High T & D losses and poor recoveries by DISCOs 7
The table below indicates the level of losses and percentage of dues being recovered by various DISCOS. System Losses and Revenue Recoveries DISCO Distribution Losses Recovery (2011-12) (2011-12) PESCO 35% 68% HESCO 28% 69% SEPCO 49% 53% QESCO 21% 36% IESCO, JEPCO, FESCO, LESCO (average) 9.5%-13.5% Source: NEPRA: State of Industry Report: 2012 95%-98% 8
DISTRIBUTION LOSSES IN DIFFERENT COUNTRIES Country %age of output Transmission &Distribution Losses Australia 7% USA 6% Canada 8% Germany 4% France 6% UK 7% S. Korea 4% Malaysia 4% Iran 17% China 5% Egypt 11% India 24% Pakistan 20% Source: World Development Indicators Report: 2012 9
Major Challenges Unsustainable tariff regime 10
Major Challenges 2% loss to GDP Impact on employment/ exports/budget deficits and circular debt 11
Major Challenges Degeneration/ Derating of Public Sector Gencos Uniform national tariff No incentive for efficiency/ better recovery/ cutting theft and losses Circular Debt/ Inability to fully operate all available generation capacity due to shortage of funds to get fuel. 12
Road Ahead: Way Forward Diversity More reliance on renewable energy (hydel/solar/wind) 2. More gas allocation Add coal based power generation 3. Improve efficiency of public sector Gencos Also introduce efficiency for industrial machinery, transport and household appliances 4. Manage demand through conservation measures 1. 13
Road Ahead: Way Forward (Cont.) 5.Rationalize tariff regime 6. More investments Public and Private sector to upgrade Power sector T & D infrastructure 7. Timely payments to avoid circular debts 8. Develop political consensus on energy security issues 14
Road Ahead: Way Forward (Cont.) 9. Improve governance to cut theft/corruption and inefficiency 10. Improve governance at policy level inter-ministerial coordination single Energy Ministry 15
Salient Features of National Power Policy 2014 To achieve the long-term vision of the power sector and overcome its challenges, following goals have been set: Build a power generation capacity that can meet Pakistan s energy needs in a sustainable manner. i. ii. Create a culture of energy conservation and responsibility 16
Salient Features of National Power Policy 2014 iii. Ensure the generation of inexpensive and affordable electricity for domestic, commercial, and industrial use by using indigenous resources such as coal (Thar coal) and hydel. iv. Minimize pilferage and adulteration in fuel supply v. Promote world class efficiency in power generation vi. Create a cutting edge transmission network 17
Salient Features of National Power Policy 2014 vii. Minimize inefficiencies in the distribution system viii. Minimize financial losses across the system ix. Align the ministries involved in the energy sector and improve the governance of all related federal and provincial departments as well as regulators 18