Enabling Precinct Management Policy and Legislation
This document discusses the challenges and opportunities in precinct management policy and legislation, focusing on sustainable, vibrant, and inclusive precincts. It highlights the need for a comprehensive framework to address varying needs across different municipalities and communities. The proposed policy aims to enhance precinct operations, promote economic development, attract private investment, and ensure good governance. Collaboration among various stakeholders is emphasized for successful implementation.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
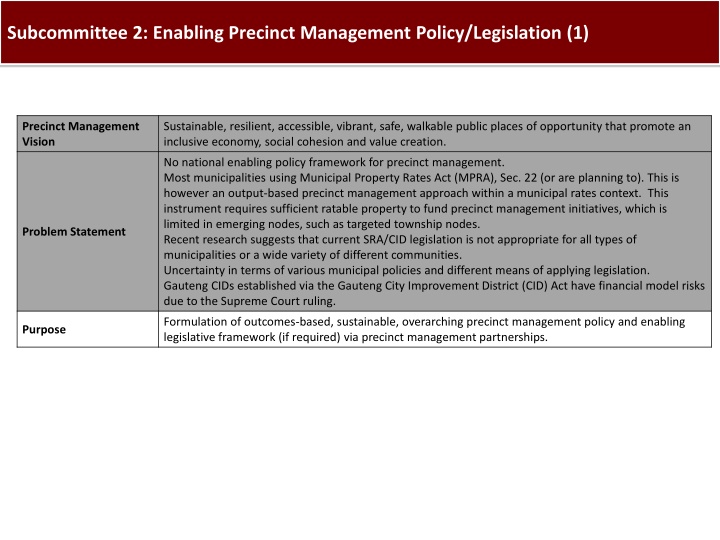
Subcommittee 2: Enabling Precinct Management Policy/Legislation (1) Precinct Management Vision Sustainable, resilient, accessible, vibrant, safe, walkable public places of opportunity that promote an inclusive economy, social cohesion and value creation. No national enabling policy framework for precinct management. Most municipalities using Municipal Property Rates Act (MPRA), Sec. 22 (or are planning to). This is however an output-based precinct management approach within a municipal rates context. This instrument requires sufficient ratable property to fund precinct management initiatives, which is limited in emerging nodes, such as targeted township nodes. Recent research suggests that current SRA/CID legislation is not appropriate for all types of municipalities or a wide variety of different communities. Uncertainty in terms of various municipal policies and different means of applying legislation. Gauteng CIDs established via the Gauteng City Improvement District (CID) Act have financial model risks due to the Supreme Court ruling. Problem Statement Formulation of outcomes-based, sustainable, overarching precinct management policy and enabling legislative framework (if required) via precinct management partnerships. Purpose
Subcommittee 2: Enabling Precinct Management Policy/Legislation (2) The Precinct Management Policy should be aimed to achieve the Precinct Management Vision in targeted precincts via the following Policy Components/Strategic Objectives: Efficient and effective precinct operations providing additional services, optimizing municipal service delivery, resolving service delivery blockages Creative public placemaking affordability, Power of 10 methodology, involvement of citizens, NGOs and businesses, enabling community cohesion Inclusive and sustainable precinct economic development increasing benefits to small businesses and local businesses (precinct and beyond) , job creation, small business creation Integrated, well-planned and sequenced intergovernmental public investment in targeted precincts Intergovernmental Governmental Project Pipeline, funding and alternative financing (e.g. Tax Increment Financing), implementation protocols between spheres and SOEs, lobbying for investment Increased levels of private Investment and retention in targeted precincts marketing, municipal land use management, public land release, incentives Good governance and financial management institutional structuring, partnership optimisation, strategic decision-making, financial sustainability, legal enablement and policy certainty Strategic Objectives (Towards SMART) Subcommittee 1: Receives strengths and weaknesses of existing policy and legislation Subcommittee 3: Provides identification of content focus areas and receives international good practice for selected policy components/strategic objectives. Consultative Forum member organizations (national and regional) Metros/municipalities with existing or planned precinct management activities (officials from the planning, policy, urban management, legal and finance/revenue departments) National and provincial departments, e.g. Departments of Public Works and Rural Development and Land Reform, Economic Development, Social Development, Small Business Donor and Research institutions, such as universities, SACN, HSRC, GIZ and KFW Links with other subcommittees Membership
Precinct Management Activities and Outcomes (Identification of Strategic Objectives) Precinct Management Well managed, sustainable, resilient, accessible, vibrant, safe, walkable public places of opportunity that promote an inclusive economy and social cohesion Governance & Financial Precinct Operations Spatial & Economic Urban Transformation Public Sector Investment Private Sector Investment Spatial Targeting Economic Development Placemaking City IZ Precinct
Subcommittee Name: Subcommittee 2 Activity Schedule - Towards a Work Plan Strategic Objective ST MT LT Precinct Operations Placemaking Economic Development Public Investment Private Investment Governance and Financial






















